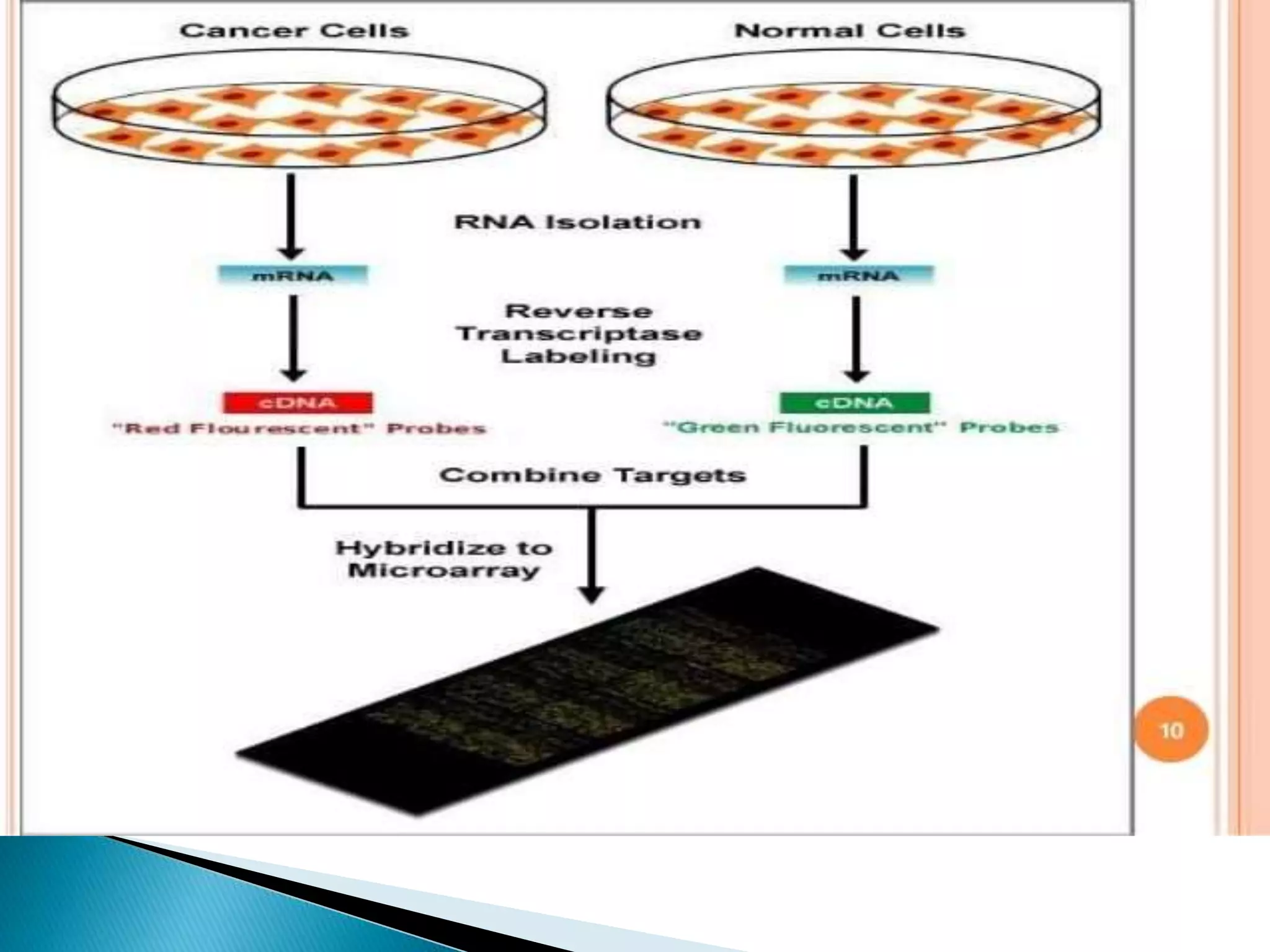
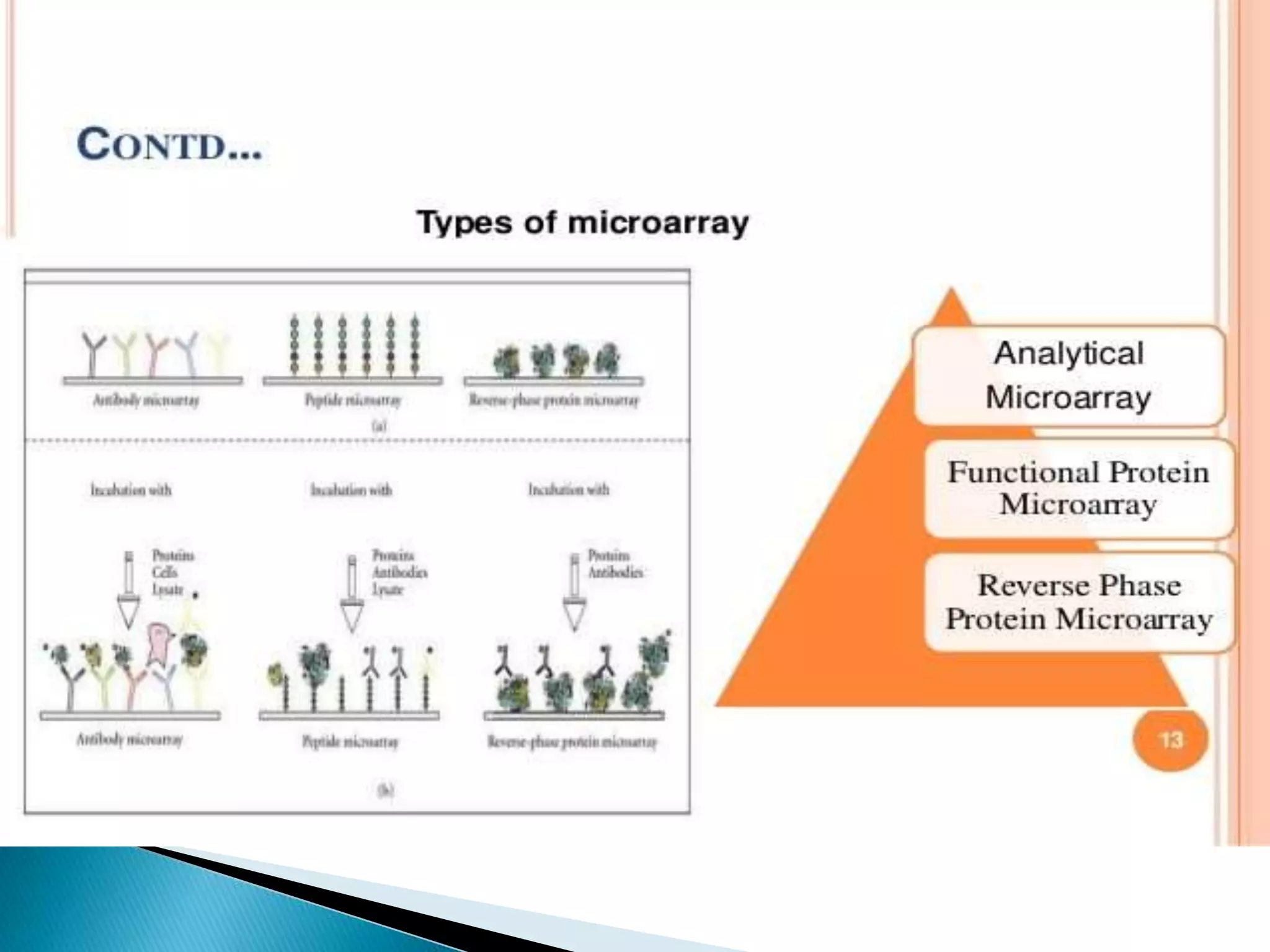
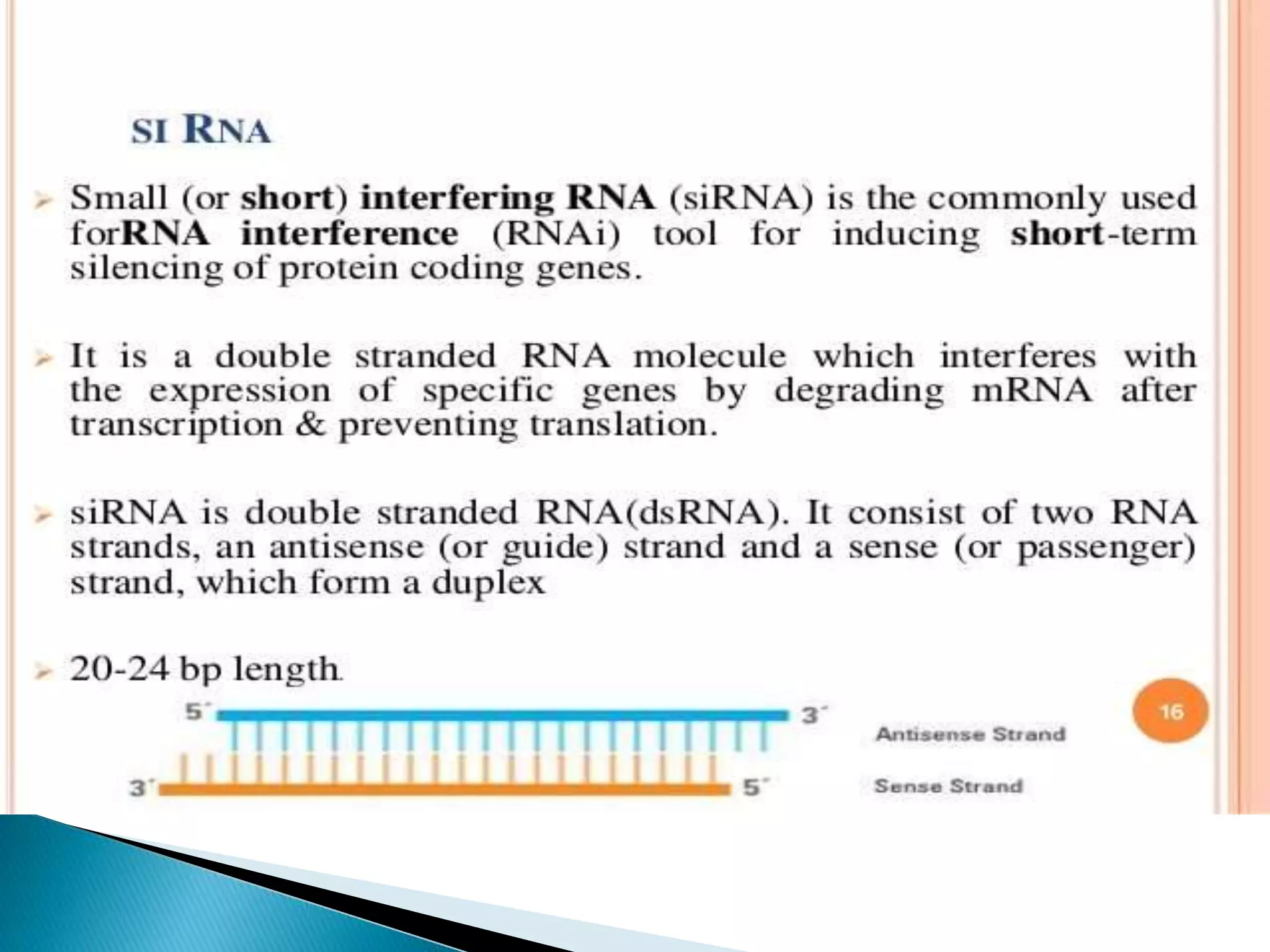
