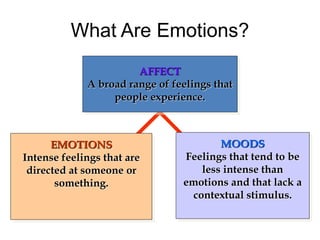
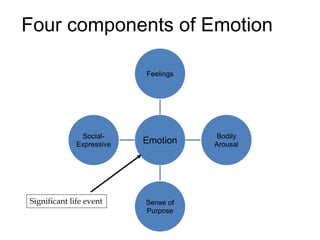
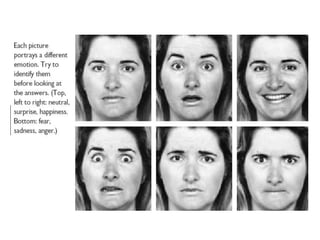
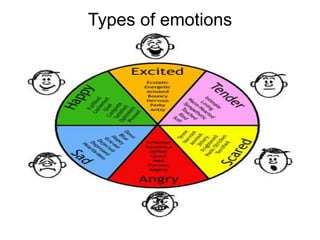
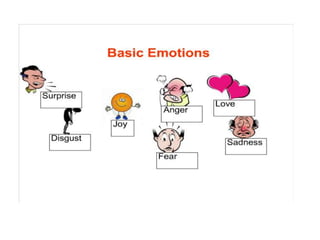
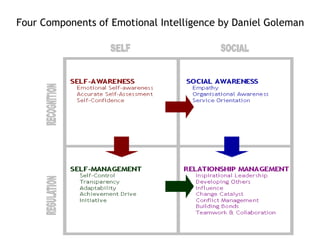
This document discusses emotions, including what emotions are, different types of emotions, and the components of emotions. It defines emotions as private conscious states that involve feelings, bodily arousal, purpose or motivation, and social expression. Emotions are more intense than moods and are directed at something. The four main components of an emotion are the feeling, bodily arousal, purposive or motivational component, and social-expressive component. Different types of emotions are discussed, as well as factors that can influence emotions like personality, culture, age, and environment. Emotional labor and intelligence are also summarized briefly.