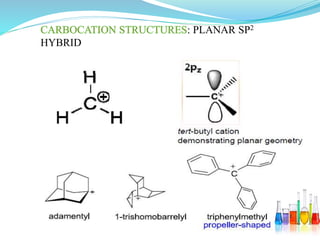
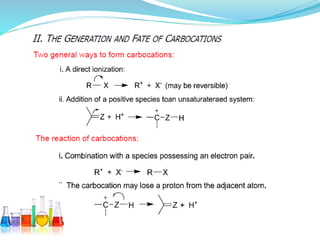
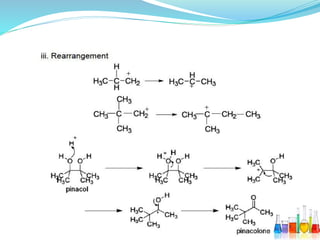
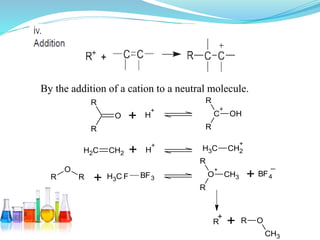
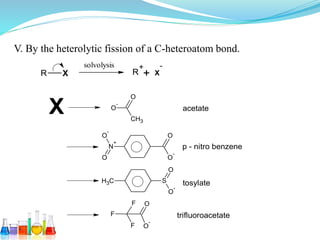
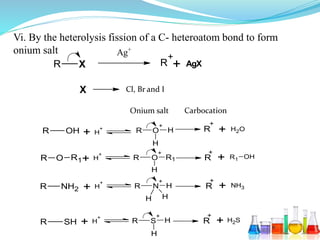
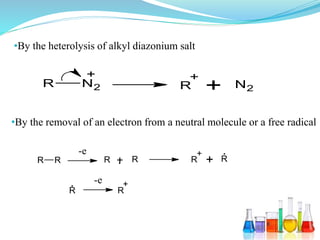
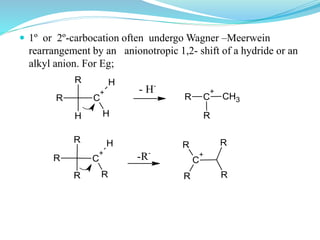
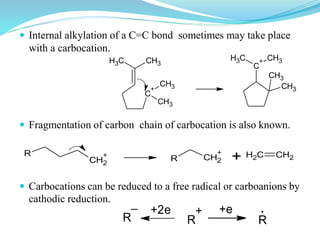
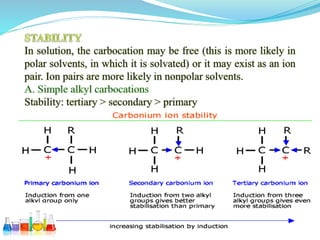
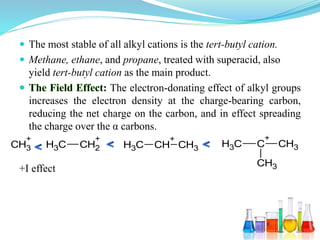
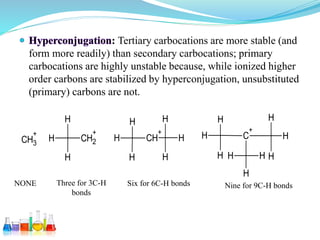
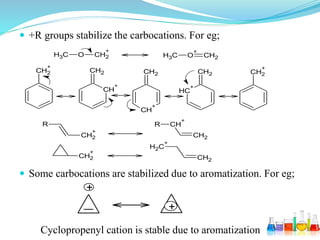
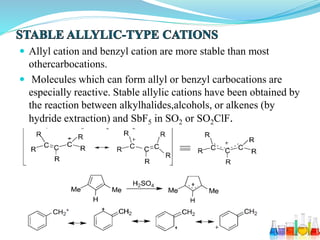
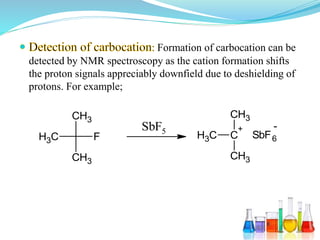
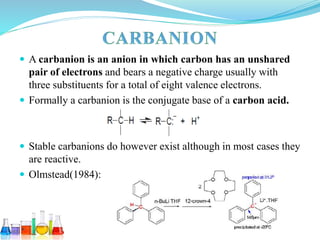
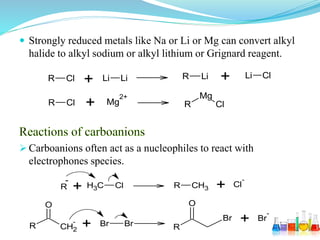
