Corynebacterial Toxins
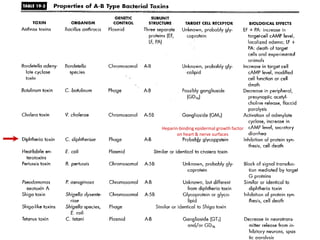
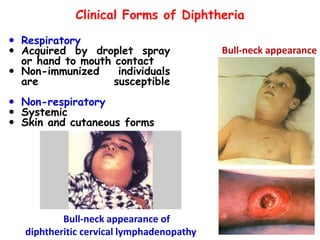
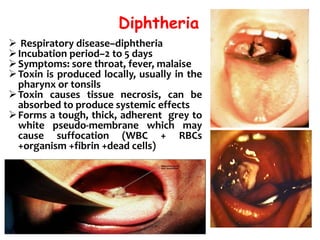
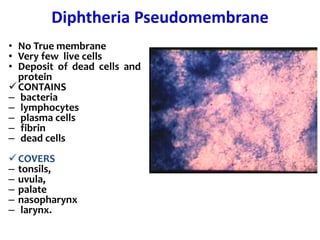
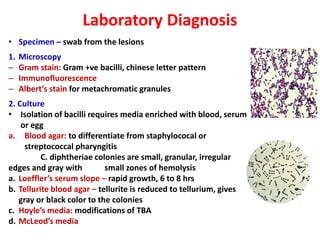
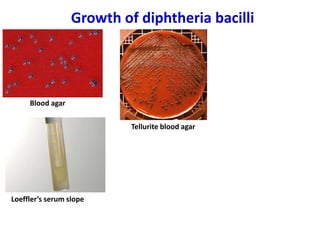
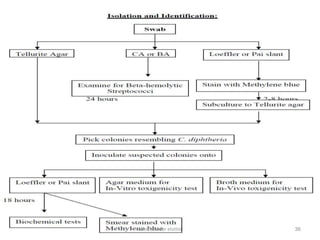
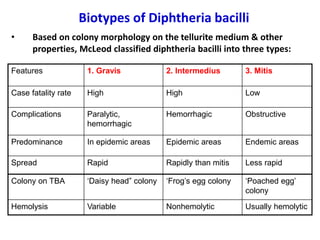
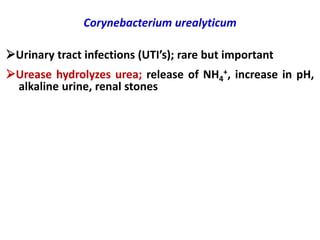
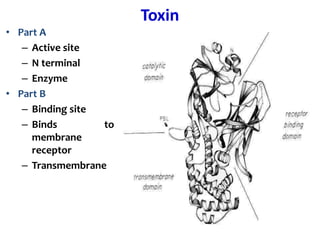
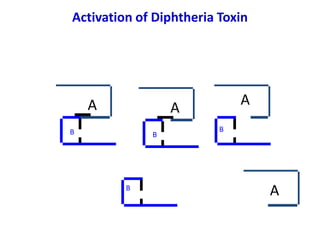
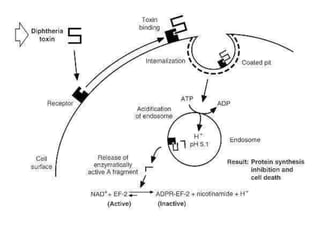
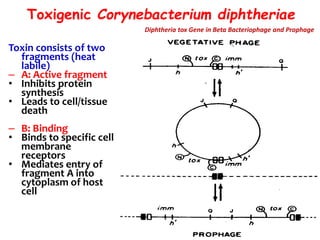
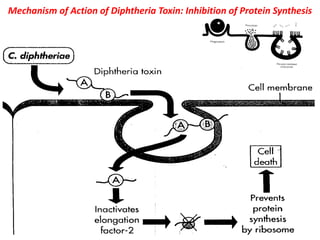
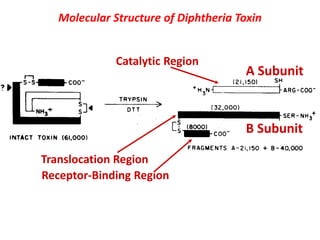
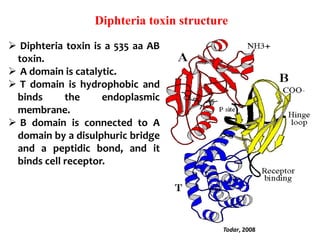
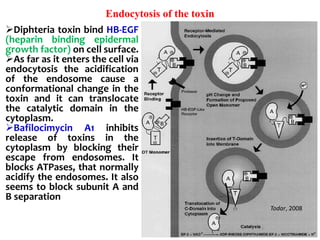
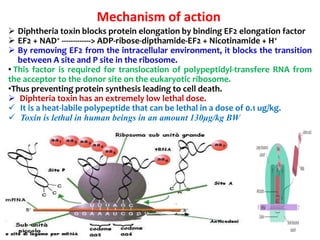
The document discusses Corynebacteria and their toxins, focusing on Corynebacterium diphtheriae, which causes diphtheria. C. diphtheriae produces a potent exotoxin that inhibits protein synthesis and causes tissue damage. The toxin has two components - component A carries the enzymatic activity, while component B binds to host cell receptors to transport component A inside cells. After entering cells, the toxin enzymatically modifies elongation factor 2, blocking protein synthesis and killing host cells. Vaccines containing toxoid have greatly reduced diphtheria incidence worldwide.









![Diphtheria Toxin
• Blocks protein synthesis
• Protein 63Kd
• controlled by Tox gene
• lysogenic phage Beta-corynephage
• Expressed if [iron] low
• 2 components A-B](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corynebacteriumtoxins-210226184751/85/Corynebacterial-toxins-12-320.jpg)


![Regulation of Diphtheria Toxin High [Fe 2+]
dtxR
Fe 2+ + apo DtxR
[Fe 2+
*DtxR]
p
C diphtheriae
dtxR= repressor protein
NO Toxin Produced
tox
Corynebacteriophage beta
o
P](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corynebacteriumtoxins-210226184751/85/Corynebacterial-toxins-25-320.jpg)
![Regulation of Diphtheria Toxin Low [Fe 2+]
Fe 2+ + apo DtxR
[Fe 2+
*DtxR]
Toxin Produced!!!
tox
Corynebacteriophage beta
o
P](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corynebacteriumtoxins-210226184751/85/Corynebacterial-toxins-26-320.jpg)