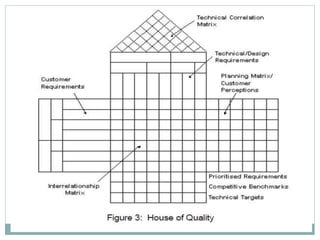
1. Quality Function Deployment (QFD) uses a matrix format called the House of Quality to capture customer requirements and translate them into engineering targets for new product design.
2. The House of Quality contains six major components: customer requirements, technical requirements, a planning matrix, an interrelationship matrix, a technical correlation matrix, and technical priorities/benchmarks and targets.
3. It helps companies determine customer needs, specify them as engineering requirements, identify how well requirements are met compared to competitors, establish connections between customer and technical requirements, and set targets for technical requirements.