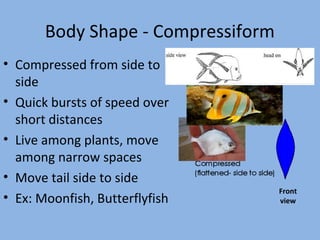
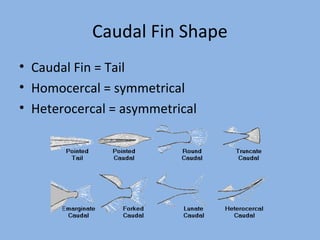
This document discusses the diversity of body shapes and tail fin morphologies in fish and how these adaptations help fish survive in their environments. It describes the main body shapes as fusiform for fast open water swimmers, compressiform for quick bursts of speed, and depressiform for bottom-dwelling fish. It also outlines different tail fin shapes including homocercal forms that are rounded, truncate, forked, or lunate and the heterocercal tail of sharks, and explains how each tail type relates to the fish's swimming ability, speed, maneuverability and environment.