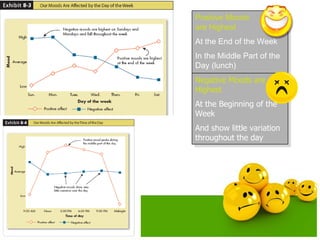
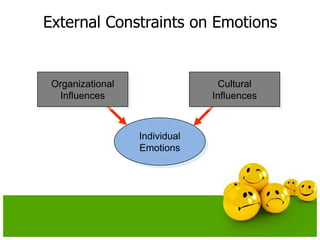
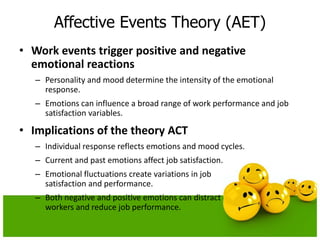
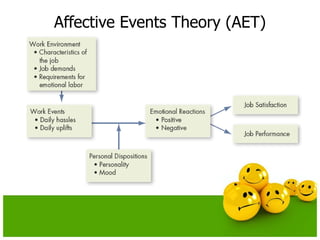
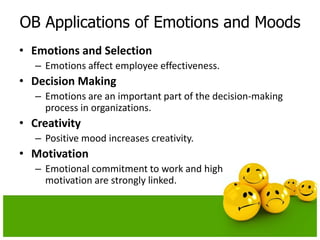
The document discusses emotions and moods in organizational behavior. It defines emotions and moods, explores their sources and impact, and examines theories like affective events theory and emotional intelligence. Some key points are that emotions were originally ignored in OB due to a focus on rationality, positive moods are highest at the end of the week and in the middle of the day, and that understanding emotions can help managers predict behavior and improve job performance.