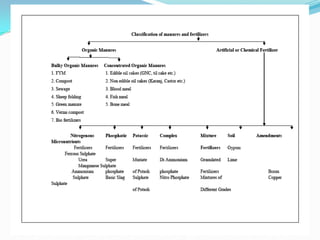
This document discusses different types of fertilizers:
- Straight fertilizers contain a single nutrient, while mix fertilizers contain two or more nutrients.
- Complete fertilizers contain nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, while incomplete fertilizers are missing at least one of these primary nutrients.
- Organic fertilizers come from animal or plant matter and slowly release nutrients, while inorganic fertilizers are chemical products that can be tailored to specific nutrient ratios.
- Soluble fertilizers dissolve in water for fertilization through irrigation, while insoluble granular or slow-release fertilizers are applied directly to soil.