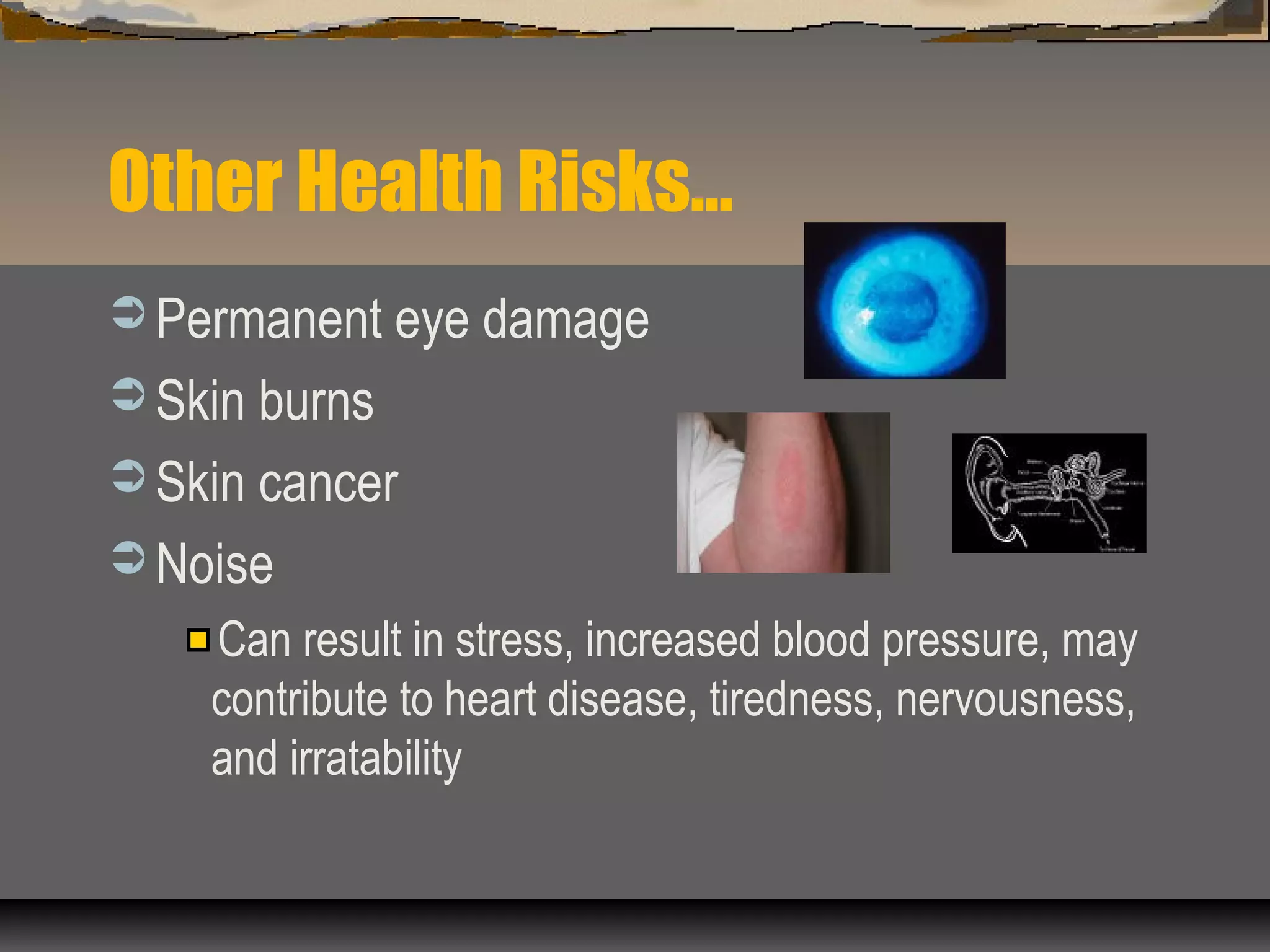
This document outlines various welding safety hazards and recommendations for reducing risks. It identifies health hazards from welding fumes, gases and particles that can cause both short-term and long-term effects. It also discusses electrical, fire, explosion, trip, fall, compressed gas, and noise hazards. The document provides tips for identifying hazards, using engineering controls, protective equipment, and following basic safety rules to reduce risks when welding.