Embed presentation
Downloaded 47 times


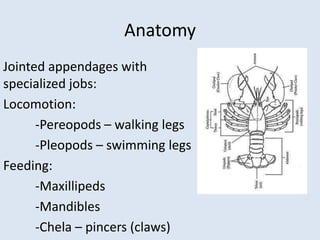
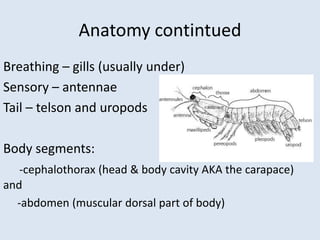
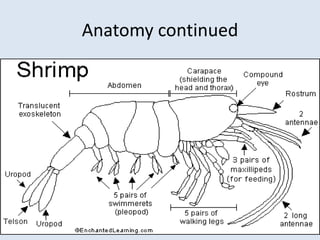
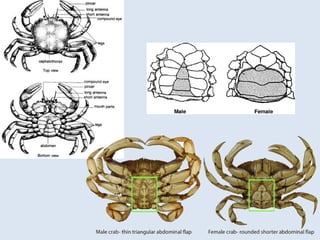


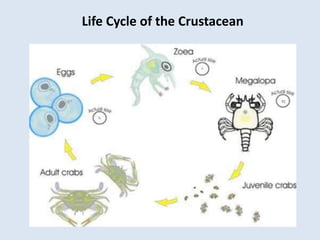

Crustaceans are arthropods in the subphylum Crustacea and include crabs, shrimp, lobsters, barnacles, copepods, krill, isopods, and amphipods. They have a jointed exoskeleton and specialized appendages for locomotion, feeding, breathing through gills, and sensing the environment. Crustaceans can be predators, scavengers, or filter feeders. They have separate sexes and males release sperm packets for females to store until fertilizing their eggs, which hatch externally.









