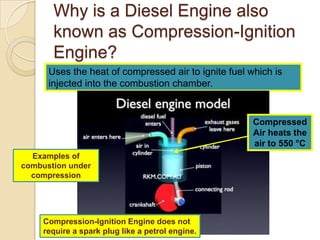
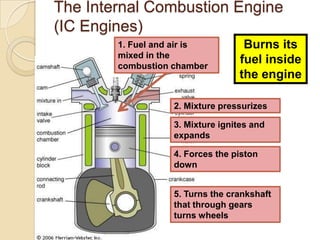
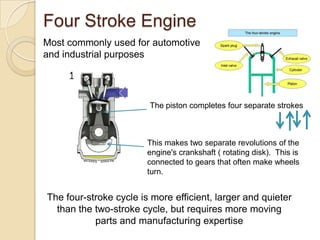
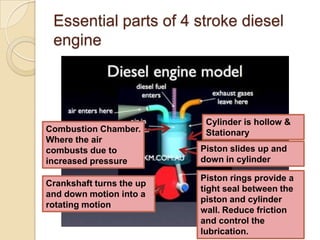
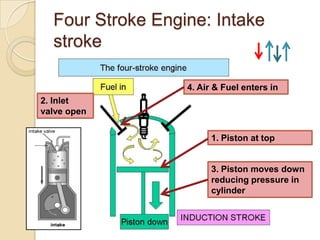
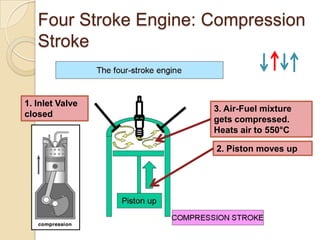
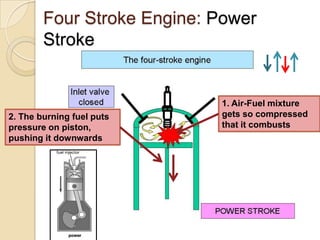
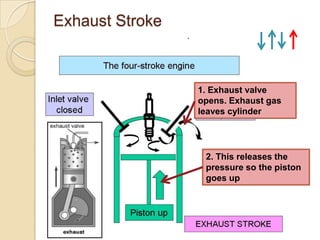
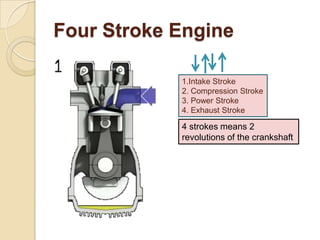
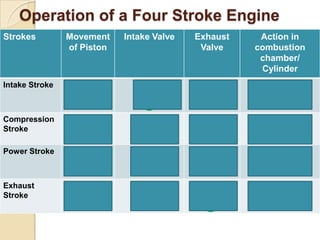
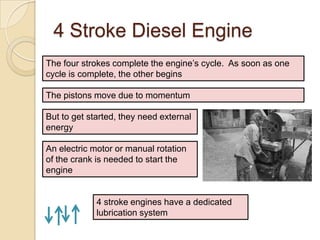
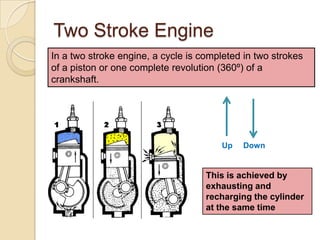
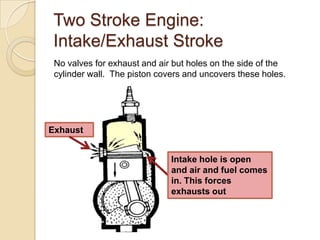
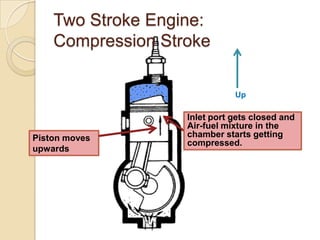
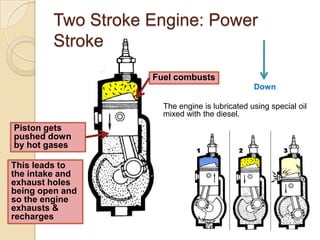
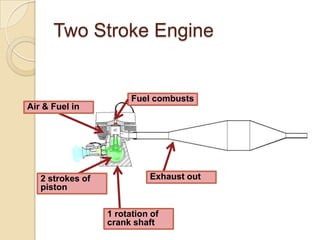
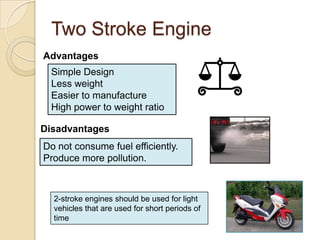
The document discusses diesel engines and how they work. It explains that diesel engines ignite fuel through heat of compressed air rather than a spark plug. It provides details on the 4-stroke diesel engine cycle including intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes. It also describes the simpler 2-stroke engine cycle and discusses advantages and disadvantages of each.