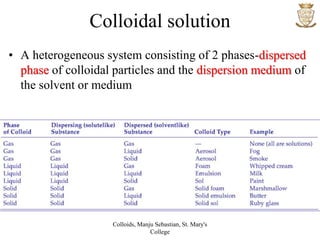
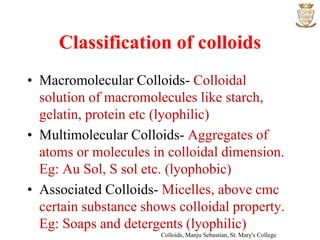
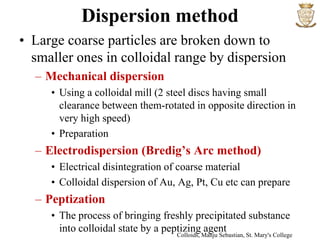
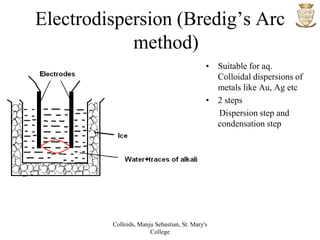
1) Colloids have particle sizes between 1-100 nm, are heterogeneous systems that cannot be filtered or separated by centrifugation, and include sols, emulsions, and gels.
2) Sols are dispersions where the dispersed phase is a solid and the dispersion medium is a liquid. They can be lyophilic or lyophobic.
3) Emulsions are dispersions where both phases are liquids, existing as oil-in-water or water-in-oil forms. Gels have a solid dispersion medium and liquid dispersed phase.
4) Colloids exhibit unique optical, kinetic, and electrical properties due to their intermediate size, including Tyndall effect, Brownian






















![Hardy-Schulze law
• The law states that “The greater the valency
of the ion bearing a charge opposite to that
on sol particles, the greater is its power to
cause coagulation”
• Na+ < Ba2+ < Al3+
• Cl- < SO4
2- < PO4
3- < [Fe(CN)6]4-
Colloids, Manju Sebastian, St. Mary's
College](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-191119011225/85/Colloids-27-320.jpg)













