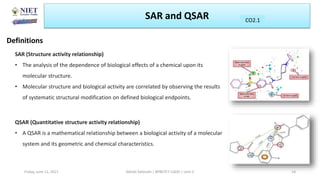
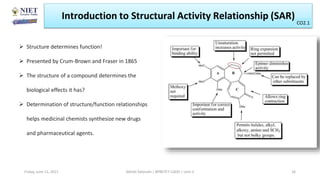
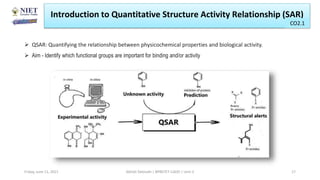
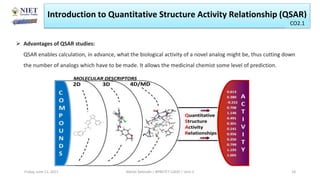
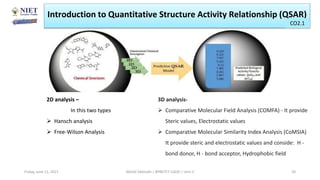
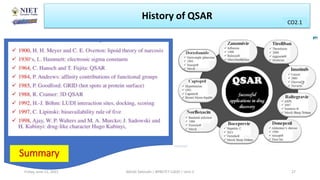
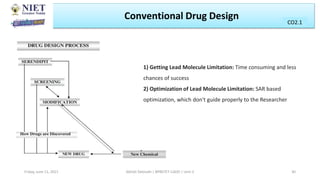
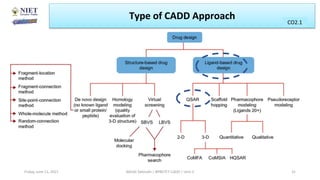
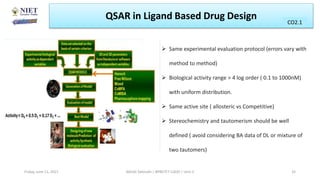
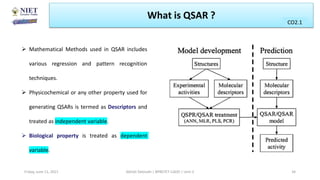
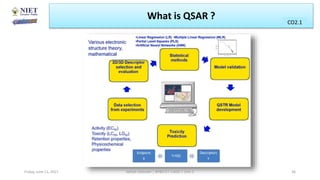
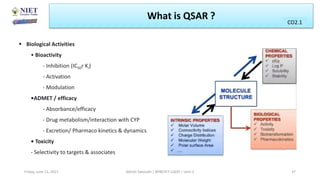
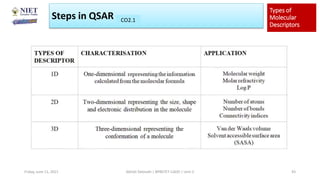
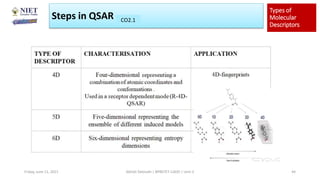
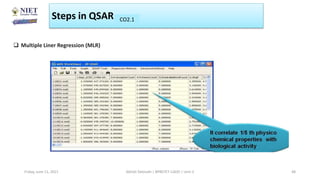
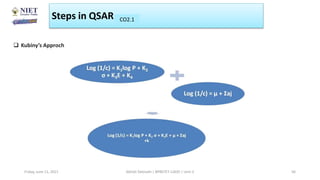
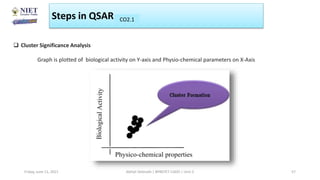
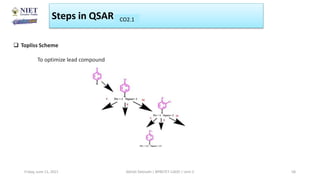
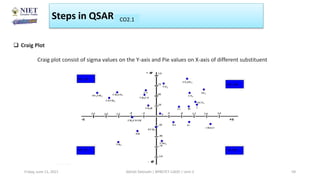
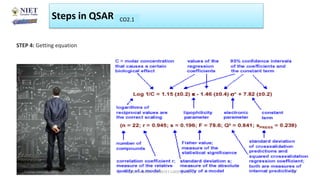
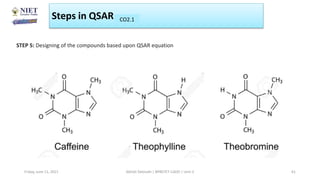
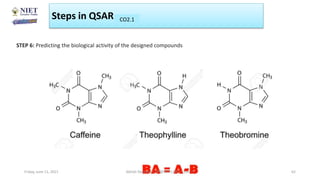
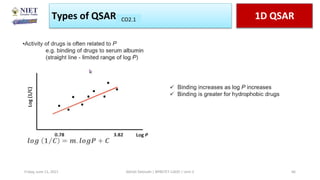
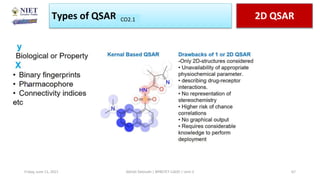
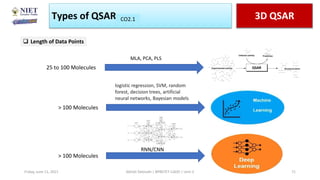
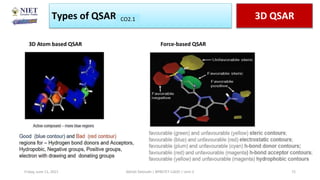
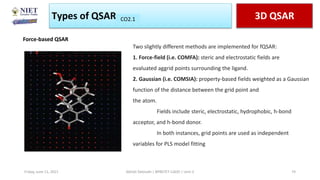
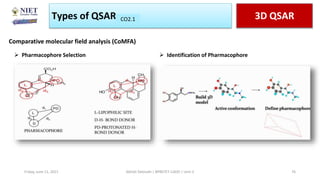
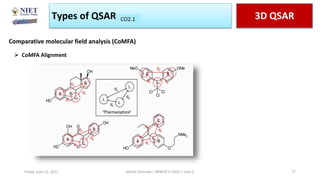
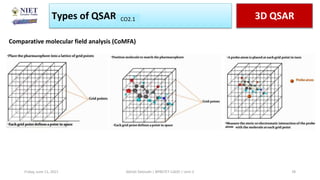
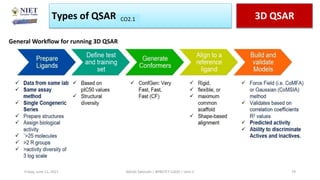
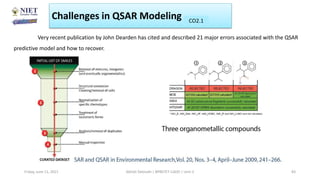
The document serves as a teaching resource for a course on quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSAR) in drug discovery, covering the history, principles, and methodologies involved. It outlines the objectives, course outcomes, and prerequisites for students, as well as the applications of QSAR in developing new pharmaceuticals. Key topics include the differences between structure-activity relationships (SAR) and QSAR, various analytical methods, and the steps involved in QSAR modeling.