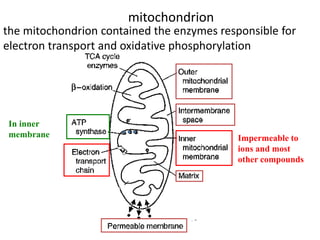
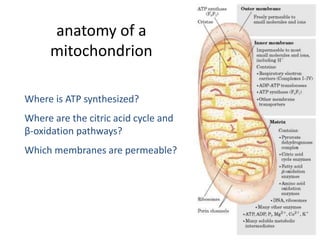
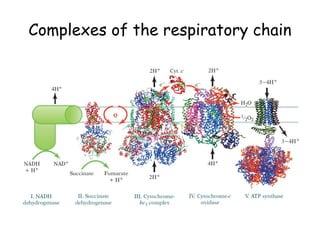
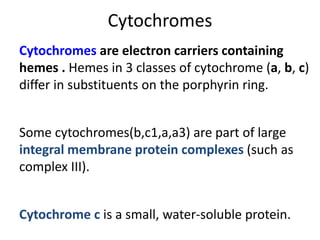
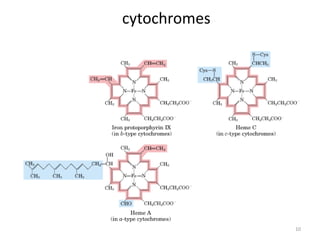
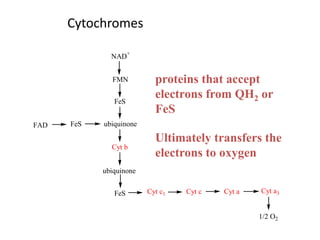
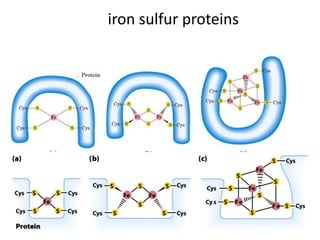
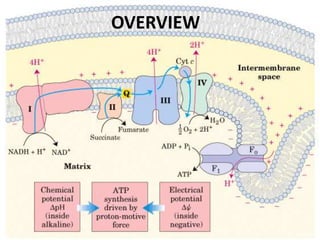
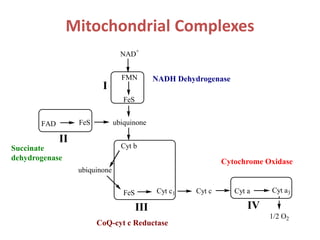
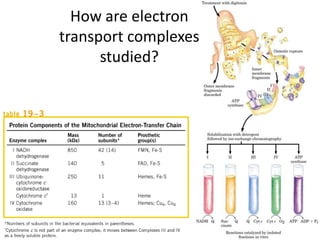
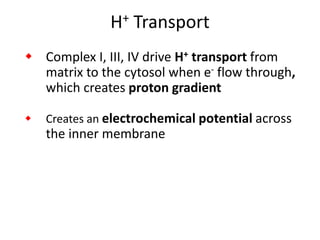
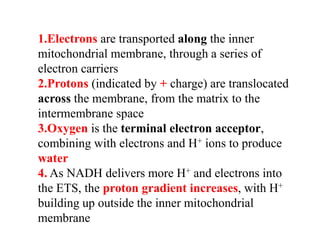
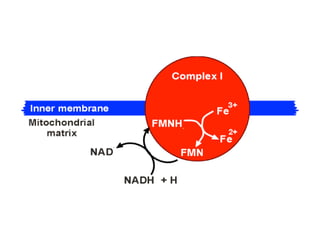
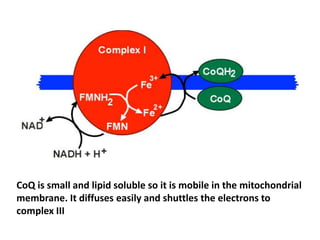
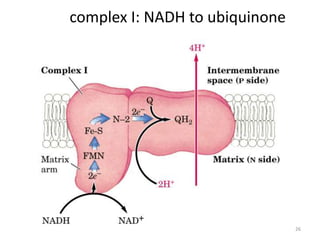
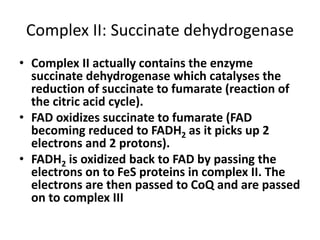
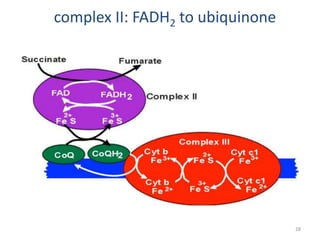
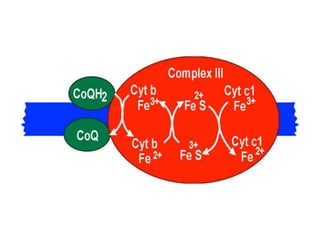
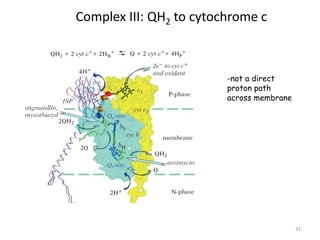
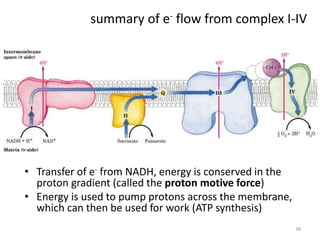
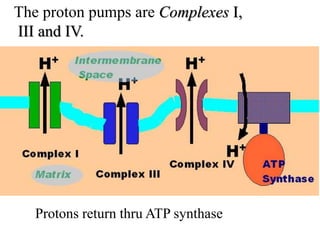
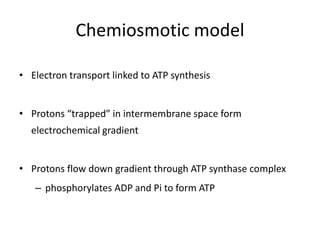
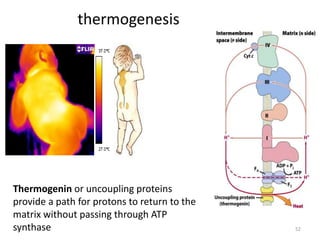
1) Oxidative phosphorylation uses electron transport chain complexes in the mitochondrial inner membrane to generate ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. As electrons are passed through Complexes I-IV, protons are pumped from the matrix to the intermembrane space, building an electrochemical gradient.
