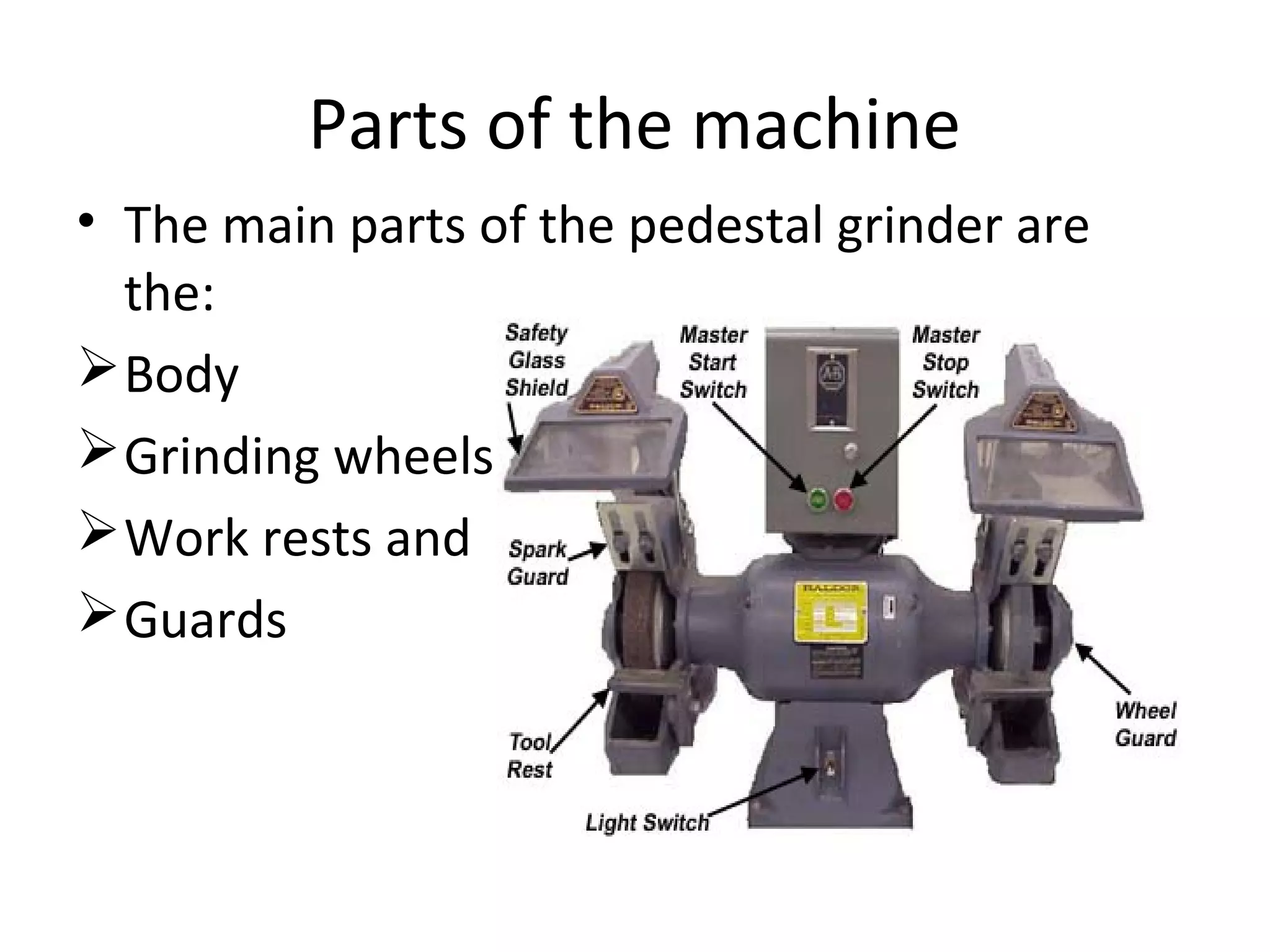
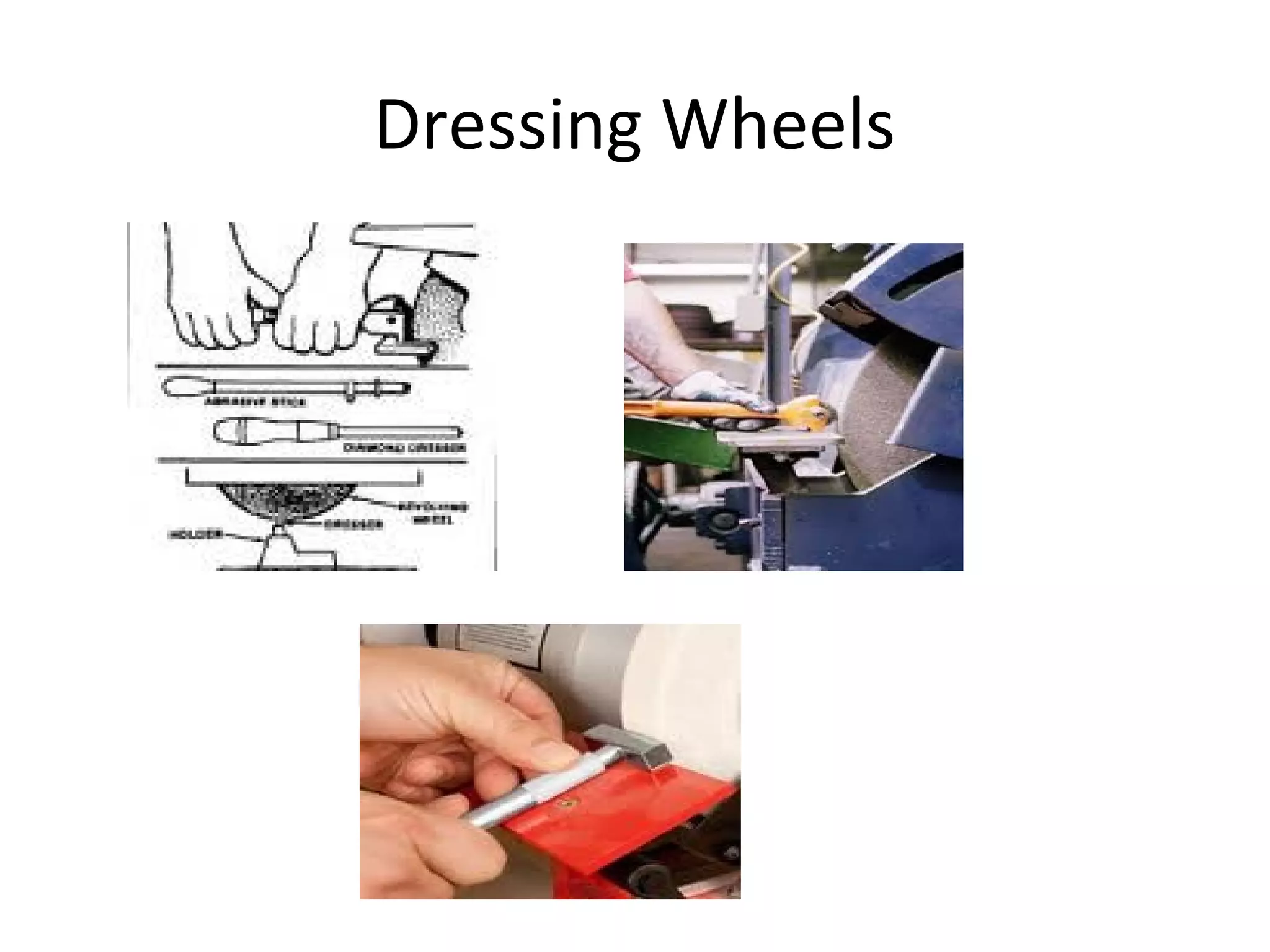
This document provides information about off-hand grinders, including safety rules, types of off-hand grinders, their main parts, selecting appropriate grinding wheels, and wheel maintenance. The key types of off-hand grinders are pedestal, bench, and portable. Safety precautions for use include wearing protective equipment and ensuring guards are in place. Proper wheel selection depends on factors like grit size and grade. Wheel dressing helps maintain efficient cutting by exposing fresh abrasive.