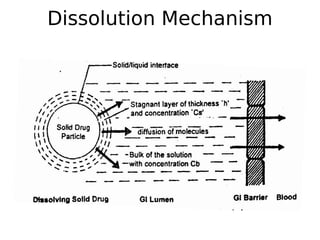
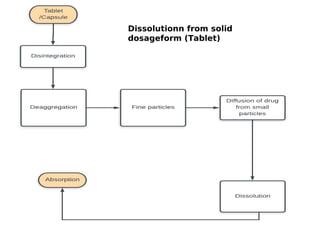
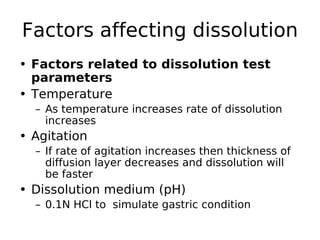
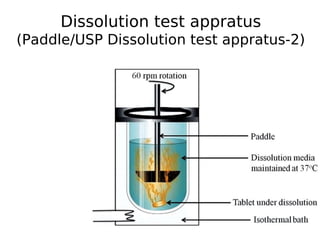
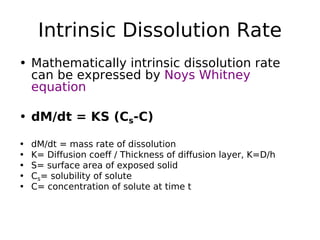
This document discusses dissolution, which refers to the process by which a solid drug product dissolves into solution. It describes the film theory of dissolution, where a saturated film forms at the solid-liquid interface and drug diffusion through this film is the rate-determining step. Factors that affect dissolution are also outlined, including drug properties like solubility and particle size, as well as dosage form properties and test parameters. Equations for describing dissolution kinetics like the Noyes-Whitney and Hixson-Crowell cube root models are provided. Intrinsic dissolution rate, which measures dissolution under standardized conditions, is also defined.











![• The drugs density is multiplied by the infinitesimal volume change .....
ρ.dV = dM....from eqn (4)
• -ρ.dV = k.S.Cs.dt --------------------------- (5)
• Equations (2) and (3) are substituted into equation (5) , to yield
• -4 ρ N Π r2 . dr = 4 N Π r2 . k .Cs .dt -------------(6)
• Equation (6) is divided through by 4 N Π r2 to give
• - ρ . dr = k Cs.dt -------------------------(7)
• Integration with r = ro at t= 0 produces the expression
• r = ro – (kCs . t/ ρ) -----------------------------(8)
• The radius of spherical particles can be replaced by the mass of N
particles by using the relationship of volume of sphere
• M = N ρ(Π/6)d3 ----------------------------(9)
• Taking cube root of the equation (9) yield,
• M1/3 = [ N ρ(Π/6)] 1/3 . d. ----------------------------(10)
• The diameter d from equation (10) ,is substituted for 2r into equation
(8) to give...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissolution-180228181758/85/Dissolution-21-320.jpg)
![• M1/3 = [ N ρ(Π/6)] 1/3 . 2r
• Mo
1/3 - M 1/3 = kt
• Mo = Original mass of drug particle
• k = [ N ρ (Π/6) ]1/3.2 k Cs/ρ = Mo
1/3 /d . 2k Cs / ρ cube
root dissolution rate constant
• t = time
• M = Nρ(π/6)d3
• N= No. of particles
• ρ = Density of particles
• d = Diameter of particles
Hixson – Crowell Cube root Law](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissolution-180228181758/85/Dissolution-22-320.jpg)
