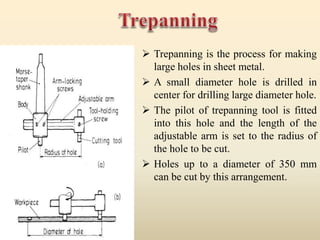
The document provides detailed information about various types of drilling machines and the drilling process, highlighting methods, tools, and safety measures in mechanical engineering. It covers specific machines such as portable, gang, and multi-spindle drilling machines, as well as different drilling operations like reaming, boring, and tapping. Additionally, it includes operational guidelines and calculations related to drilling parameters and material removal rates.