Embed presentation
Downloaded 19 times




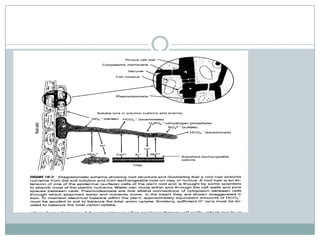


Nutrients reach plant roots through three mechanisms: mass flow with water, diffusion along concentration gradients, and root interception as roots extend. Roots absorb nutrients both passively through membranes or actively through ion-specific carriers. To maintain electrical balance, plants absorb cations and excrete hydrogen ions or produce organic anions, while absorbing anions and excreting bicarbonate ions or compensating cations. Nutrients can also be absorbed through leaves via stomata, allowing rapid uptake to correct deficiencies, though this does not build soil fertility and can cause toxicity.






