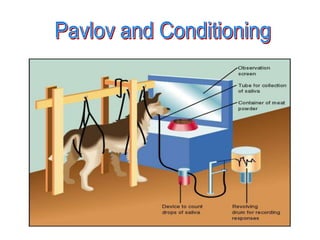
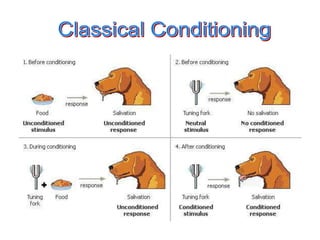
Stimulus-response theories propose that learning occurs through associations between environmental stimuli and behavioral responses. The three main theories are classical conditioning by Pavlov, instrumental conditioning by Thorndike, and operant conditioning by Skinner. Cognitive theories focus on mental processes like memory, problem-solving, and language that influence learning. Social learning theories emphasize that people can learn through observation of and interaction with others. Experimental learning theories propose that experience and reflection are central to learning new skills and concepts.