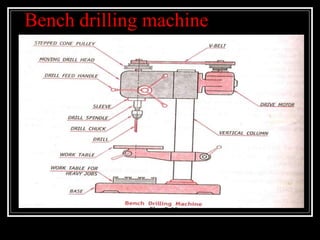
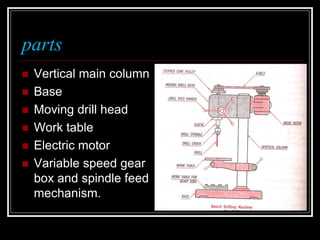
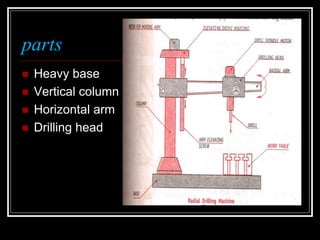
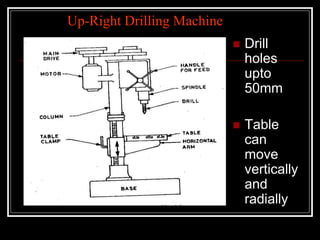
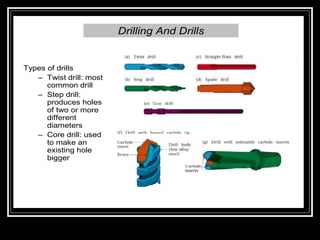
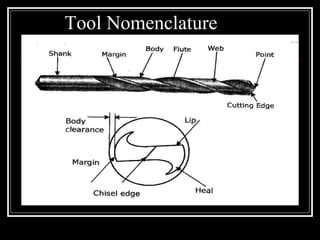
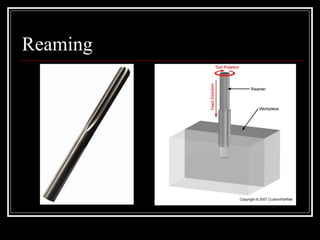
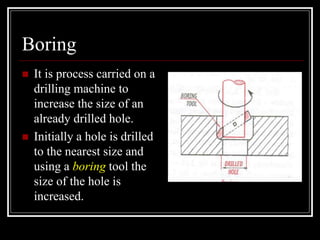
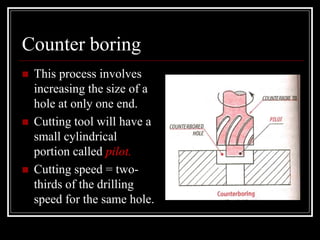
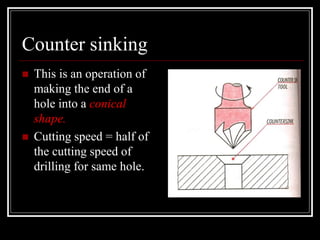
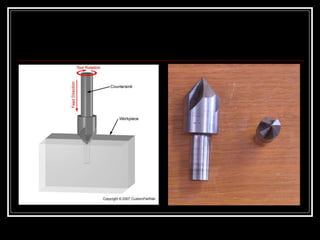
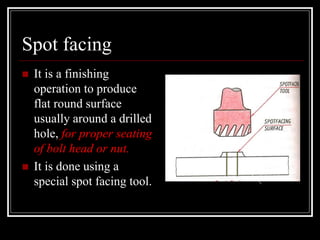
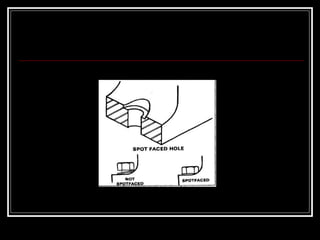
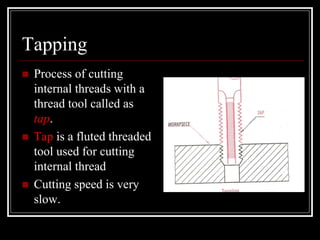
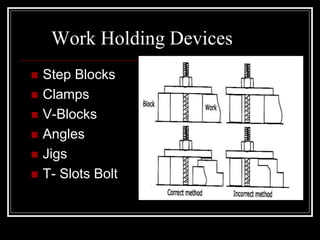
This document discusses drilling machines and drilling operations. It describes different types of drilling machines including bench drilling machines, radial drilling machines, and upright drilling machines. It also covers drilling tools and operations such as reaming, boring, counterboring, countersinking, spot facing and tapping. Safety precautions for operating drilling machines and definitions of cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut are provided.