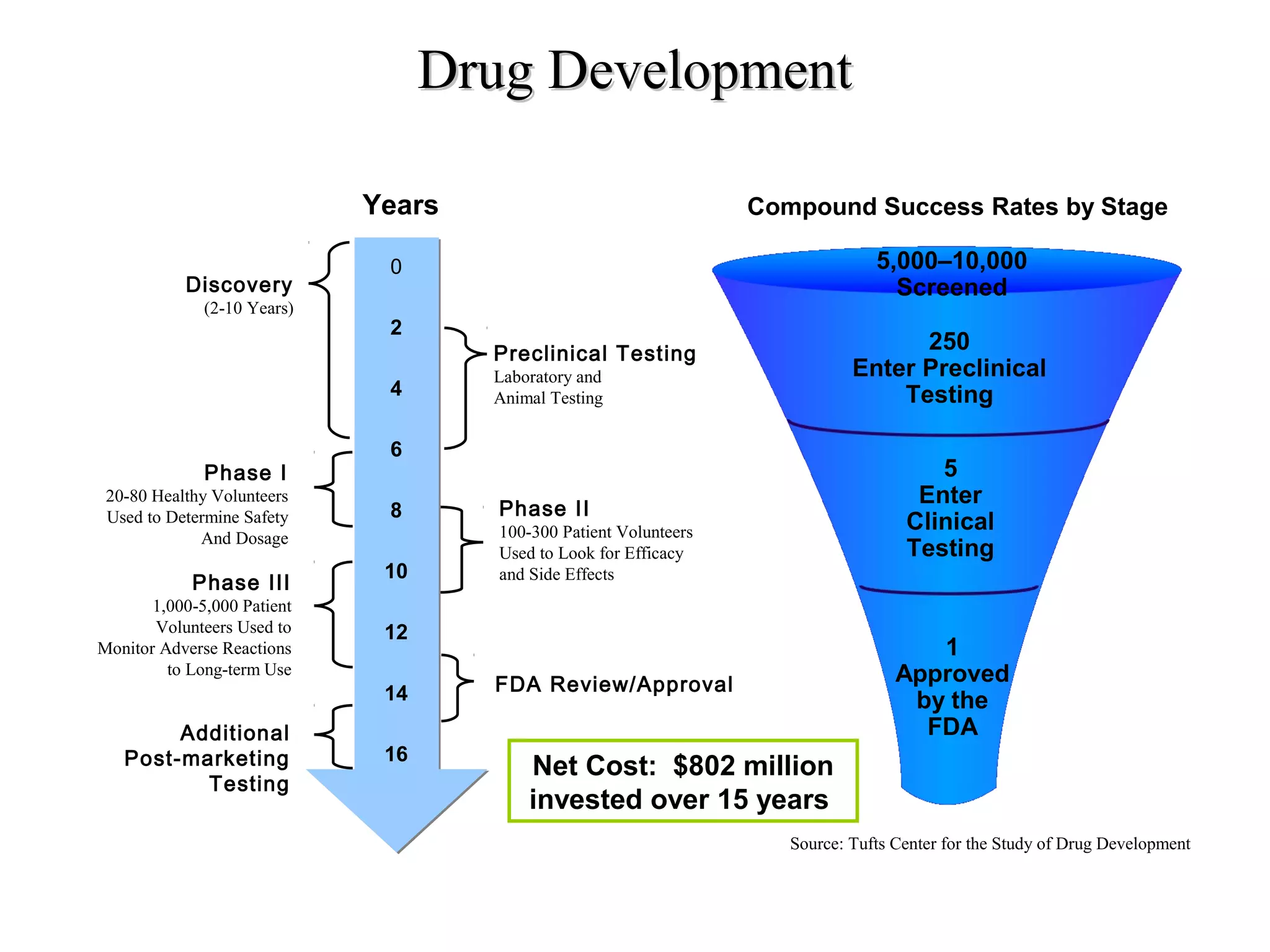
Drug discovery and development is a long, expensive, and complex process averaging about 12 years and $500 million to bring a new prescription medication to market. Only 1 in 10,000 compounds eventually becomes an approved drug. The process involves discovery, preclinical research, clinical trials, and regulatory approval. Discovery aims to identify candidate drug molecules, while preclinical research studies their safety and efficacy in animal models before human testing. Clinical trials then evaluate new drugs with patients for safety and effectiveness over several phases before regulatory approval and marketing.