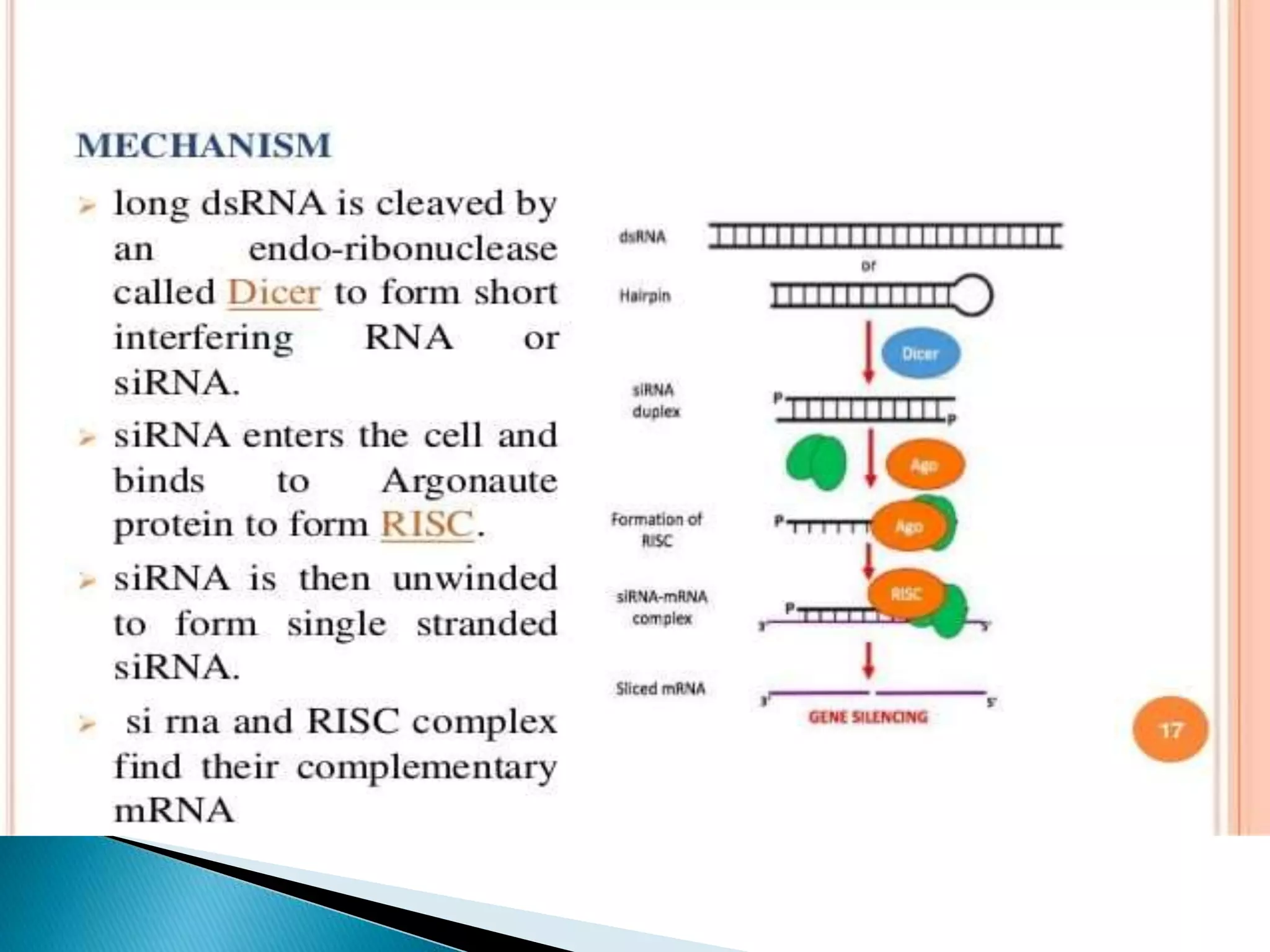
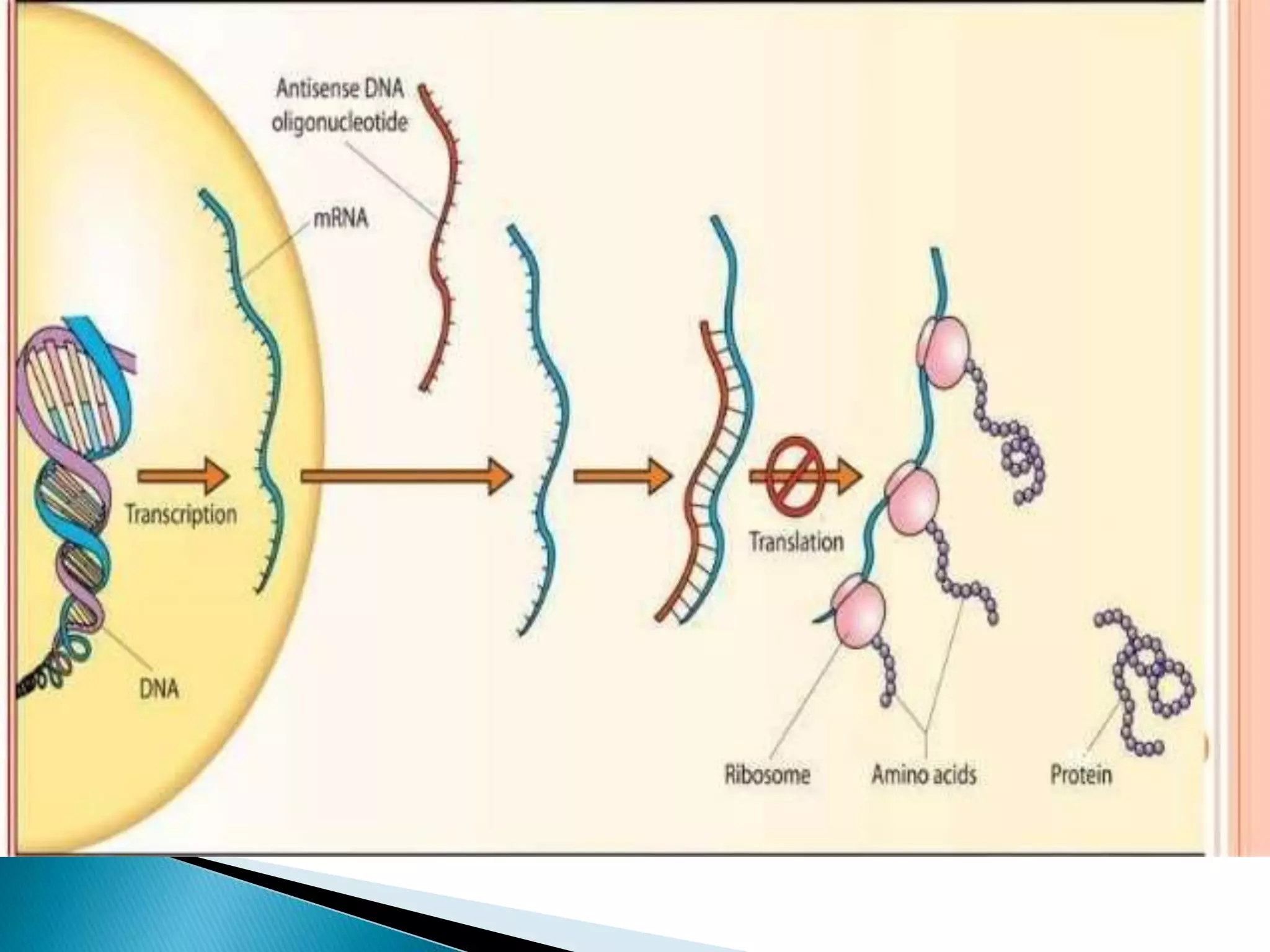
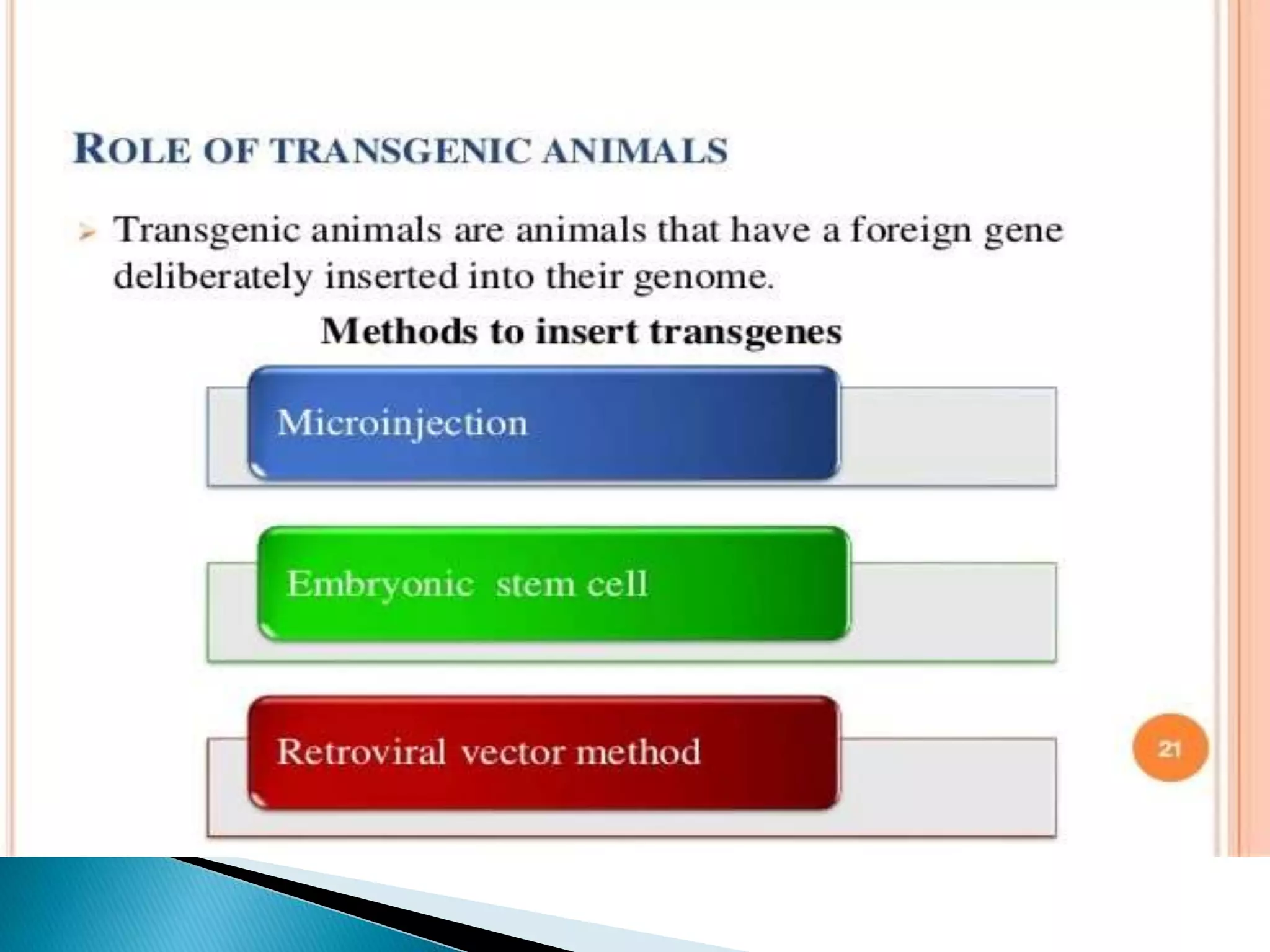
This document discusses drug discovery and the process of identifying potential new drug targets. It outlines the need for drug discovery to develop treatments for diseases without existing therapies. The key steps in drug discovery include target identification using genomics and proteomics to study the genome and map protein-protein interactions, as well as target validation using techniques like RNA interference and transgenic animal models. Bioinformatics plays an important role in analyzing large datasets to aid in drug target discovery and validation.