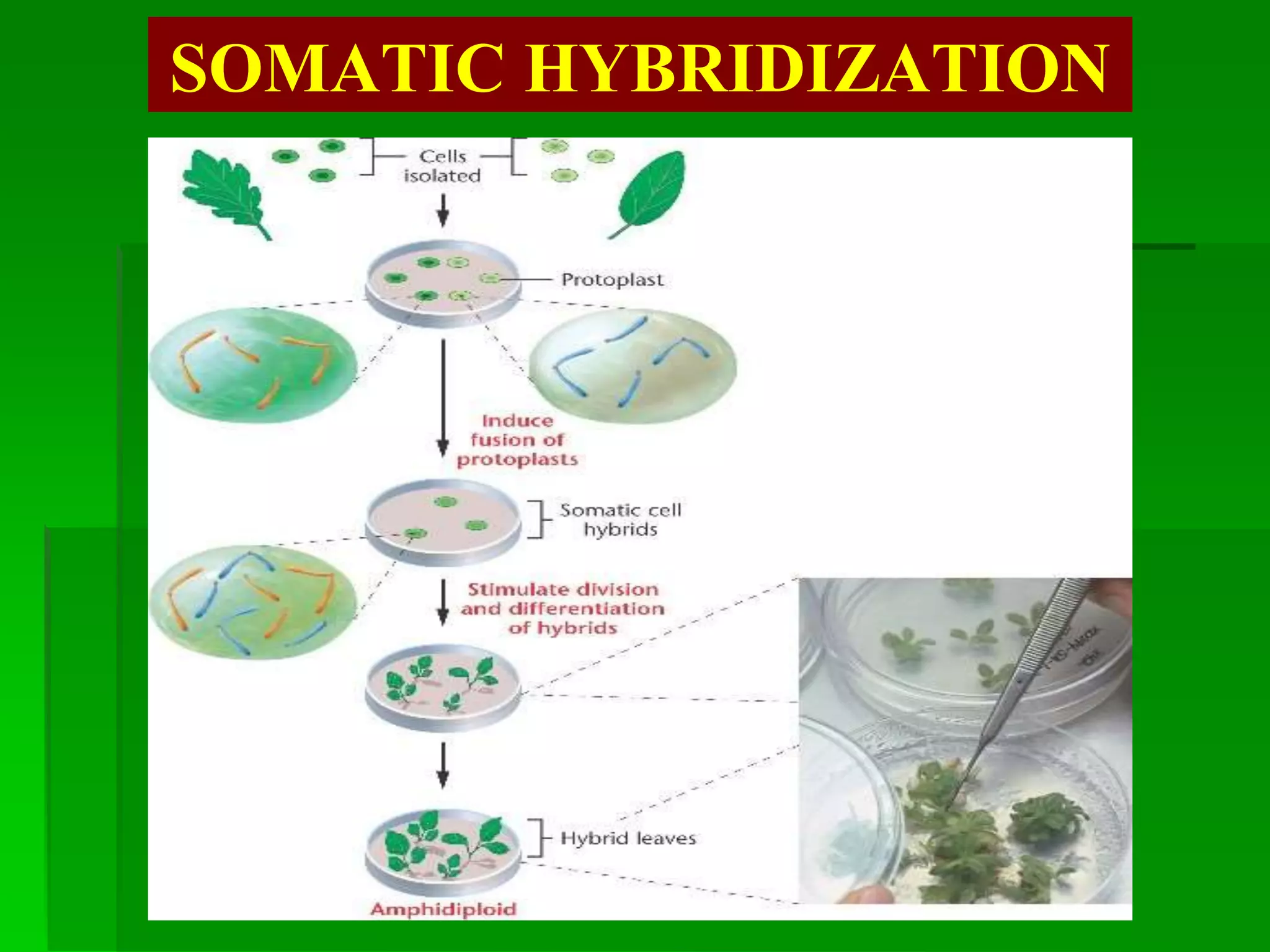
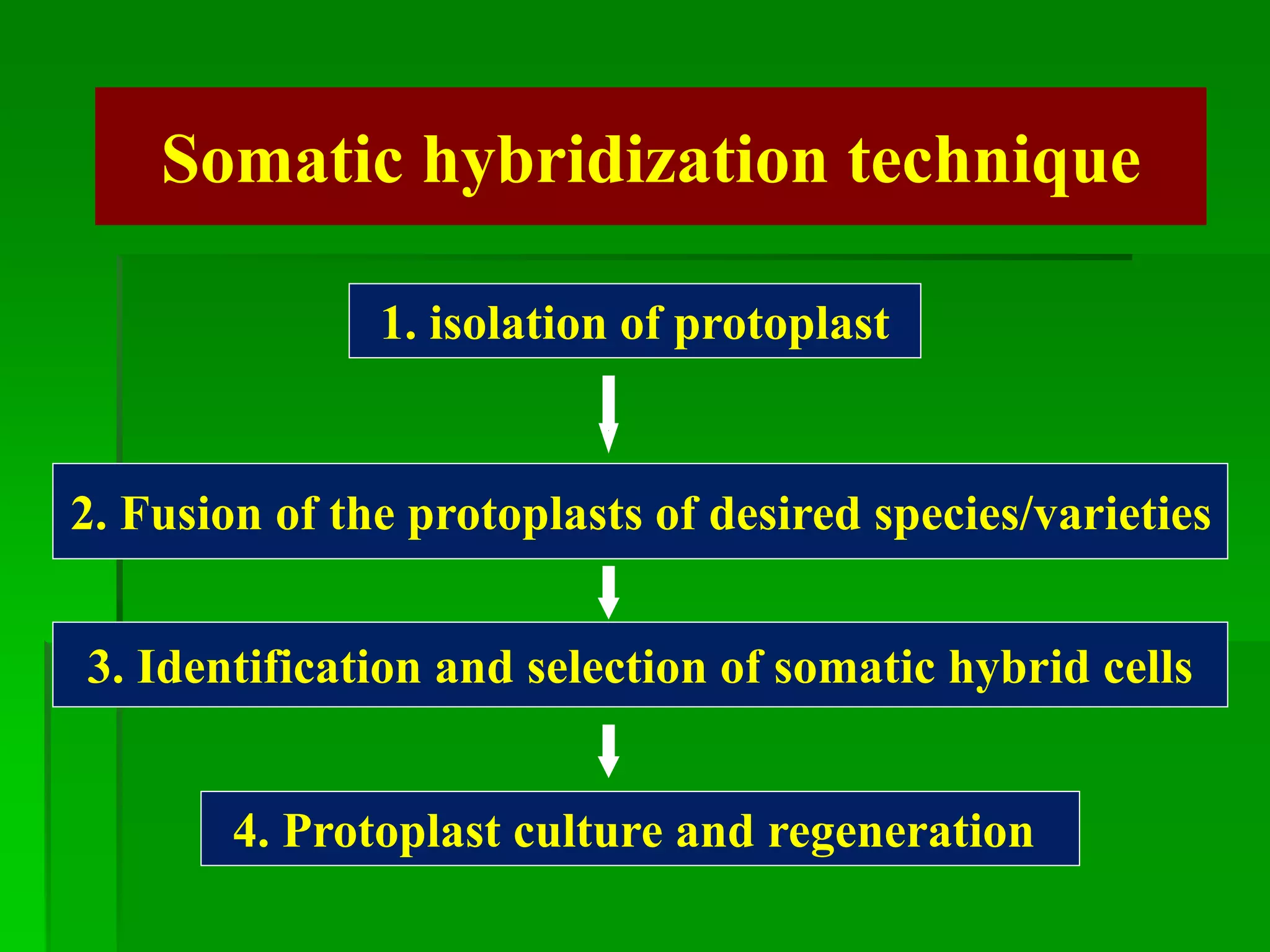
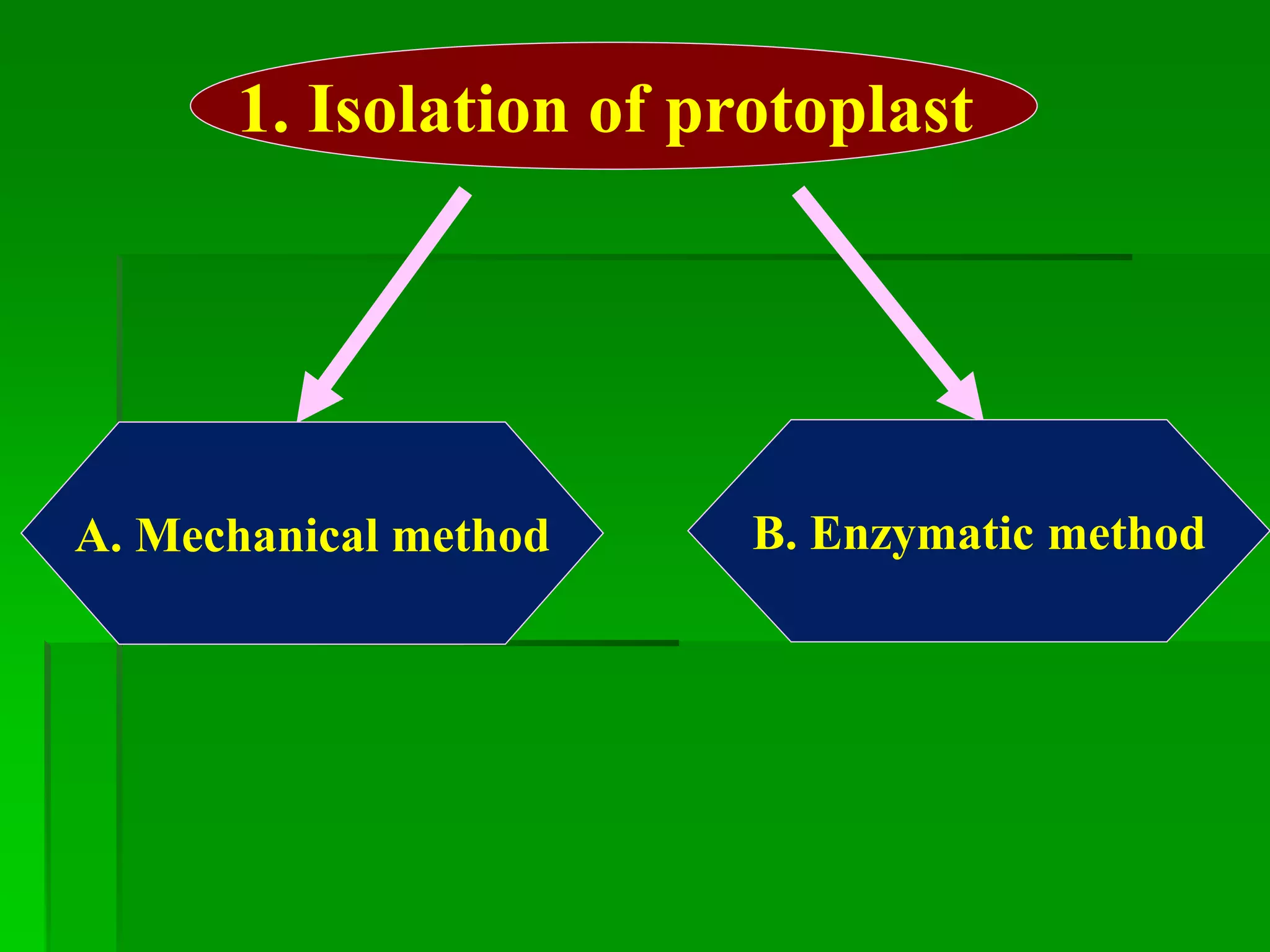
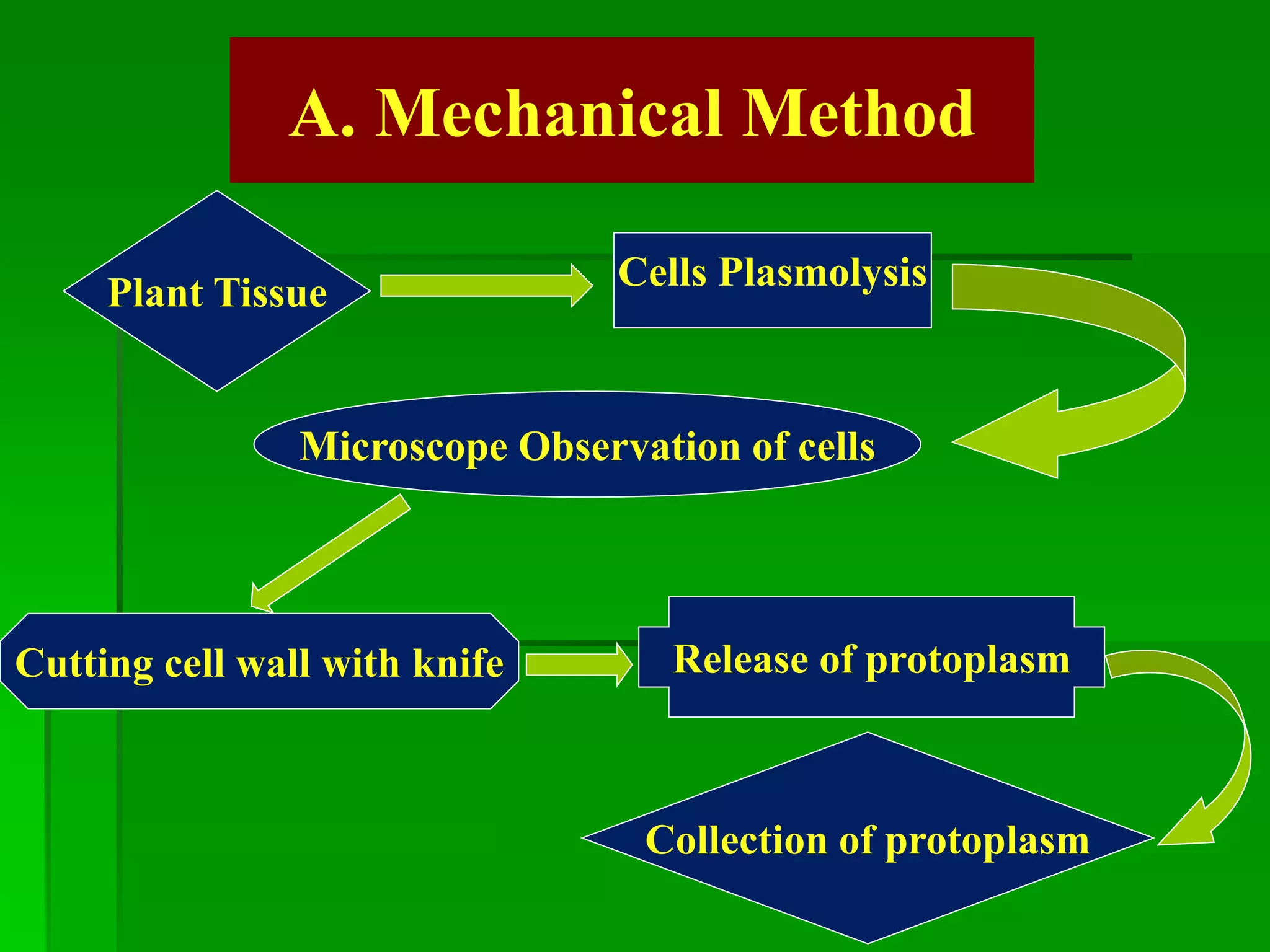
