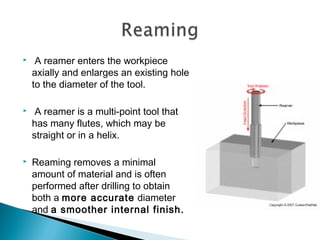
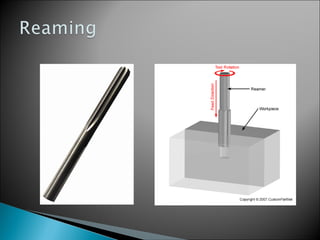
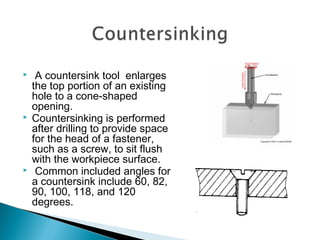
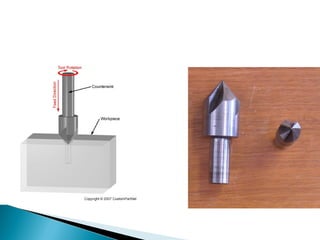
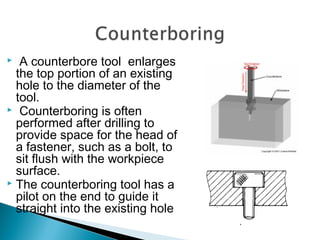
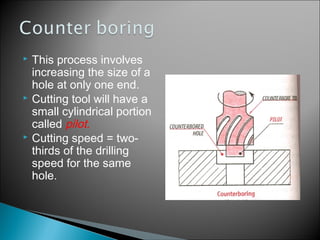
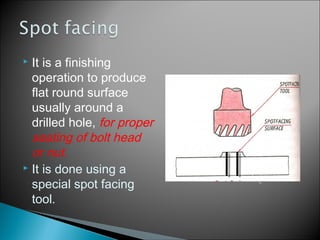
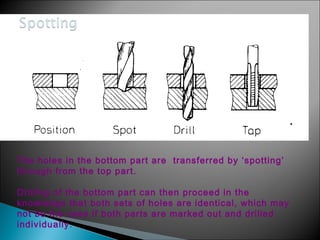
This document discusses various machining operations that can be performed in a drilling machine, including: drilling, reaming, boring, counterboring, countersinking, and spot facing. It provides details on what each operation involves, how each tool is shaped, and how each operation is performed relative to an existing hole. Reaming enlarges and smoothes an existing hole. Countersinking and counterboring enlarge the top of a hole to allow for fastener heads. Spot facing creates a flat surface around a hole for proper seating of bolts or nuts.