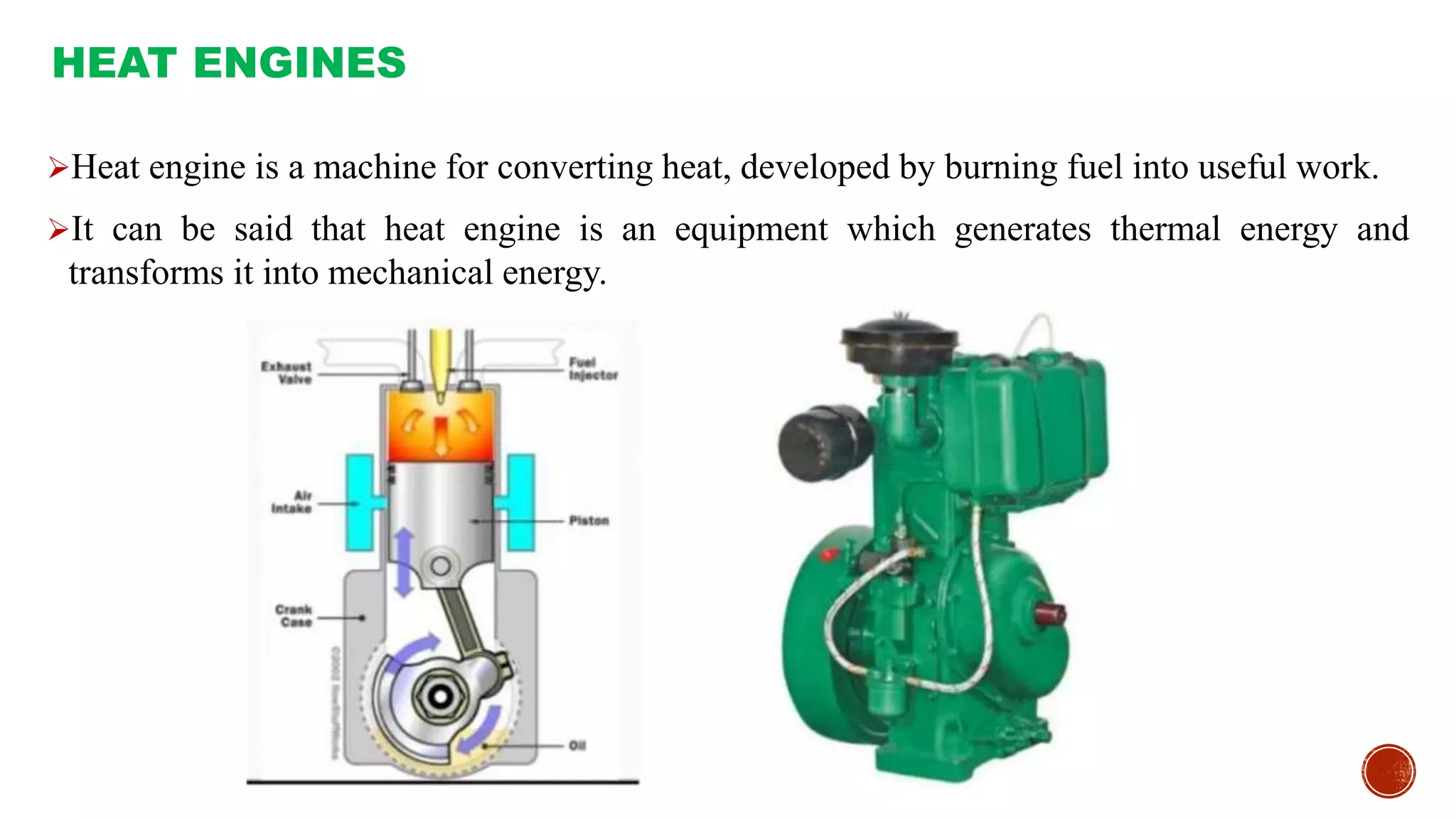
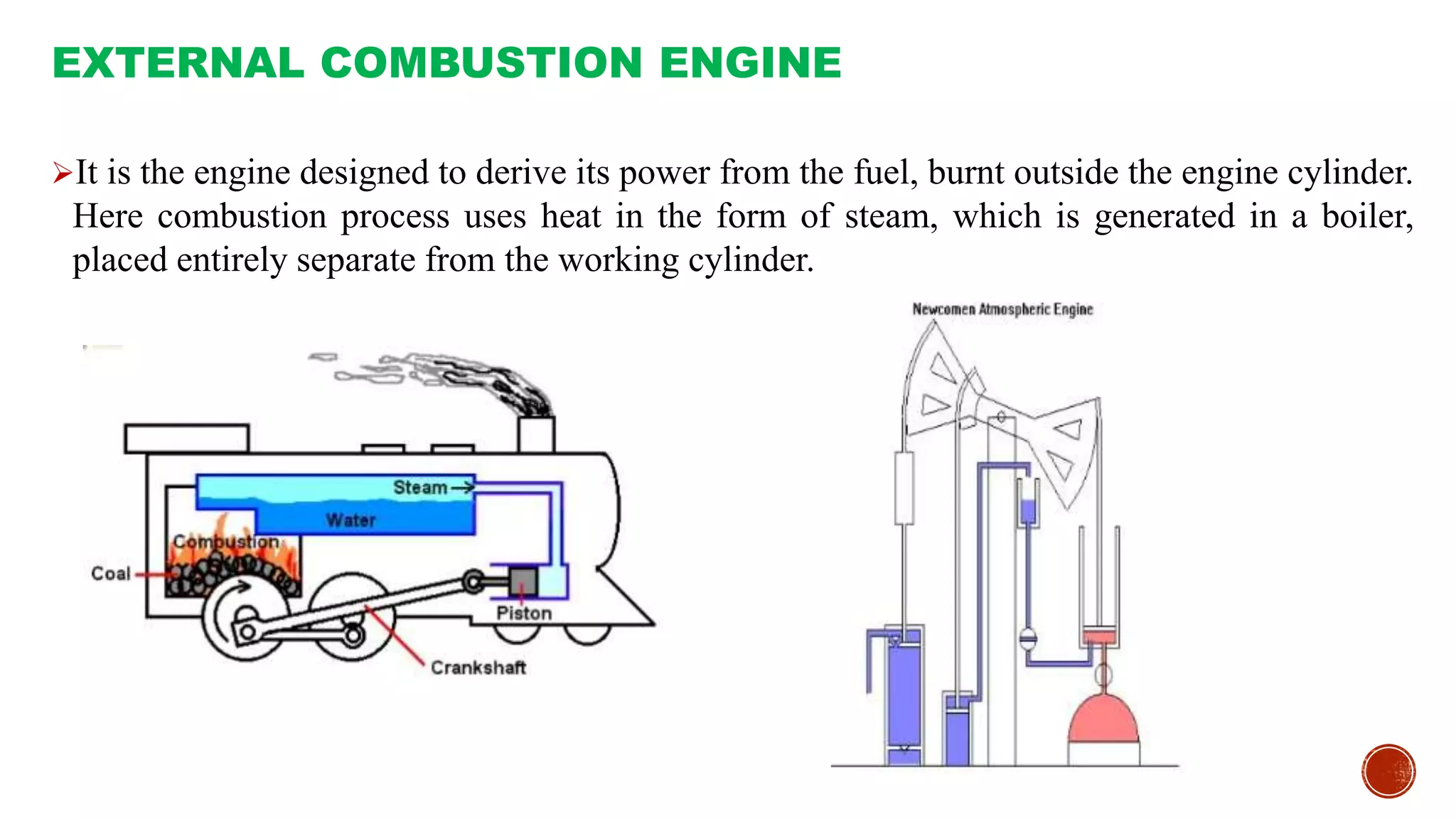
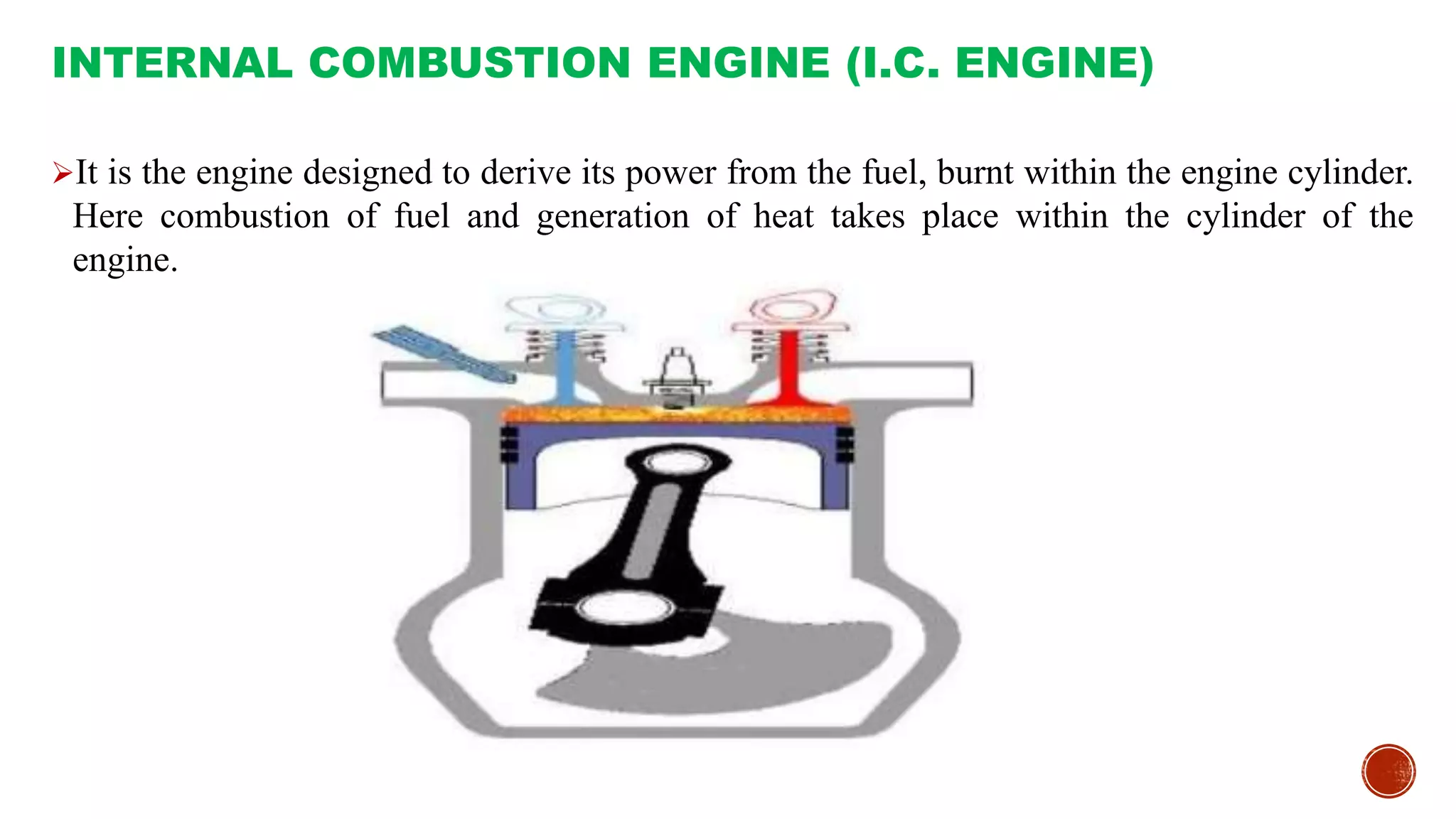