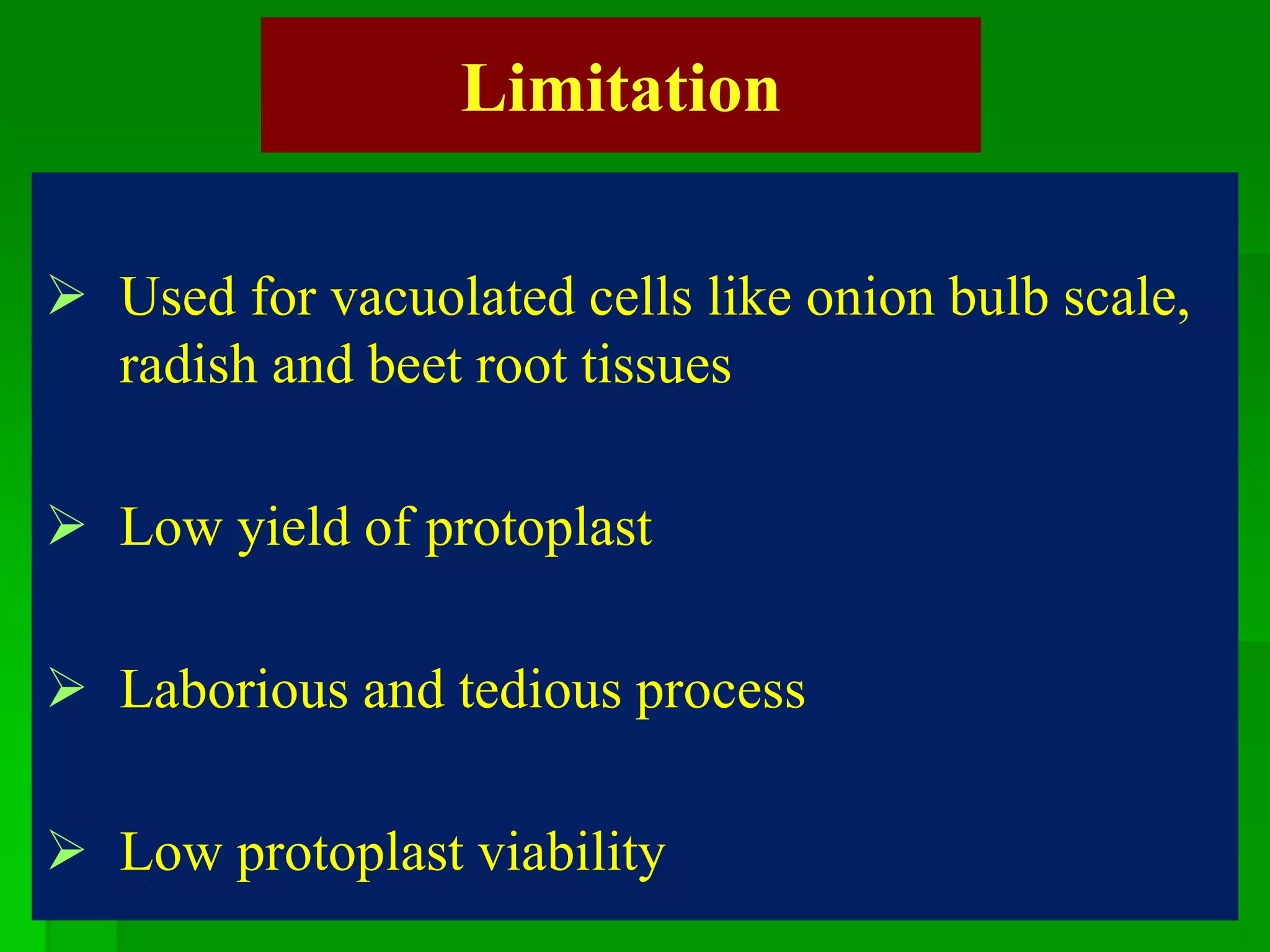
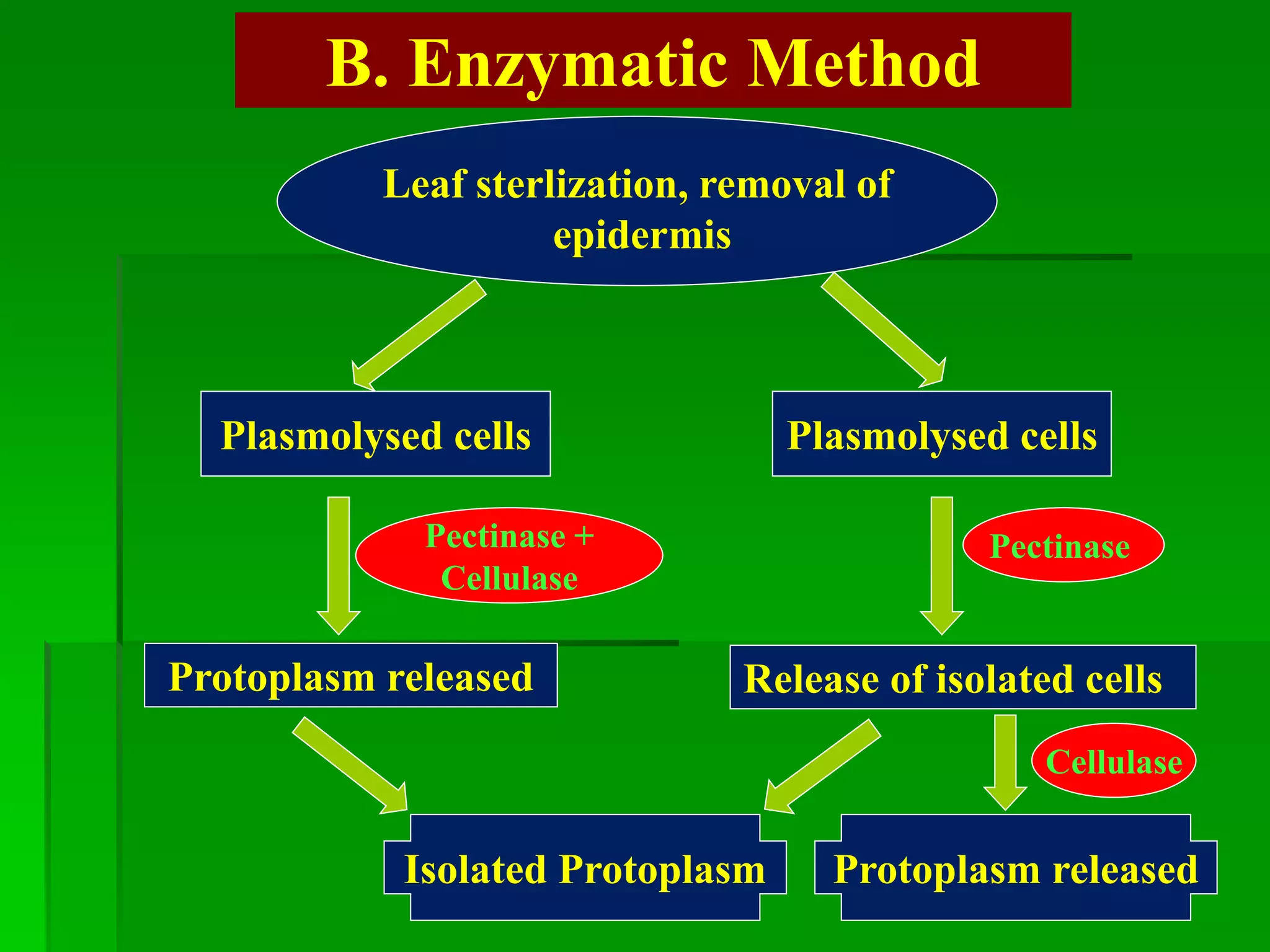
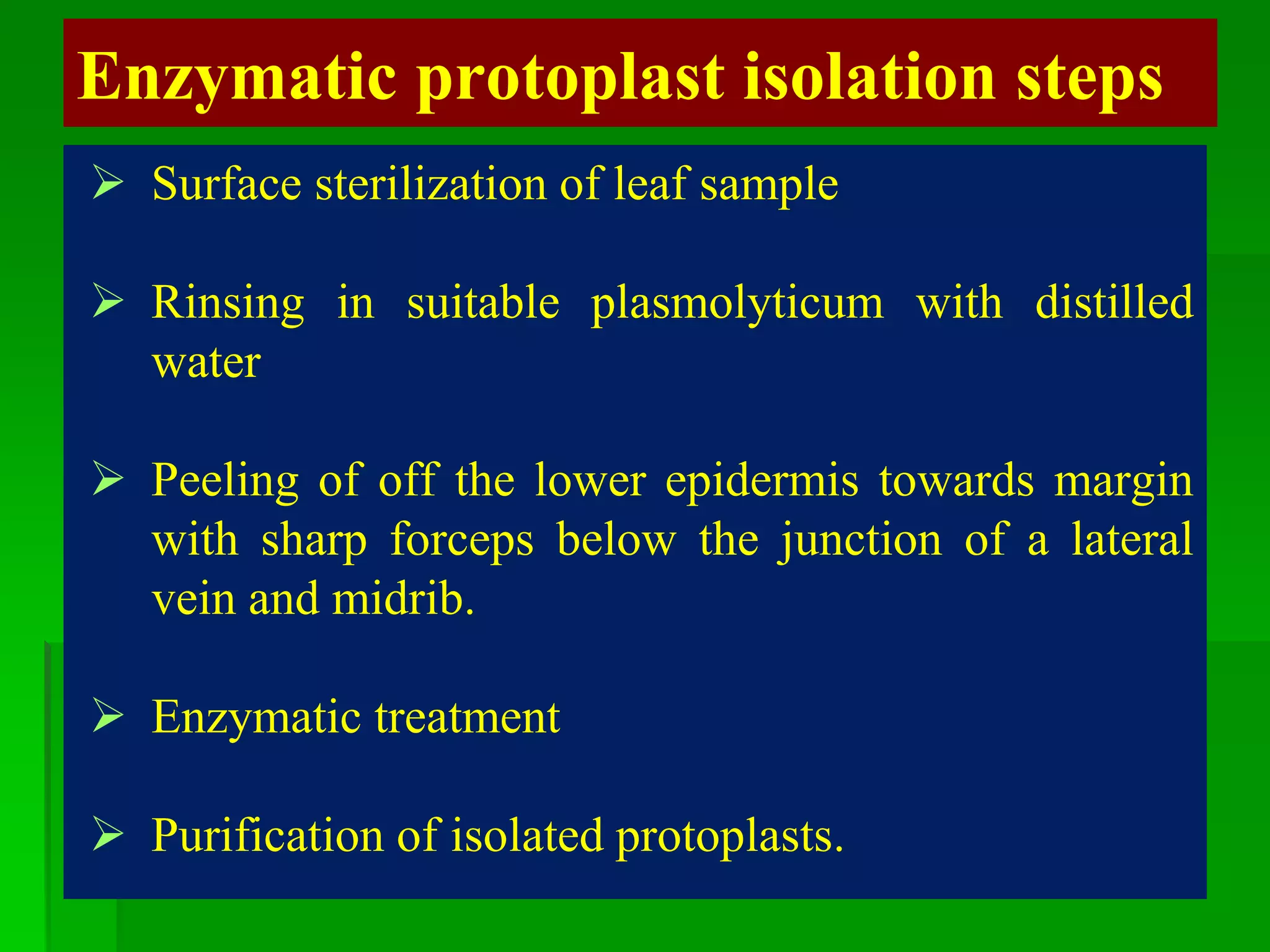
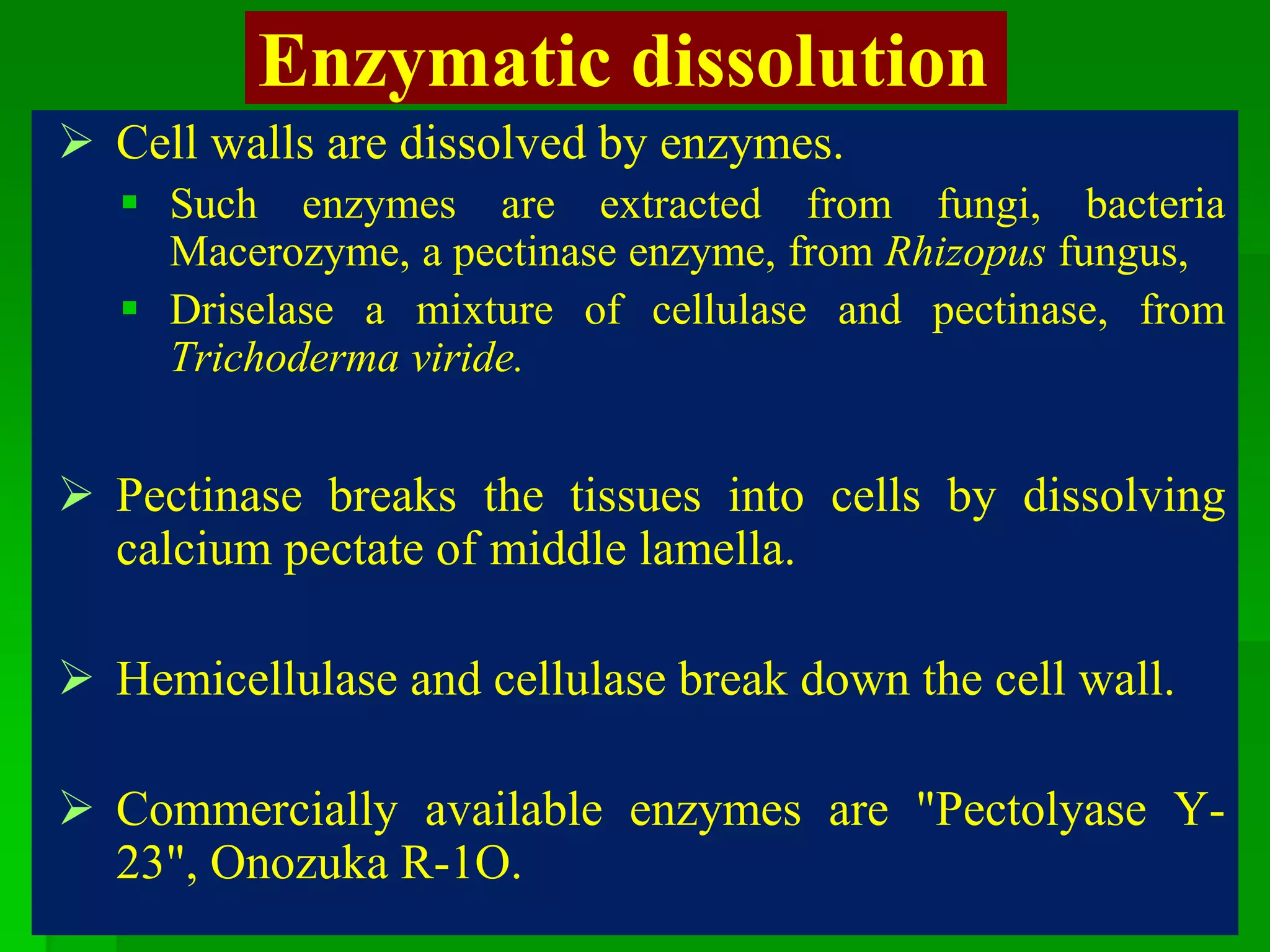
