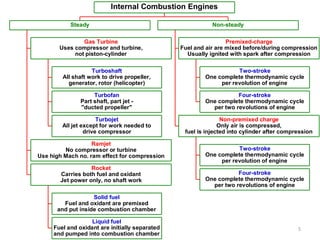
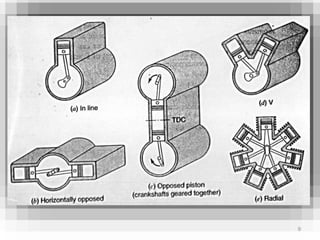
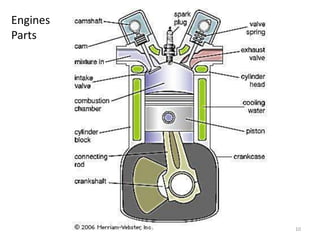
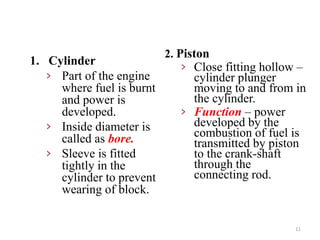
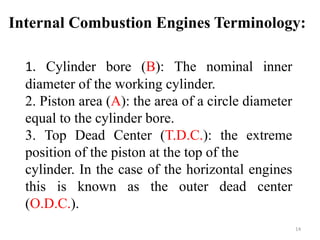
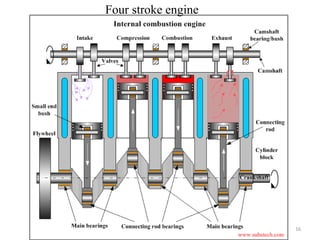
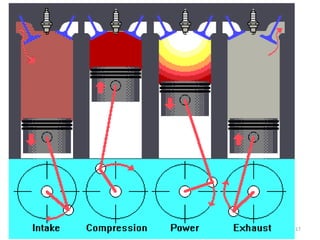
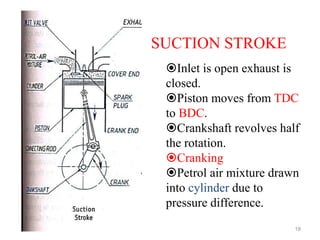
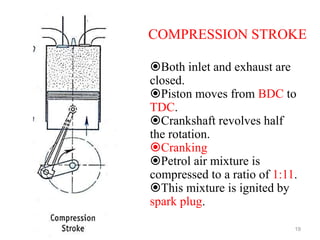
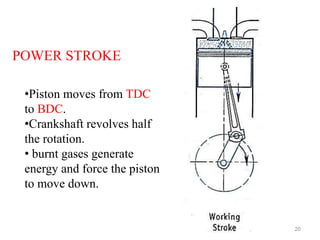
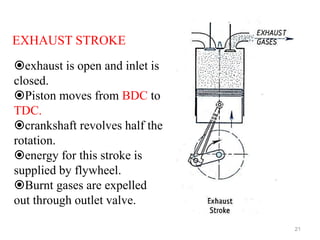
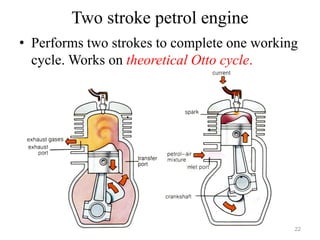
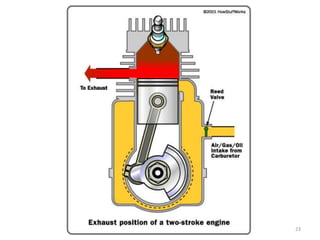
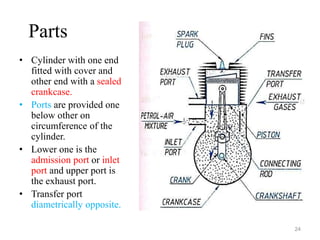
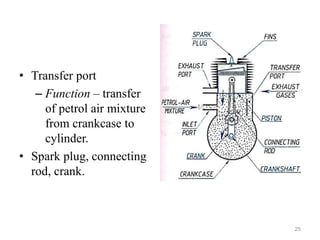
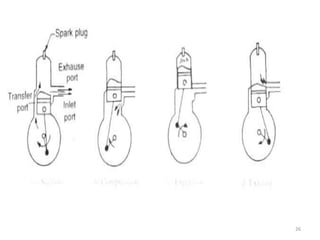
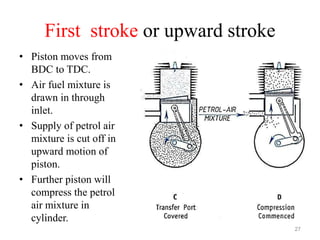
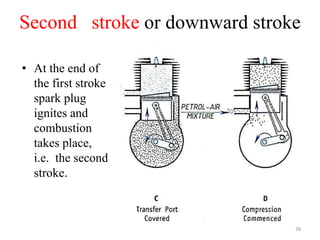
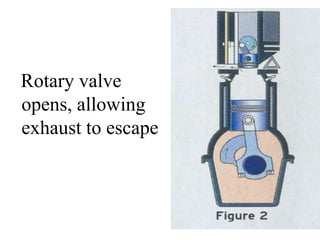
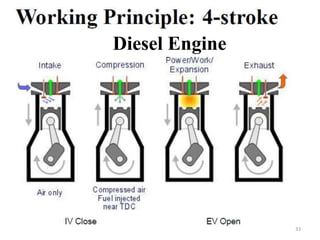
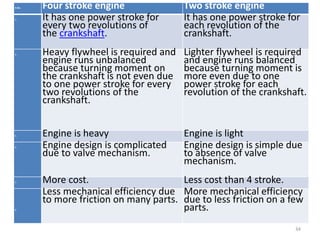
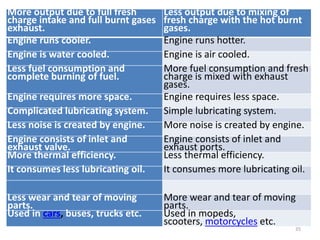
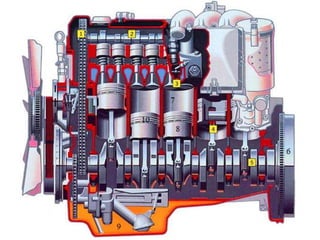
An internal combustion engine uses combustion of fuel to drive pistons that convert the energy to mechanical energy. The first modern internal combustion engine was created by Nikolaus Otto in 1876. There are different types of internal combustion engines classified by fuel, strokes, ignition, cycle, number of cylinders, and cooling method. The key parts include the cylinder, piston, connecting rod, valves, crankshaft, and flywheel. A four-stroke engine intakes air/fuel, compresses it, combusts it to push the piston, and exhausts gases over two revolutions, while a two-stroke engine does this in one revolution.