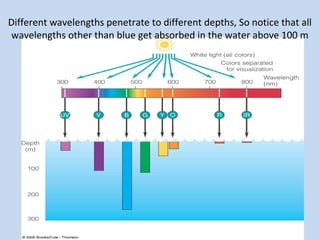
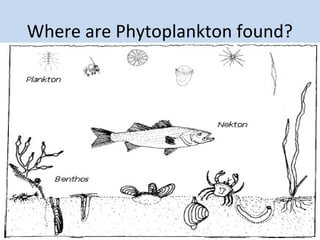
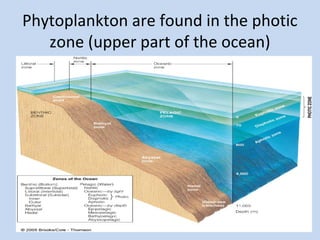
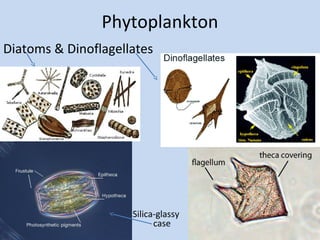
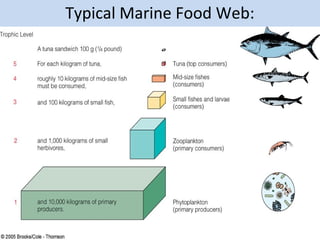
Plankton are tiny organisms that drift or float in the waters of seas, lakes, and rivers. They can be either autotrophs, which produce their own food through photosynthesis (phytoplankton like diatoms and dinoflagellates), or heterotrophs, which consume other organisms for food (zooplankton like tiny crustaceans). Phytoplankton are the base of the oceanic food web and are found in the photic zone where there is enough sunlight for photosynthesis. Some phytoplankton can bloom rapidly and be dangerous. Plankton play an important role in marine ecosystems.