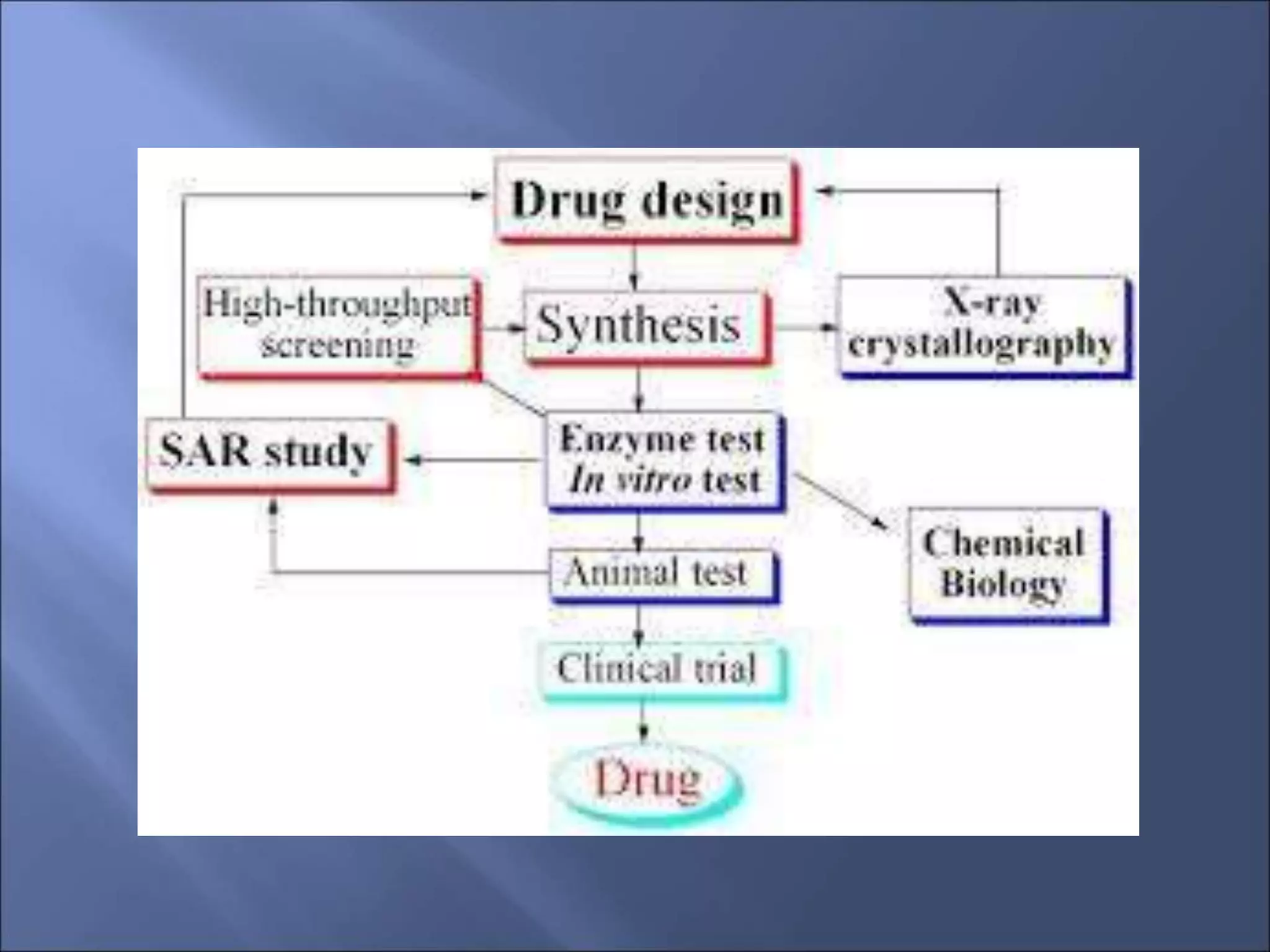
High throughput screening (HTS) is a process used in drug discovery to quickly test large numbers of chemical compounds and biological agents for biological activity against a disease state or condition of interest. The goal of HTS is to identify "hits" or "leads" that show desired activity at low concentrations and have a new chemical structure. Cell-based assays are an important type of HTS that uses live cells to more accurately model biological systems and provide information on bioavailability, cytotoxicity, and effects on biochemical pathways. Key elements of cell-based assays include a cellular component, a target molecule to detect cellular responses, and instrumentation to conduct and analyze the assay.