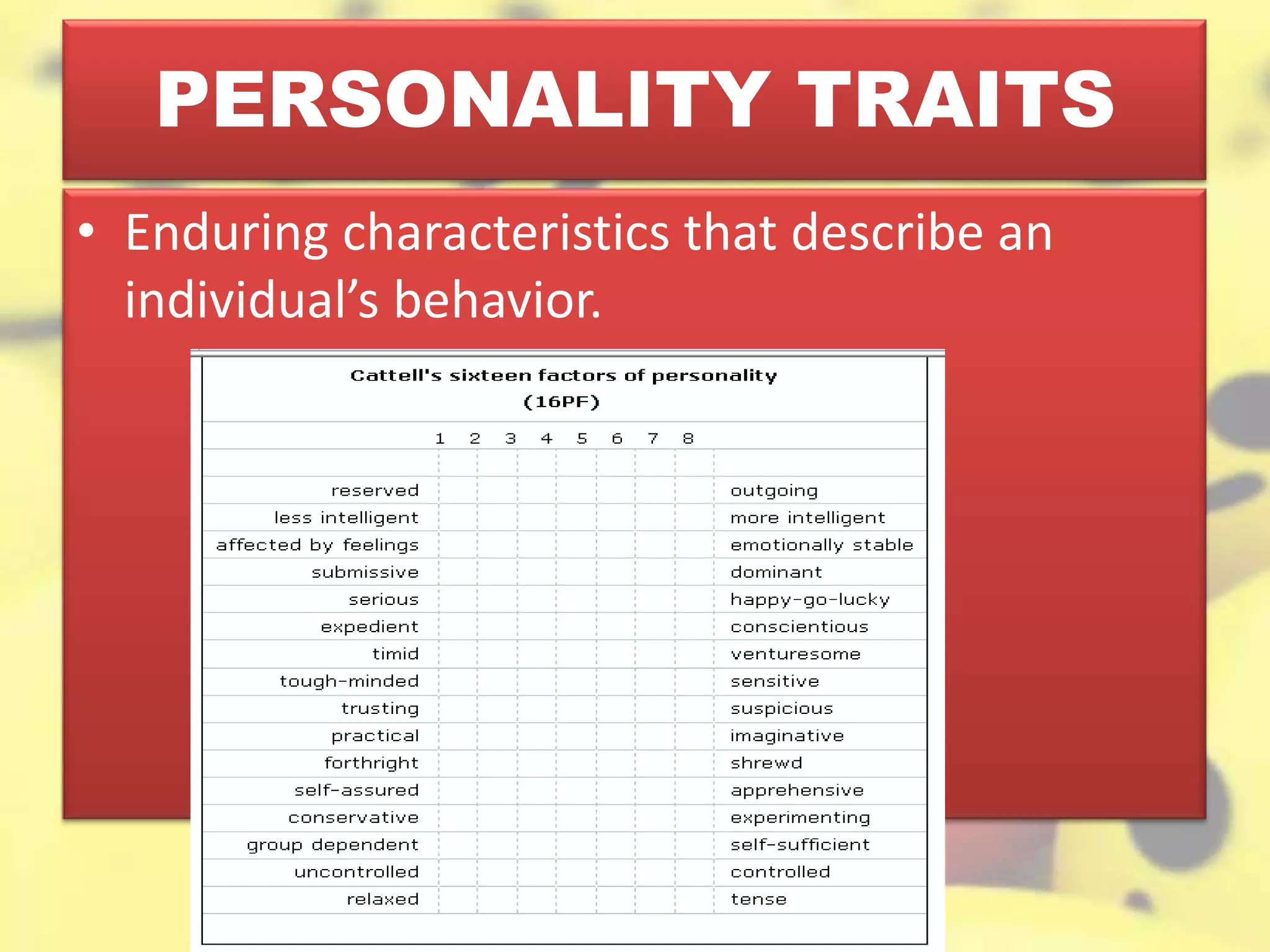
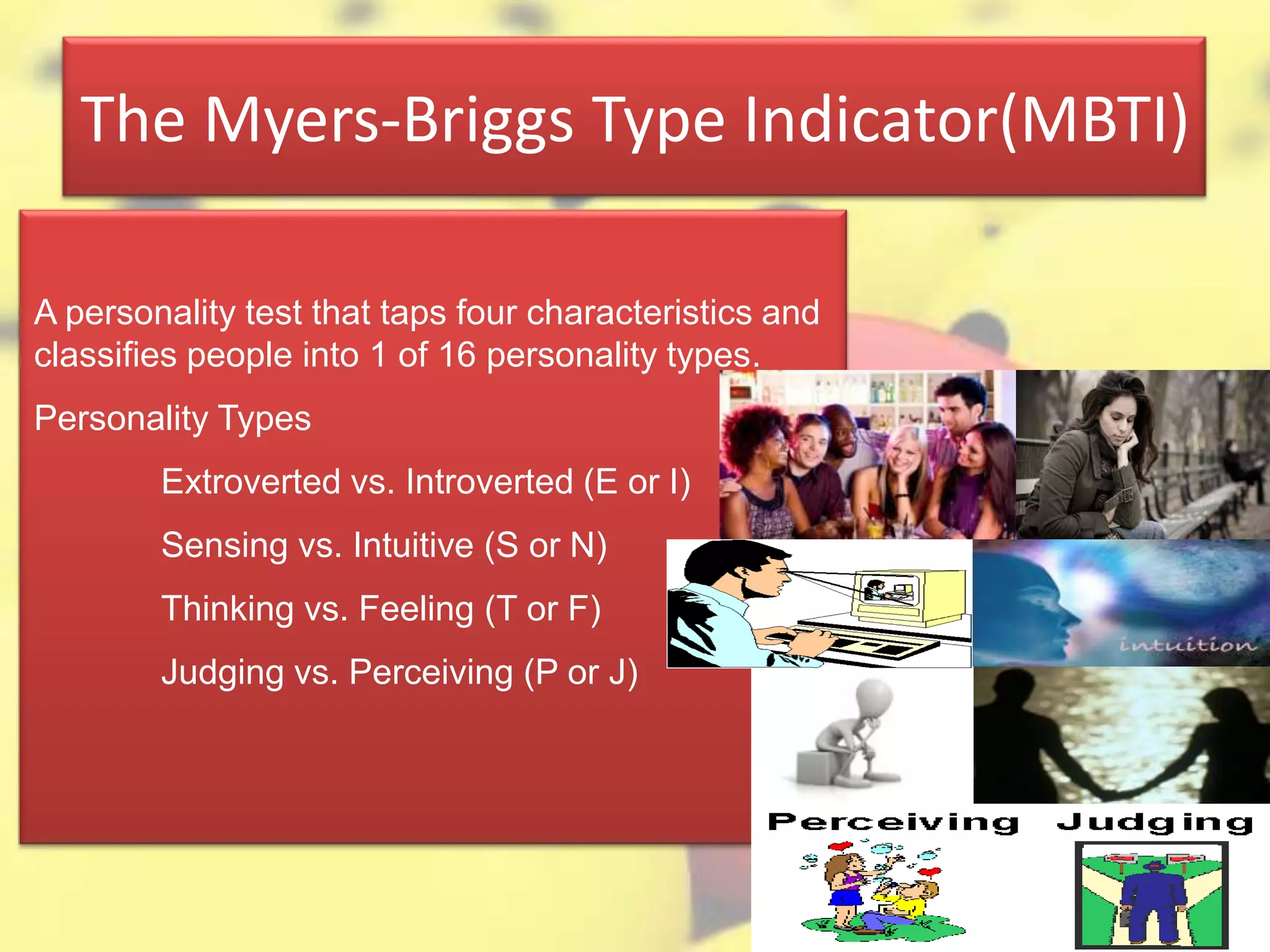
Personality is defined as a relatively stable set of characteristics that influence behavior and interactions with others. It is determined by heredity, environment, situation, culture, and family background. Major theories of personality include trait theory, psychodynamic theory, humanistic theory, and the integrative approach. The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator assesses four traits to classify individuals into one of 16 personality types. The Big Five model describes five broad personality traits: extroversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, emotional stability, and openness to experience. Trait theories posit that personality traits are stable over time and across situations and can be used to predict behavior.