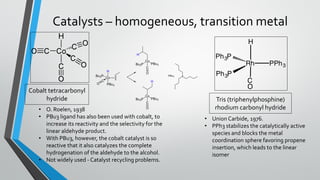
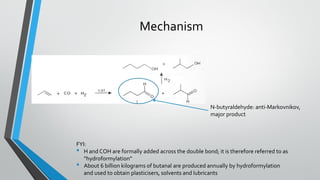
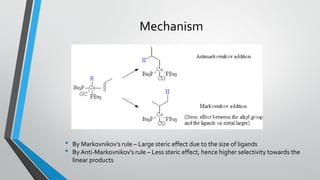
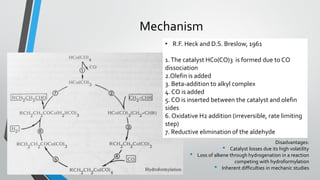
This document summarizes hydroformylation, an industrially important reaction that uses cobalt or rhodium catalysts to produce aliphatic aldehydes from olefins and synthesis gas. It discusses the uses of aldehydes produced via hydroformylation, the homogeneous transition metal catalysts used, including cobalt tetracarbonyl hydride and tris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium carbonyl hydride, the reaction mechanism, and several industrial processes employing cobalt catalysts, such as the BASF-oxo, Exxon, and Shell processes.