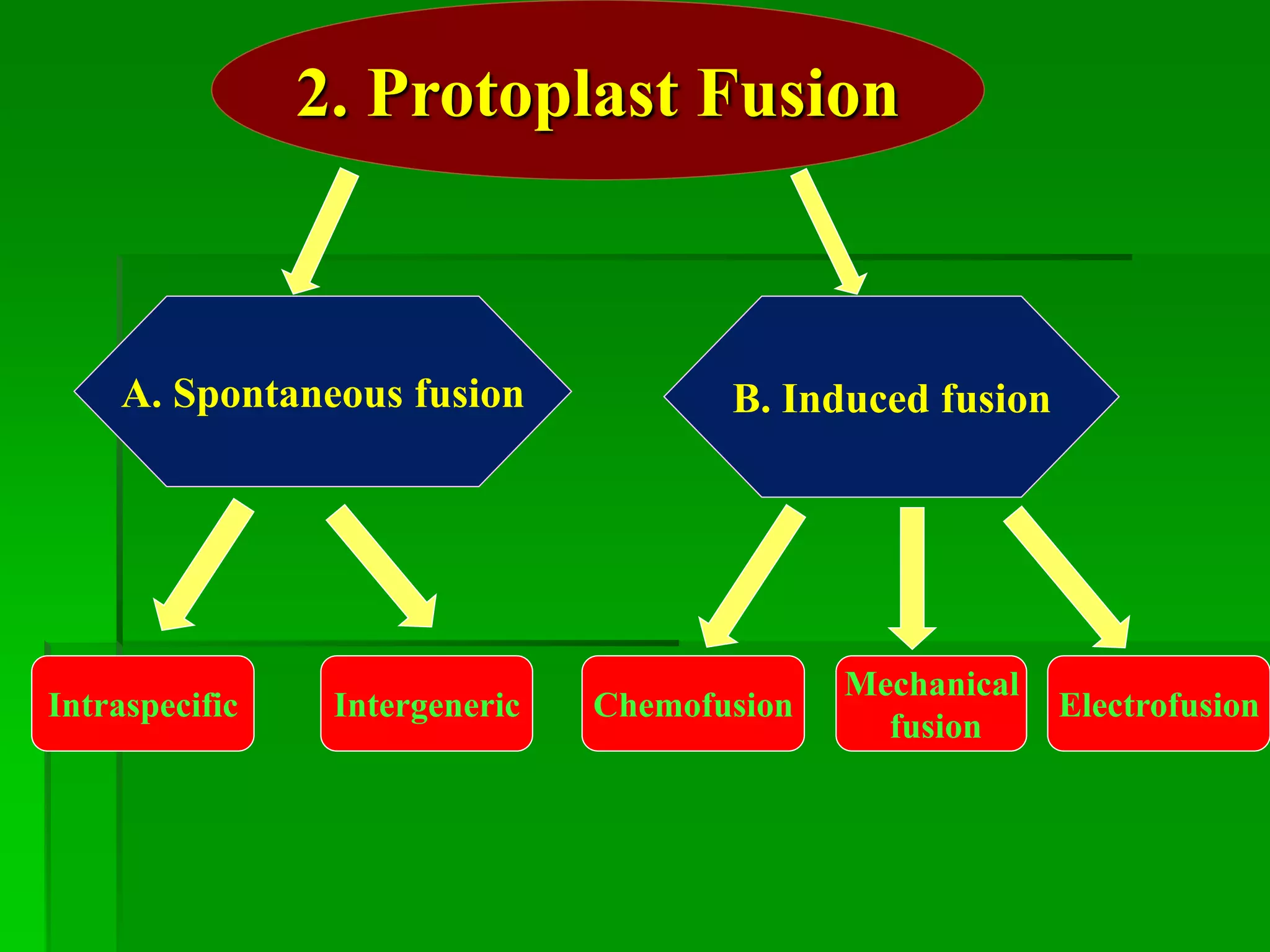
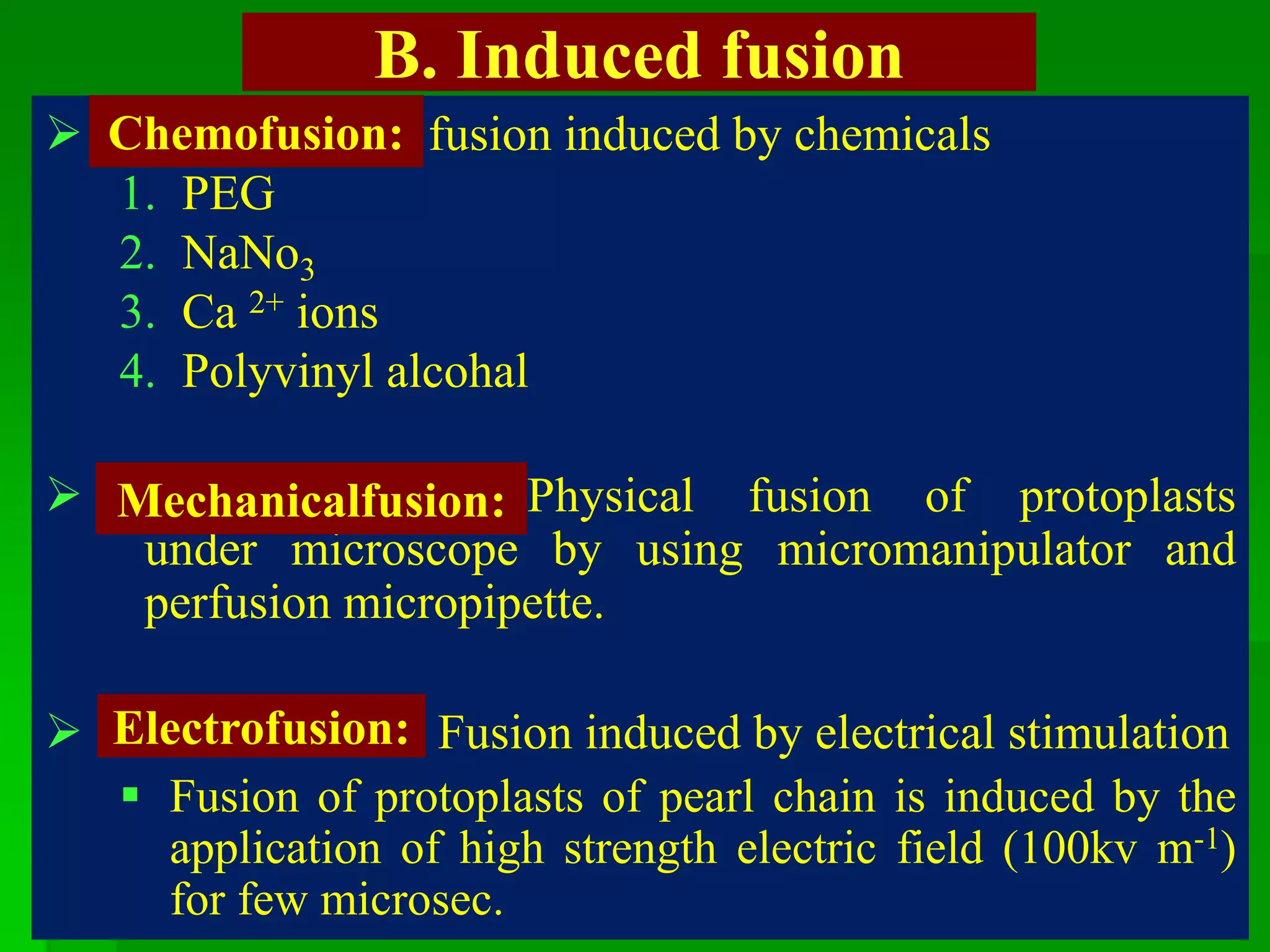
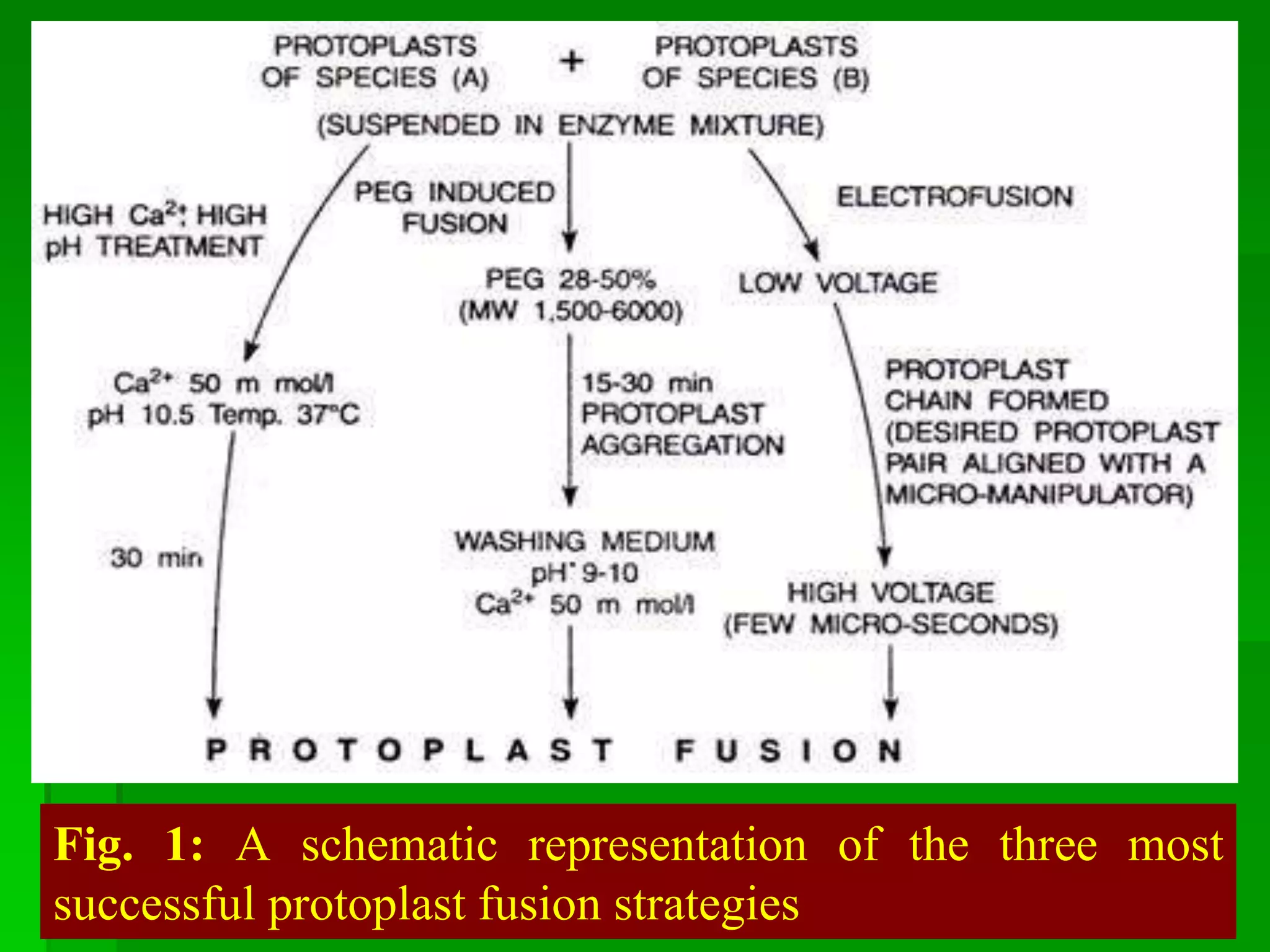
