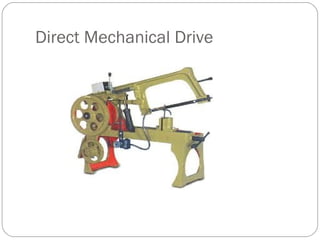
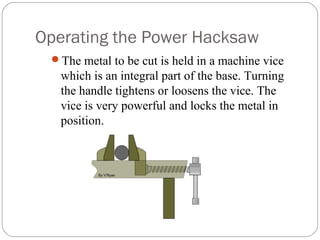
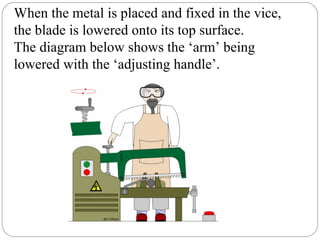
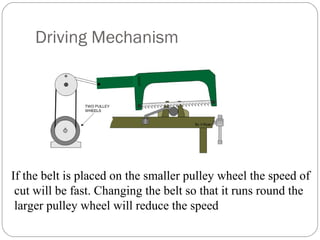
This document discusses power hacksaws, which are used to cut large pieces of metal like steel that would be difficult to cut by hand. It describes the main parts of a power hacksaw, including the reciprocating frame that moves the saw blade back and forth to cut the metal. The document outlines different types of power hacksaw drives and feed mechanisms that control the downward pressure of the blade. It provides guidance on operating a power hacksaw safely, including using coolant fluid to lubricate the blade and prevent overheating.