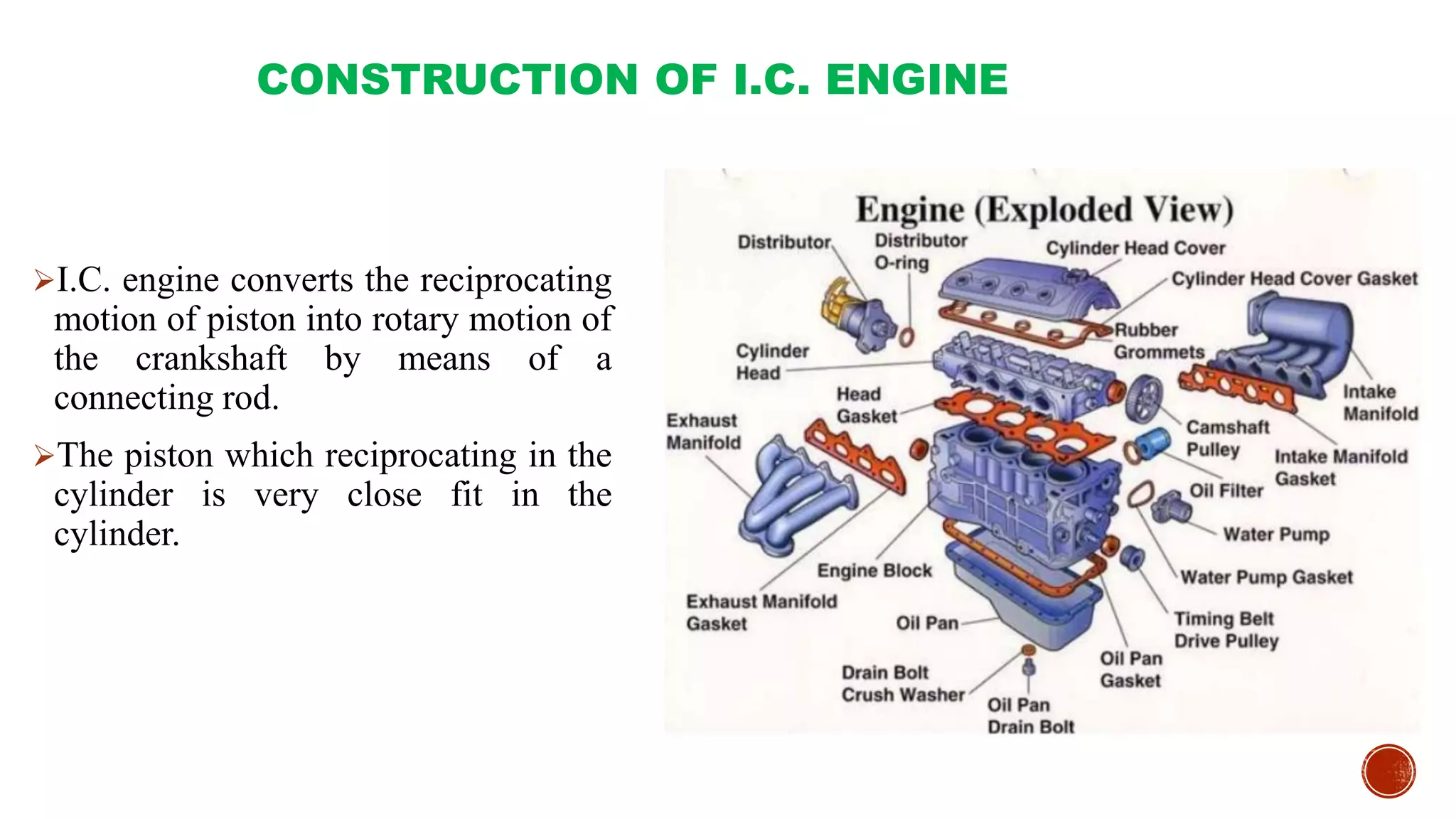
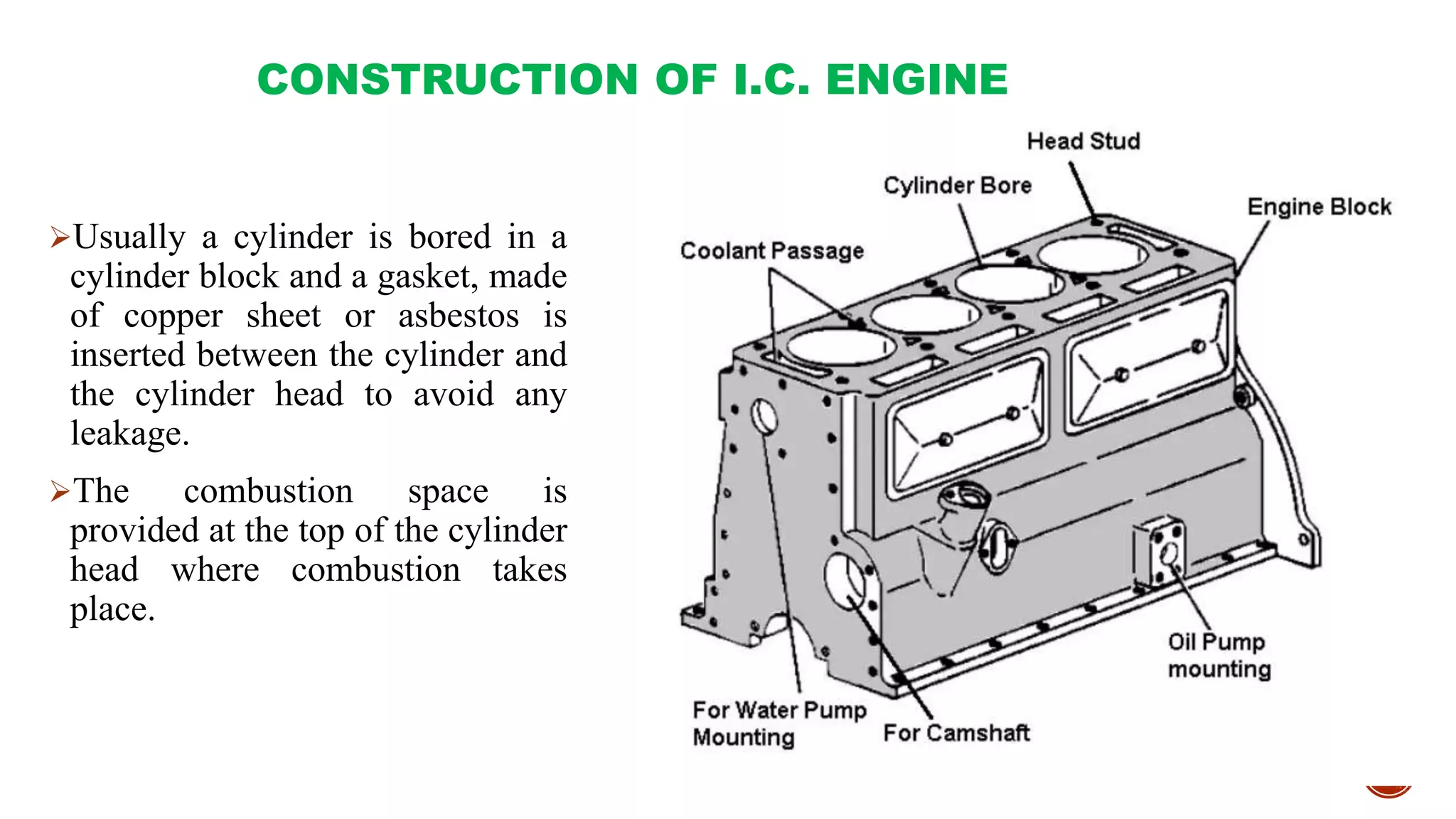
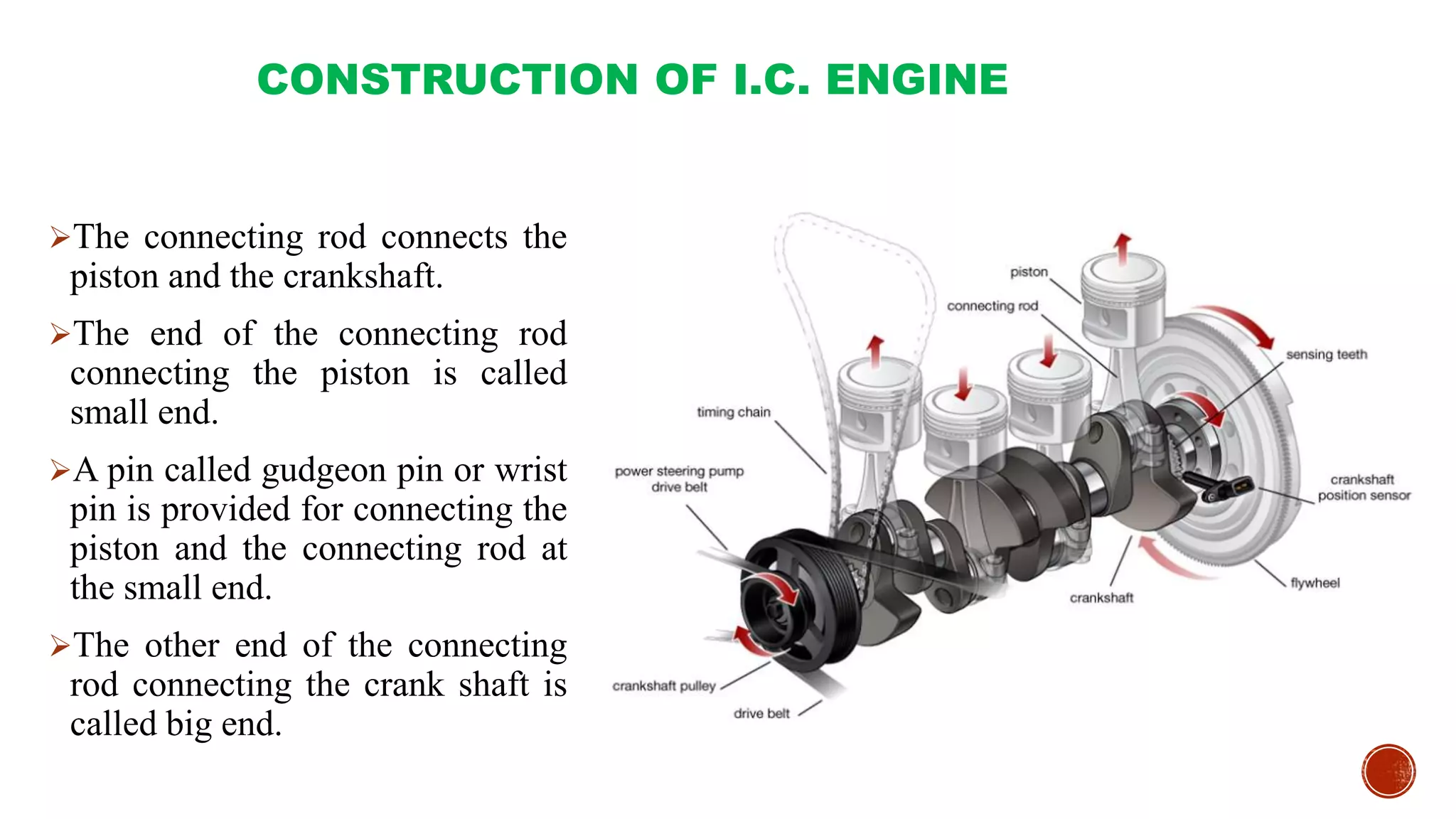
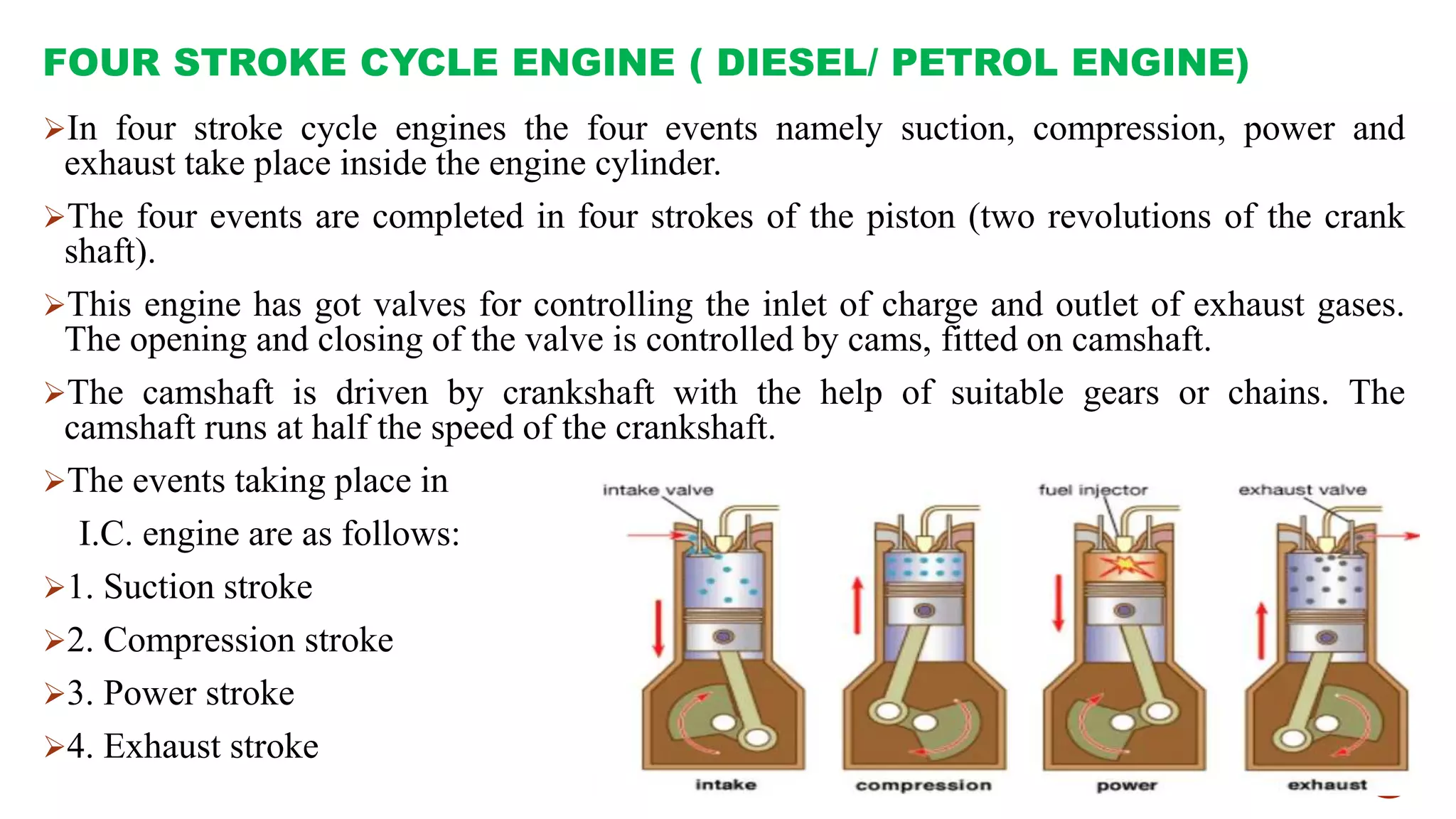
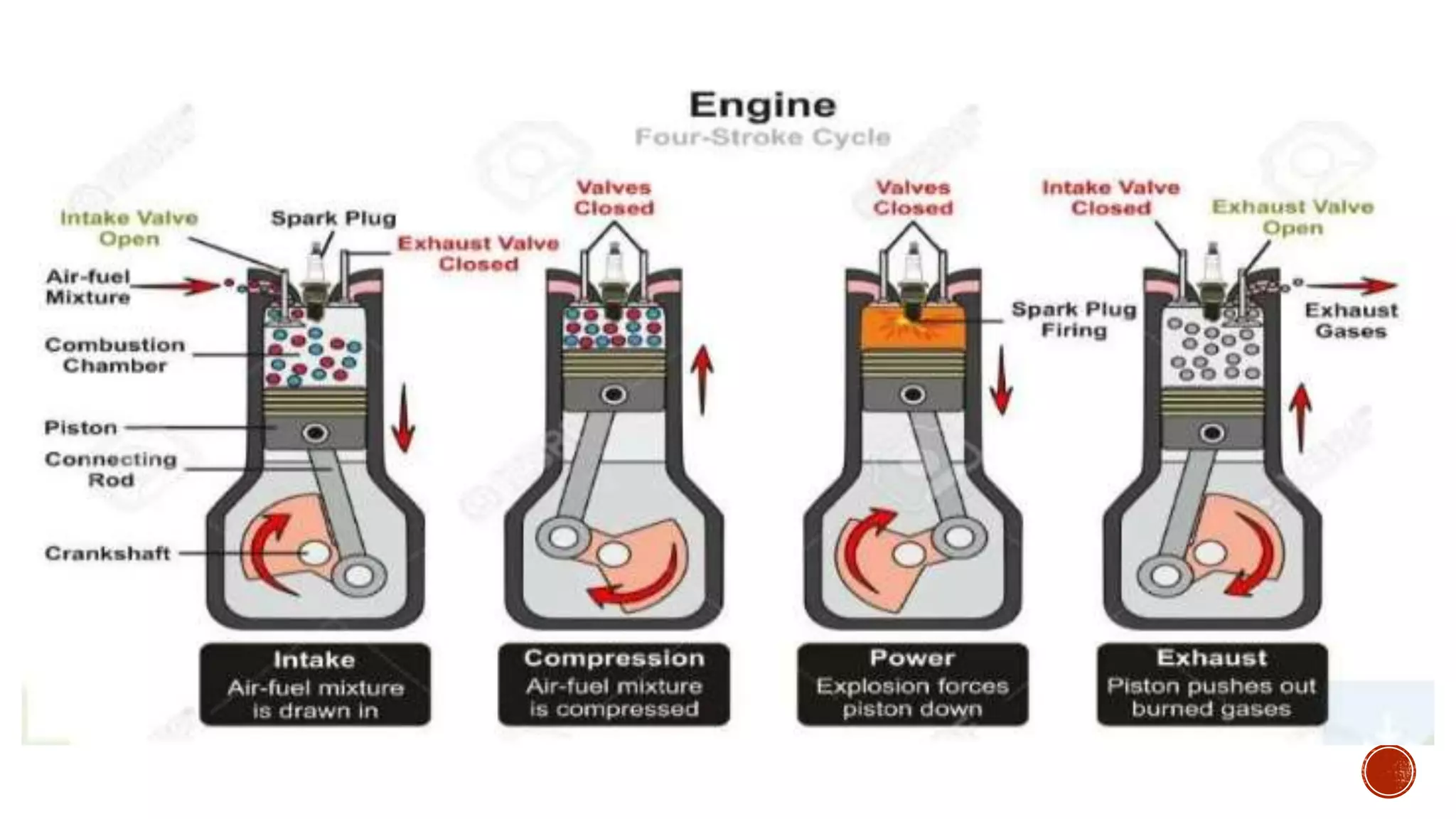
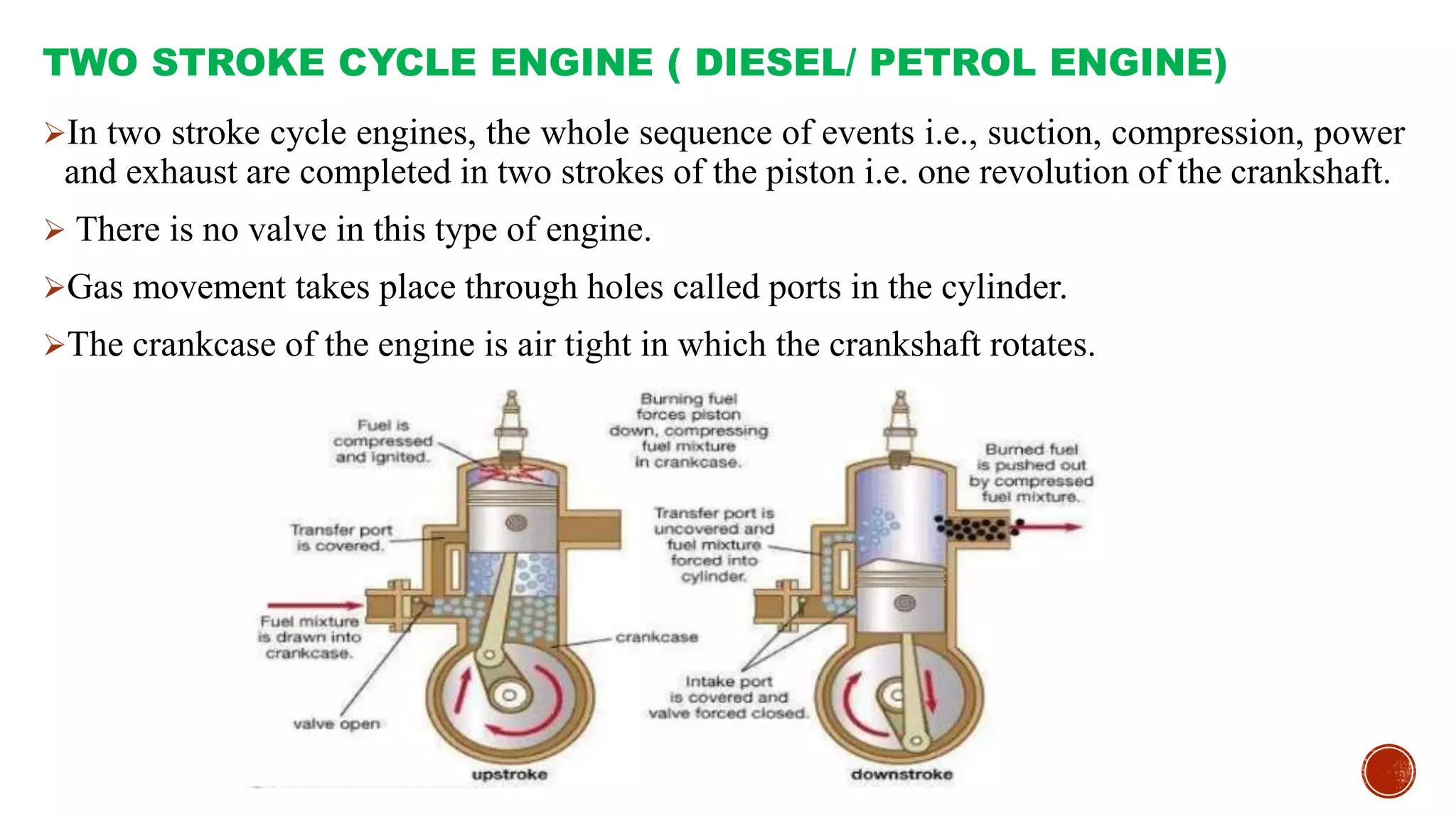
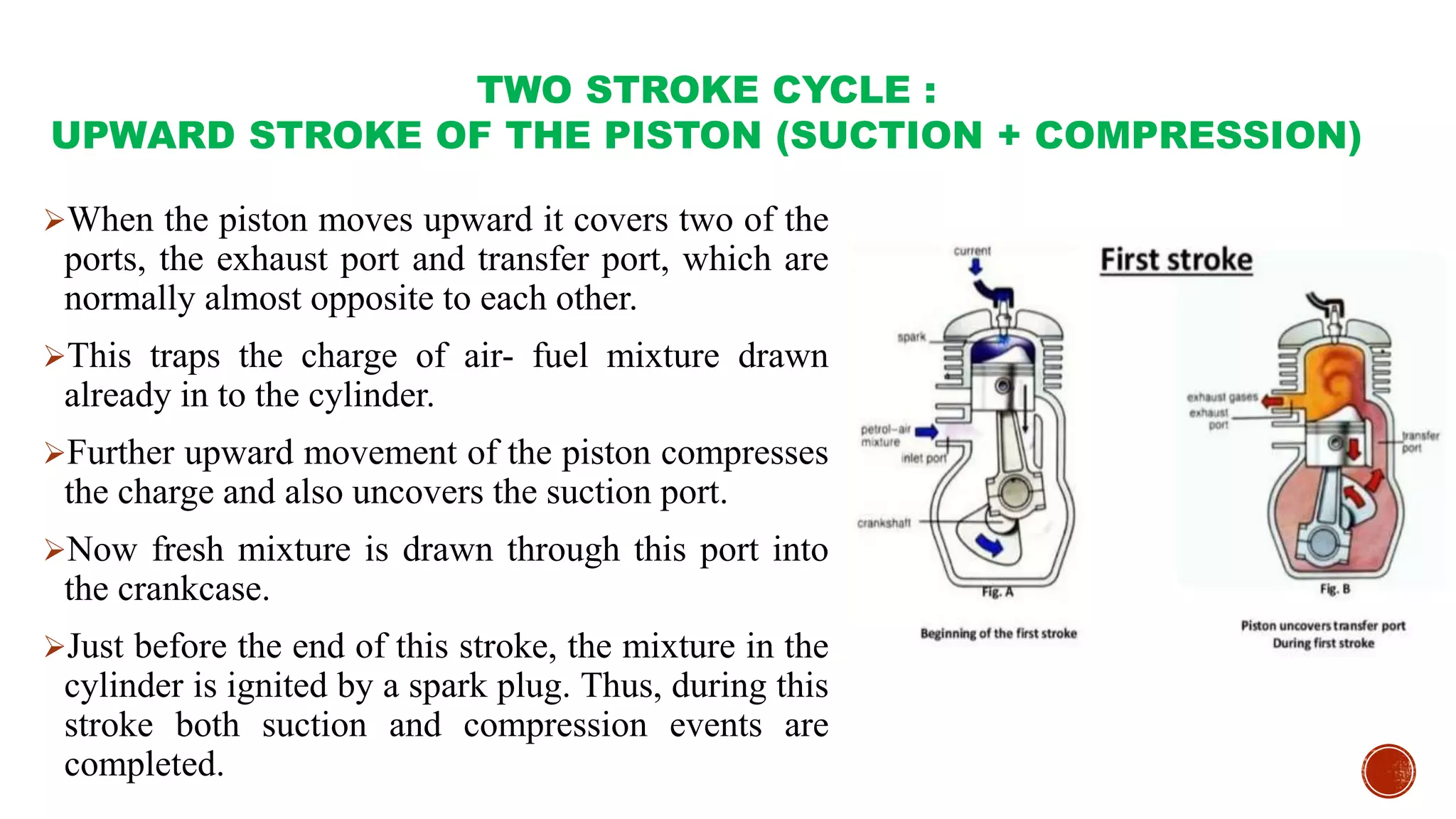
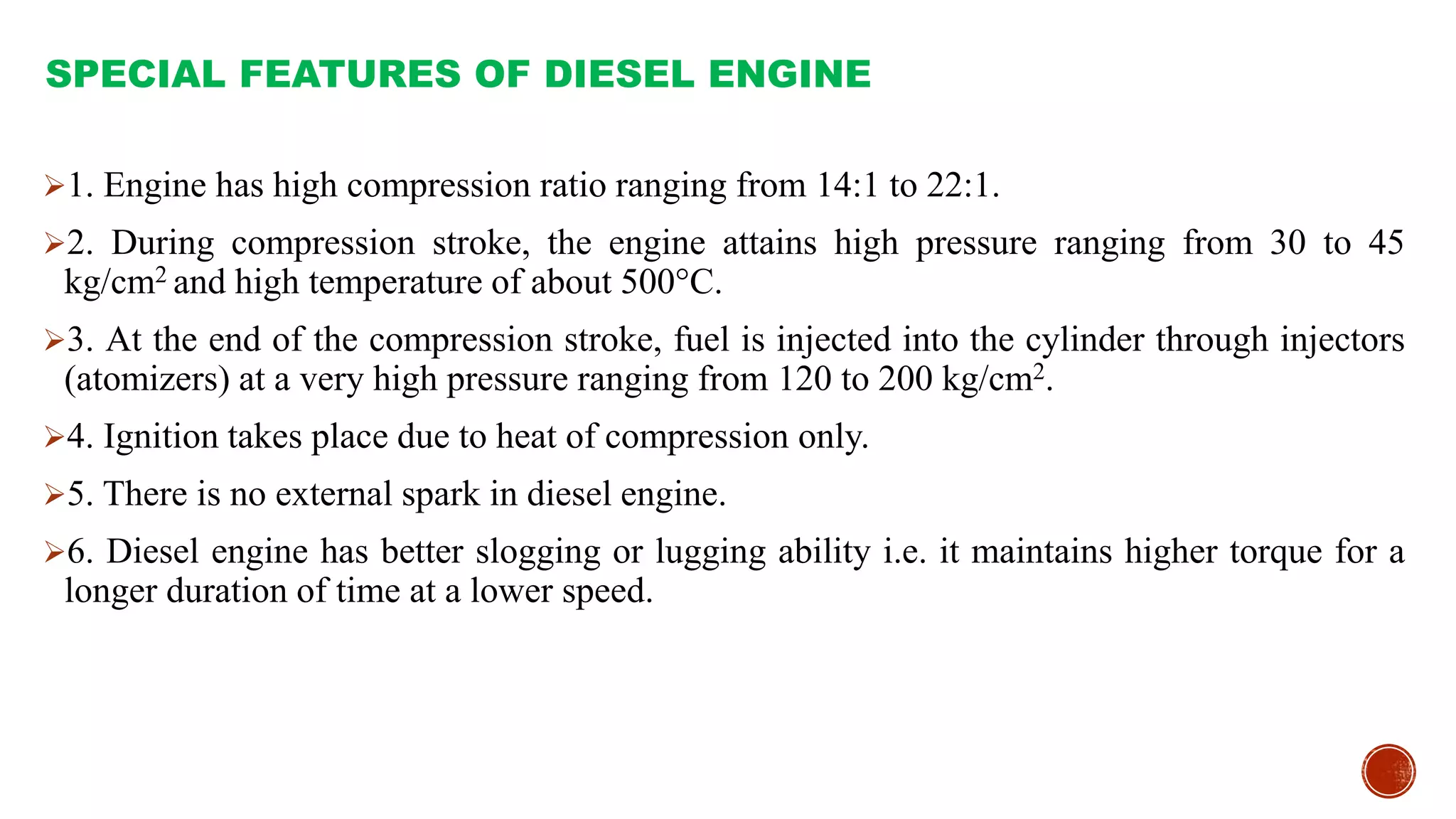
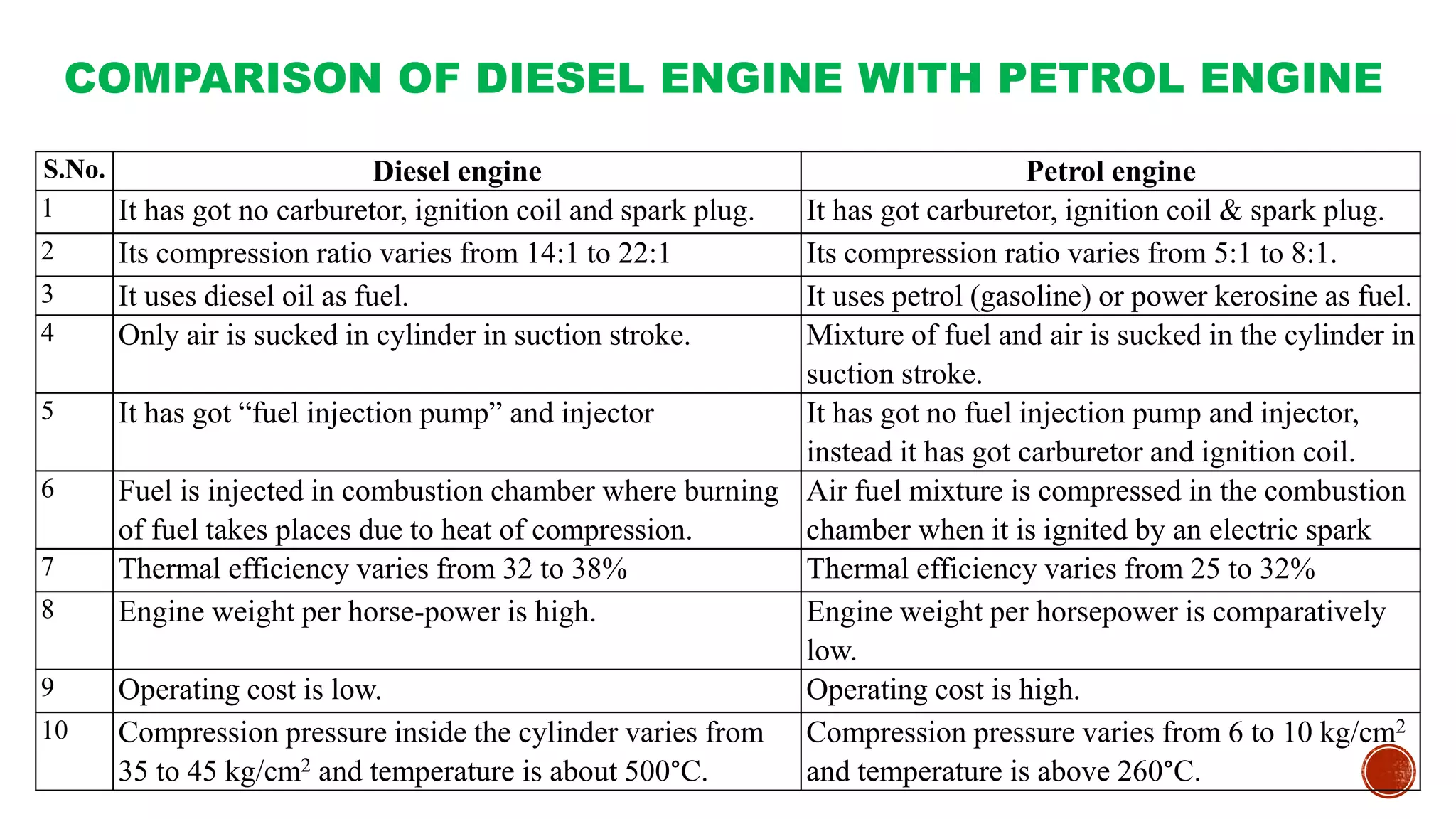
The document provides an overview of internal combustion engines, explaining their types, constructions, and operational principles. It details the differences between four-stroke and two-stroke engines, including their working cycles, parts, and performance characteristics. Additionally, it compares diesel engines and petrol engines in terms of features, efficiency, and operational costs.