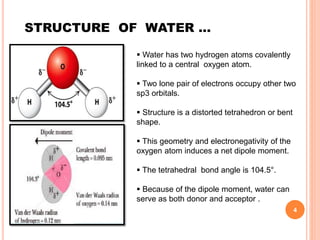
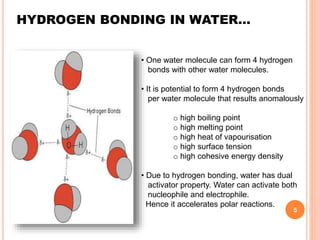
The document discusses the advantages of water as a green solvent, highlighting its environmental benefits, safety, and efficiency in synthetic methodologies. It details the physical properties and structure of water that enable its function in various chemical reactions, such as Diels-Alder and Michael reactions. The conclusion emphasizes the growing importance of using water in organic synthesis for its cost-effectiveness and reduced environmental impact.



![REACTIONS IN AQUEOUS MEDIUM…
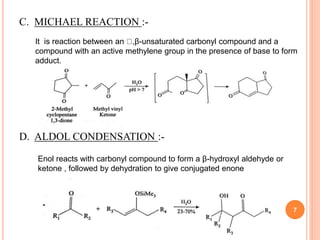
A. DIELS – ALDER REACTION :-
It is [4+2] cycloaddition reaction between a conjugated diene (4
electron system) and a dienophile (2 electron system) to form an adduct.
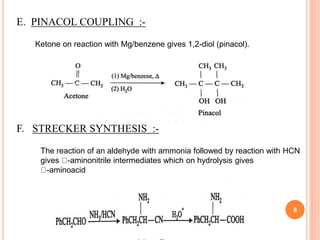
B. CLAISEN REARRANGEMENT :-
The reaction involves allyl phenyl ether on heating undergo 3,3-
sigmatropic rearrangement.
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/waterasgreensolvent1-191206164426/85/Water-as-green-solvent-6-320.jpg)