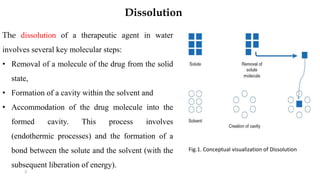
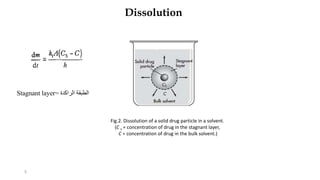
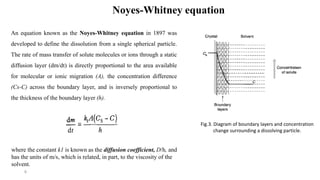
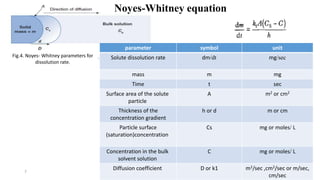
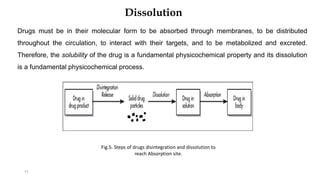
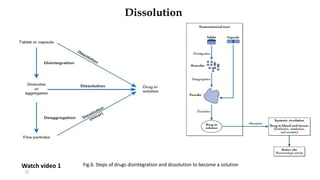
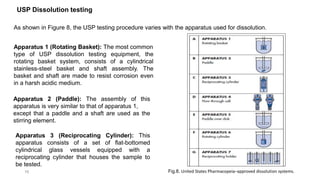
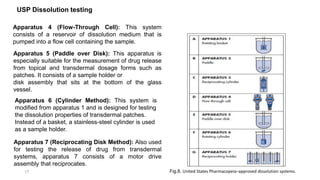
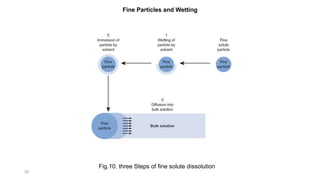
This document discusses solubility and dissolution of solids in liquids, which are important processes in pharmaceutical solutions. It describes dissolution as a process where a substance goes into solution. Solubility is defined as the capacity of a solute to dissolve in a pure solvent. The document then discusses key steps in the dissolution process including removal of drug molecules from the solid state, formation of solvent cavities, and accommodation of drug molecules into the cavities. It presents the Noyes-Whitney equation, which describes dissolution rate in terms of surface area, concentration gradient, and diffusion coefficient. Finally, it notes that quality control dissolution testing is required by the FDA to ensure batch-to-batch uniformity of pharmaceutical formulations.