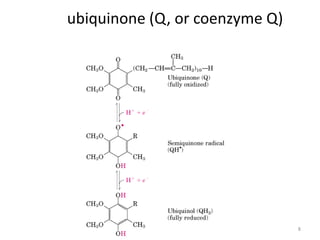
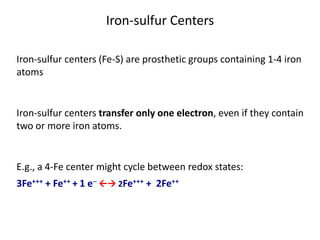
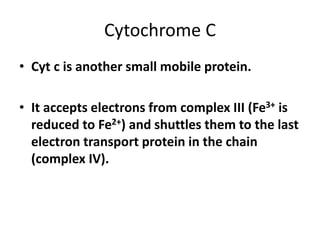
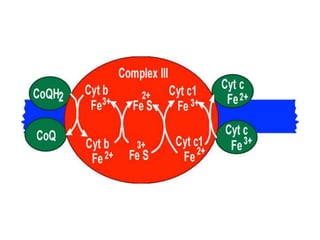
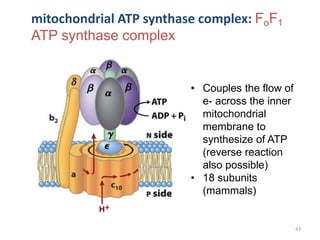
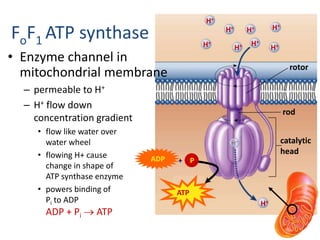
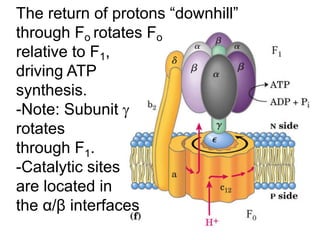
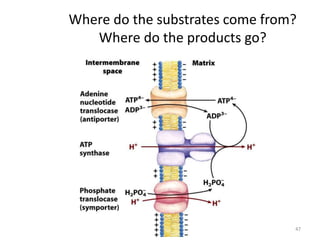
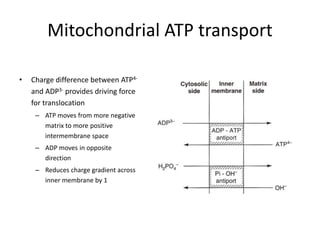
2) Protons flow back through ATP synthase, driving the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP in the matrix. The electron carriers, including ubiquinone and cytochrome c, shuttle electrons and protons between the complexes.
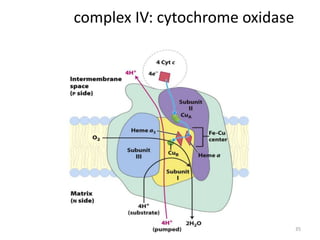
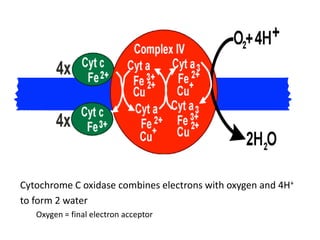
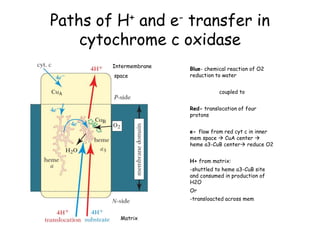
3) Oxygen is the final electron acceptor, being reduced to water along with protons in Complex IV. This chemiosmotic mechanism couples electron transport to ATP synthesis via the proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane