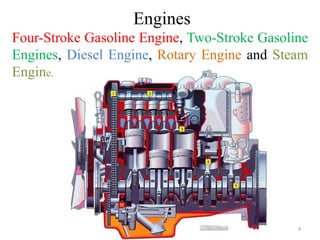
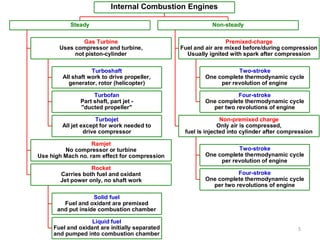
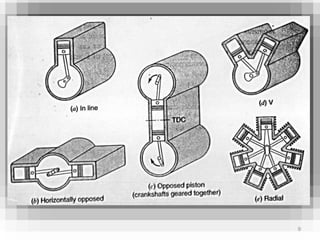
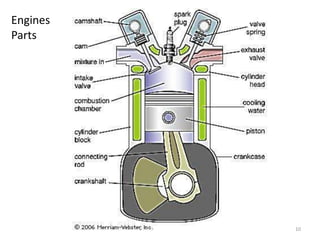
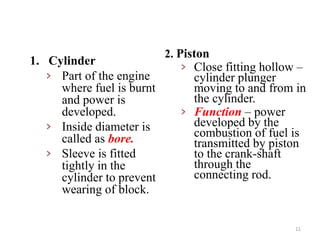
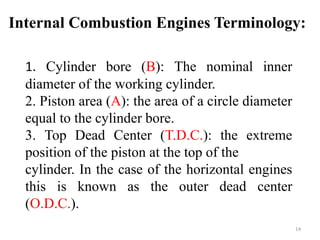
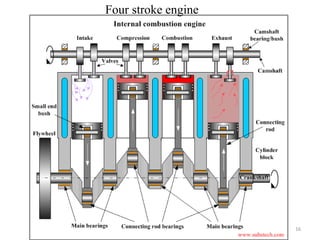
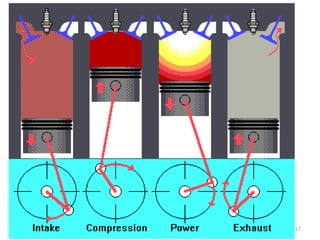
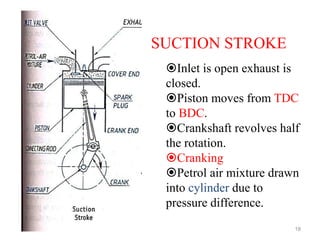
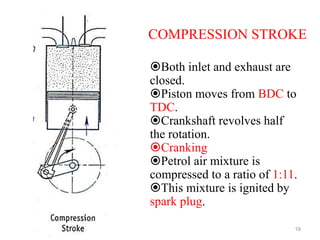
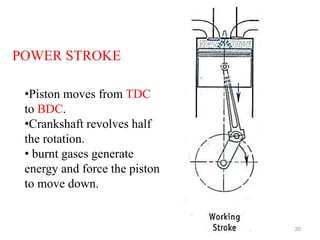
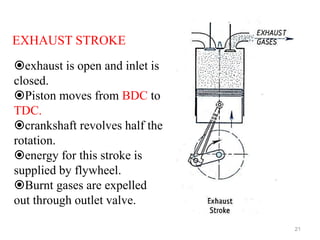
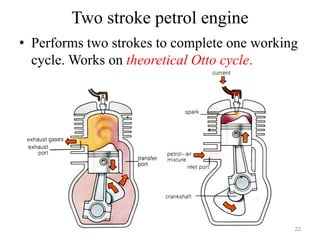
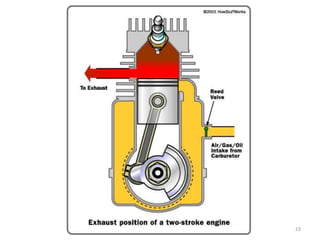
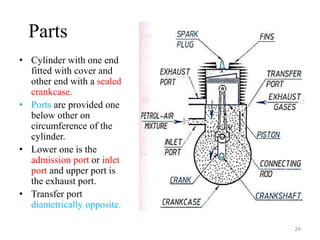
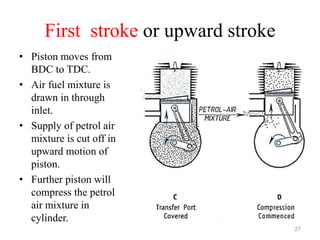
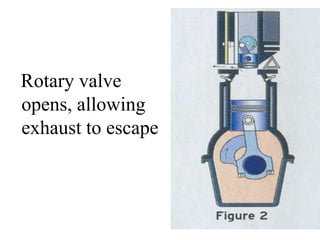
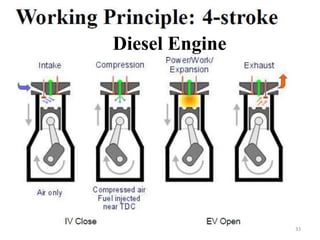
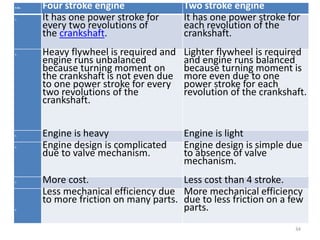
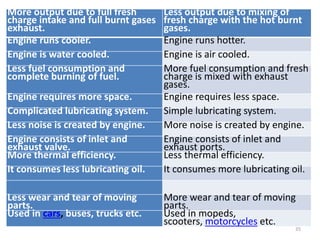
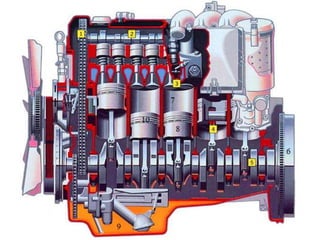
An internal combustion engine uses combustion of fuel to drive pistons that convert the energy to mechanical energy. The first modern internal combustion engine was created by Nikolaus Otto in 1876. There are several types of internal combustion engines including four-stroke gasoline engines, two-stroke gasoline engines, diesel engines, and rotary engines. Engines can also be classified based on their fuel, number of strokes, ignition method, combustion cycle, number of cylinders, and cylinder arrangement. The key parts of an internal combustion engine include the cylinder, piston, connecting rod, valves, crankshaft, and flywheel.