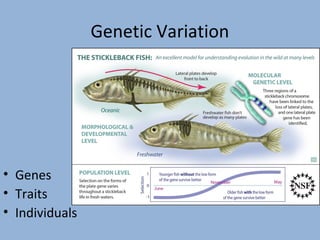
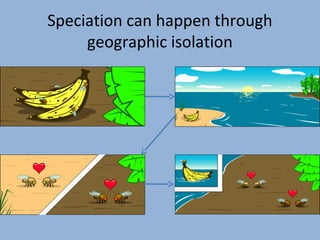
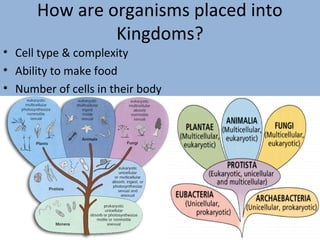
This document provides an introduction to key concepts in biological oceanography, including evolution, causes of evolution, and evidence of evolution. It defines evolution as change over time that occurs between species through processes like mutation, genetic drift, gene flow, natural selection, and non-random mating. The document also discusses concepts like overproduction, competition, genetic variation, adaptation, natural selection, speciation, classification, and the criteria used to place organisms into kingdoms.