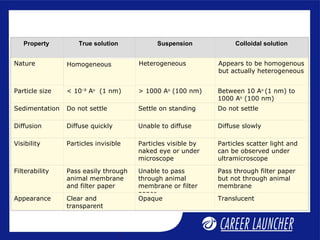
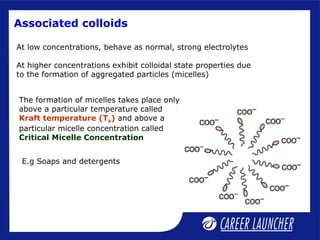
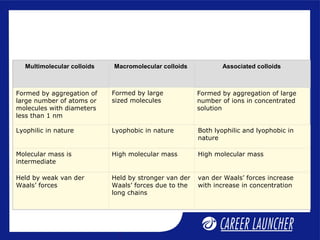
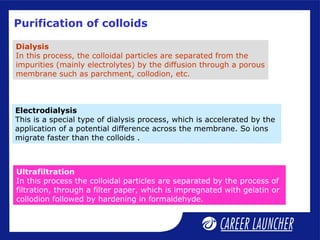
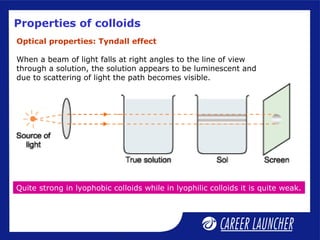
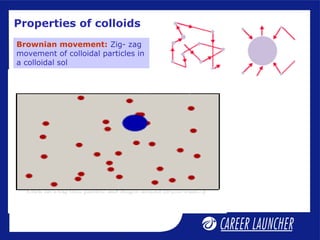
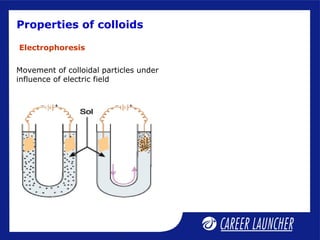
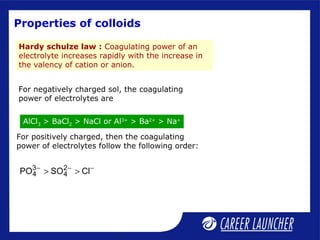
This document defines and classifies colloids. Colloids have particle sizes between 1-1000 nm, which are larger than true solutions and smaller than suspensions. Colloids are classified based on the physical state of the dispersed and dispersion medium (solid-liquid, liquid-liquid, etc.), interaction between the phases (lyophobic or lyophilic), and particle type (multimolecular, macromolecular, associated). Common colloids include emulsions, gels, sols, and foams. Properties include the Tyndall effect, Brownian motion, and coagulation with electrolytes. Colloids find applications in products like rubber, soaps, and medicines.