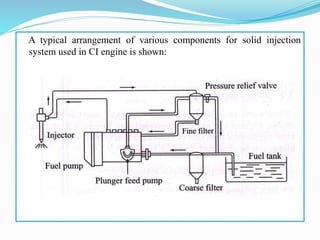
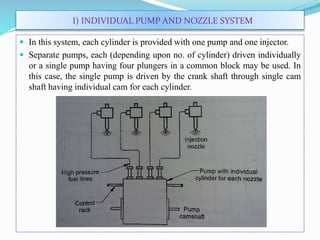
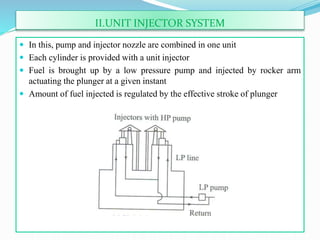
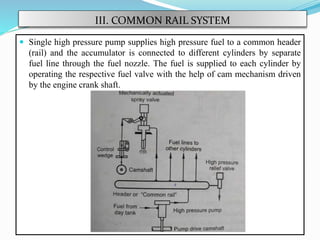
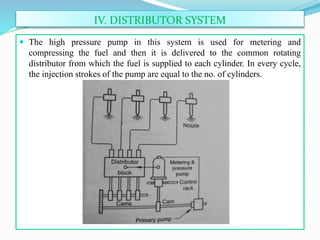
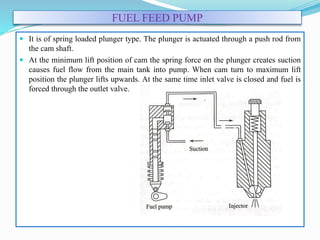
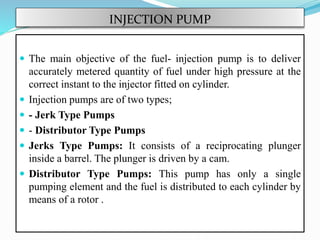
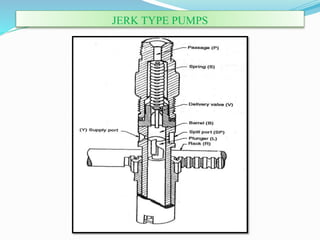
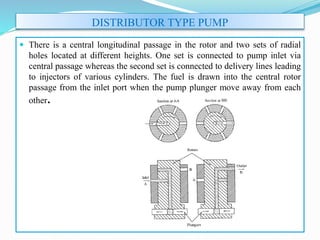
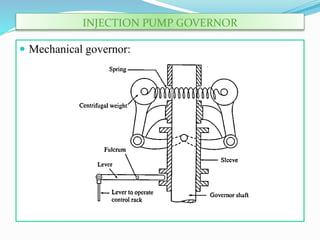
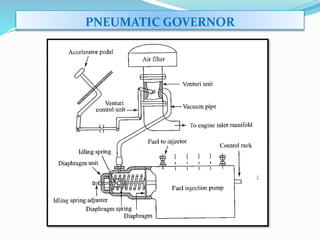
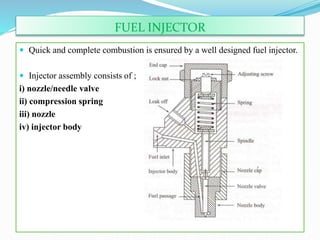
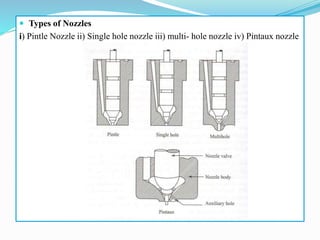
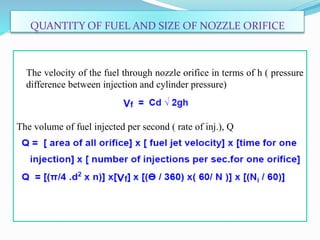
The document discusses mechanical fuel injection systems for diesel engines. It describes the key components of such a system including the fuel tank, fuel feed pump, injection pump, injectors, and filters. It then covers four main types of injection systems - individual pump and nozzle, unit injector, common rail, and distributor systems. For each system, it explains the basic configuration and operation. The document also discusses injection pumps, governors, injectors, nozzles, spray formation, and equations for determining fuel velocity and injection rate. In summary, it provides an overview of the components, classification, and functioning of mechanical fuel injection systems for diesel engines.