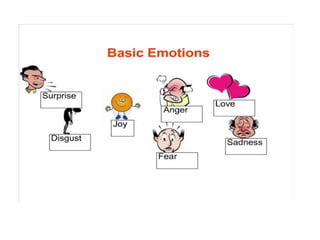
The document discusses emotions and emotional intelligence. It defines emotions as internal conscious states that involve feelings, bodily arousal, purposive motivation, and social expression. Emotions can be positive or negative, and are influenced by factors like personality, culture, stress, age, and environment. The document also discusses emotional labor, where workers must display certain emotions as part of their job. Additionally, it defines emotional intelligence as the ability to identify, assess, and manage one's own emotions and the emotions of others. Emotional intelligence involves self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management. The document argues that emotional intelligence can lead to advantages like greater productivity and better conflict resolution.