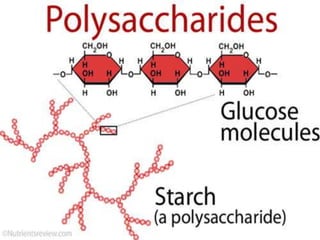
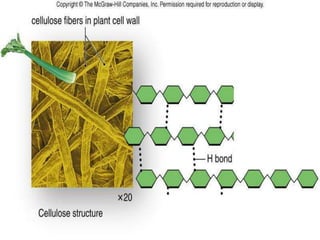
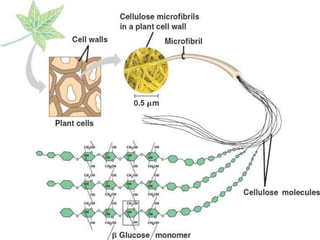
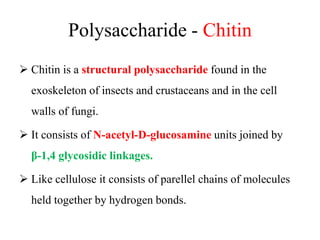
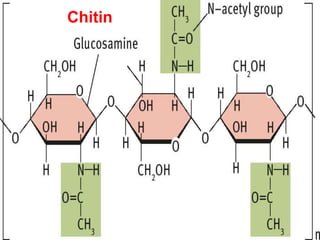
Polysaccharides are complex biomacromolecules made of monosaccharide units linked by glycosidic bonds, classified into structural and storage types. Key examples include cellulose, a structural polysaccharide in plant cell walls, and starch, a storage polysaccharide in plants. Their primary functions are to provide structural support, store energy, and facilitate cellular communication.