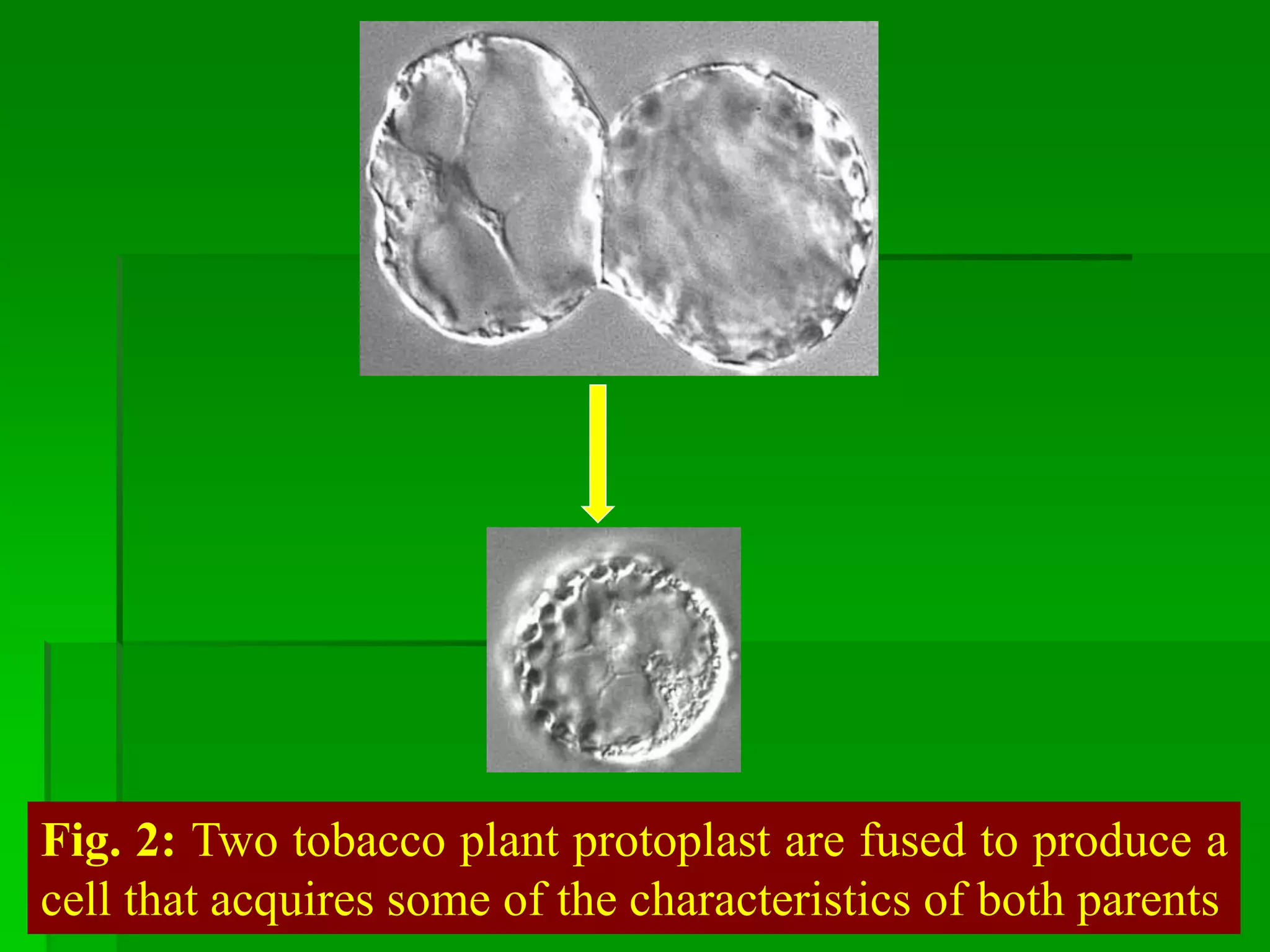
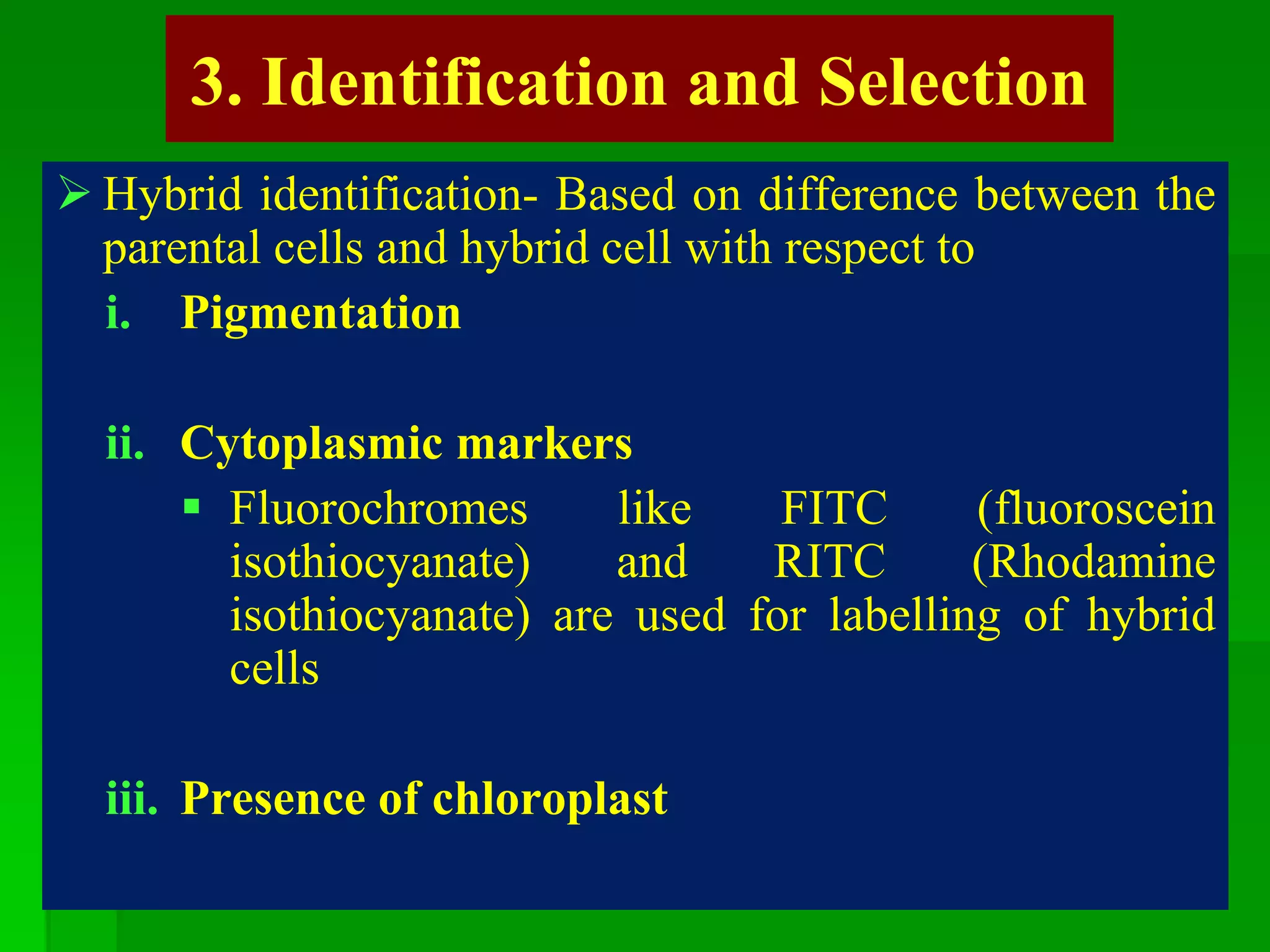
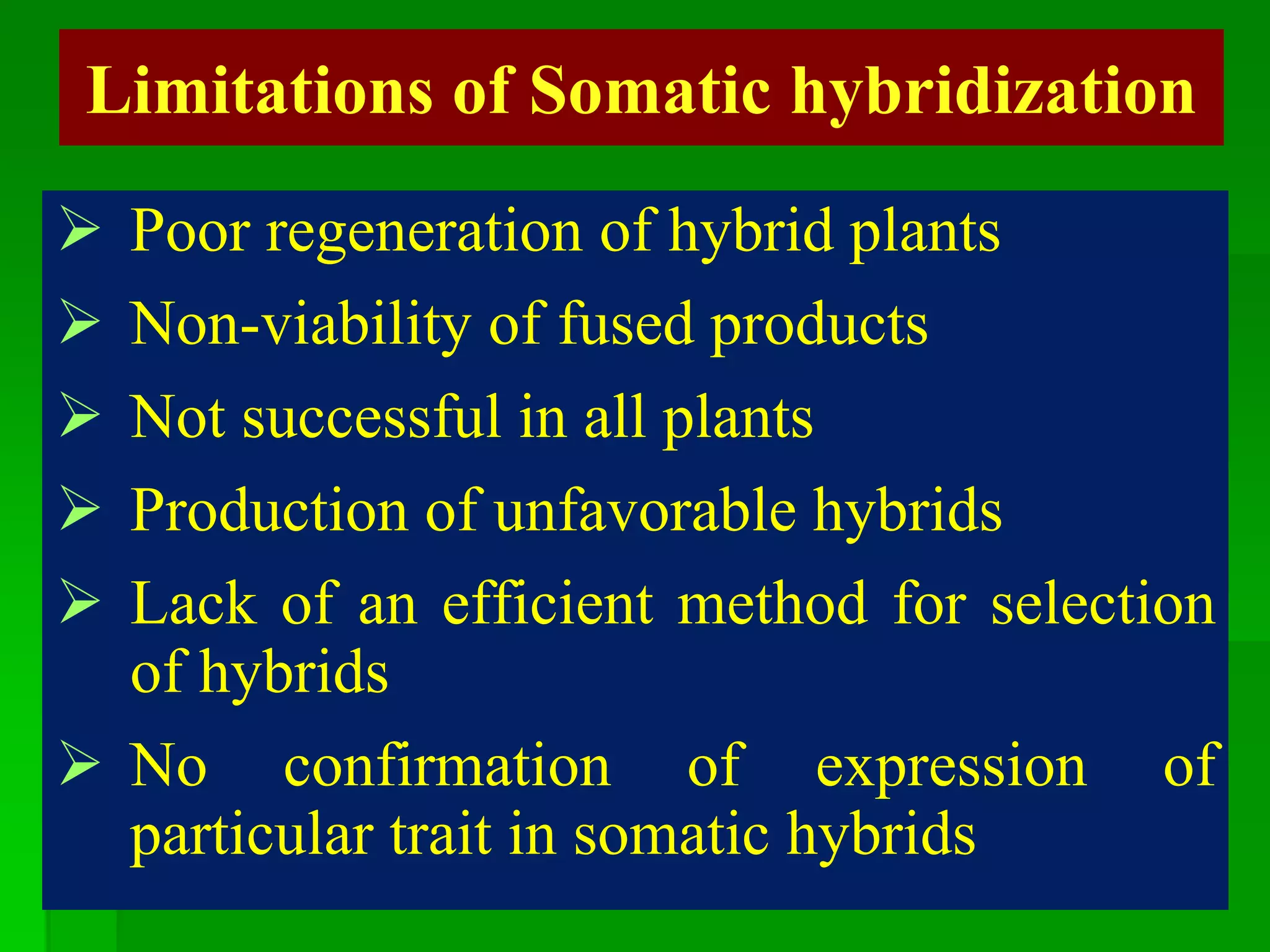
This document discusses somatic hybridization, which involves fusing plant protoplasts from two different species or varieties to create a hybrid plant. It describes the process of somatic hybridization, including isolating protoplasts, fusing them using spontaneous or induced methods, selecting hybrid cells, and regenerating plants from hybrid callus tissue. The advantages are producing novel hybrids and transferring genes between incompatible species. The limitations include low regeneration rates and viability of fused cells. Somatic hybridization has applications in crop improvement by introducing traits like disease resistance from wild relatives.