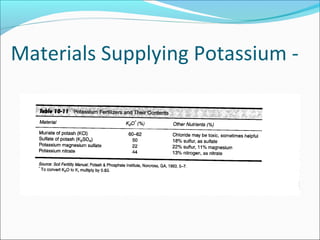
This document discusses macro and micro nutrients that are important for plant growth. It defines macro nutrients as those needed in large amounts, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium and sulfur. Micro nutrients, also called trace elements, are needed in small amounts and include iron, copper, zinc, boron, molybdenum and manganese. It provides details on the functions and deficiency symptoms of each of the major macro and micro nutrients.