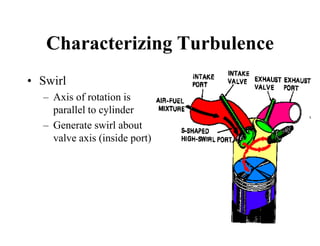
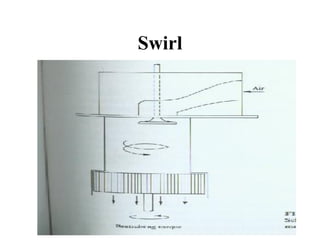
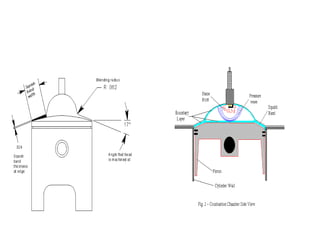
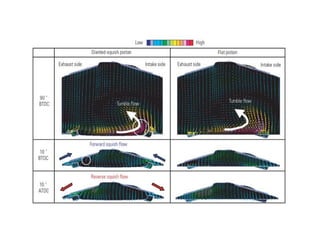
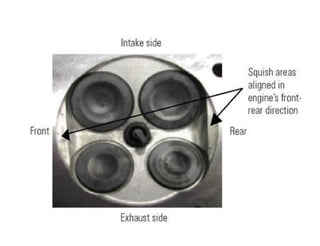
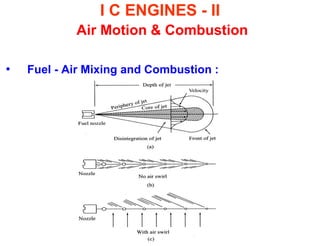
This document discusses air motion and combustion in internal combustion engines. It describes how swirl, tumble, and squish generate motion within the cylinder to promote fuel-air mixing and combustion. Swirl involves rotation around the valve axis, while tumble is perpendicular to the cylinder axis. Squish occurs as the piston approaches top dead center and compresses the mixture towards the combustion chamber. The document also mentions crevice flows and blowby, which involve gas escaping into engine crevices and crankcase. Finally, it describes how fuel is injected into the compressed air in CI engines to initiate combustion through fuel-air mixing.