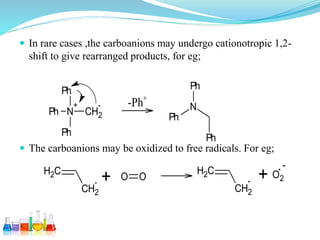
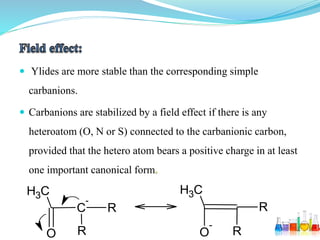
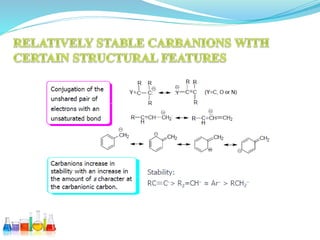
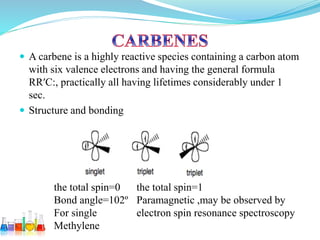
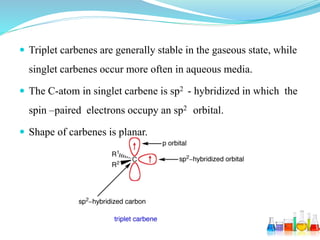
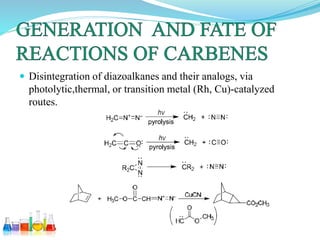
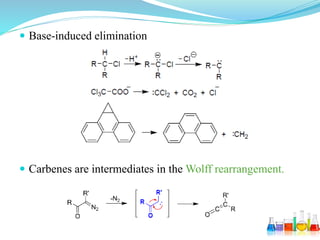
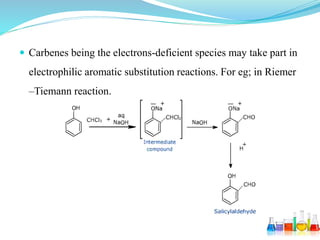
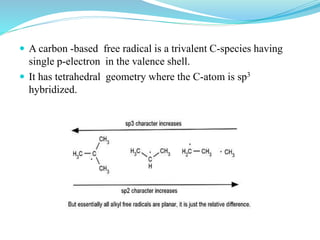
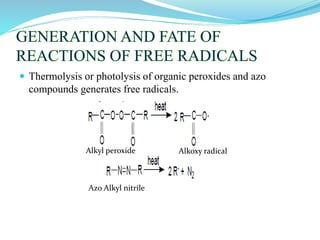
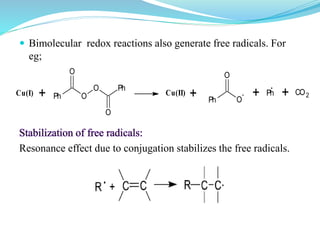
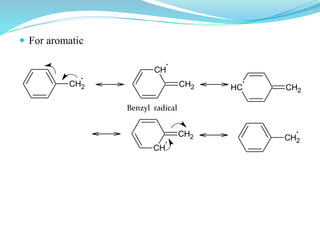
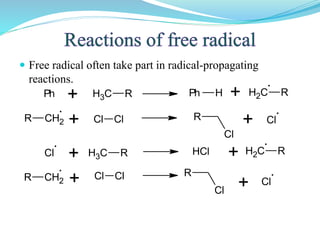
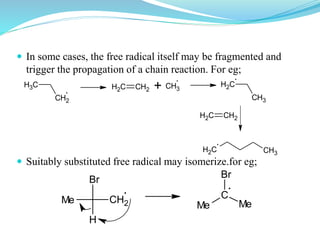
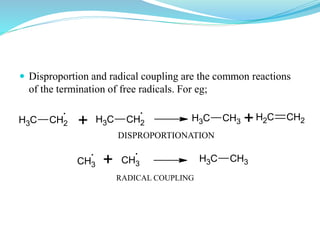
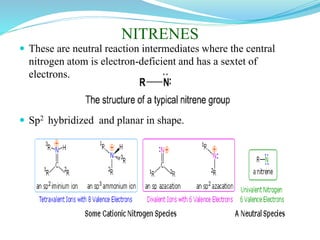
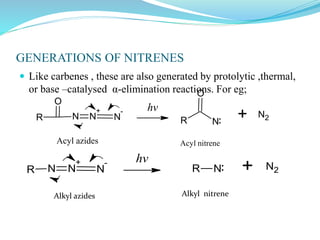
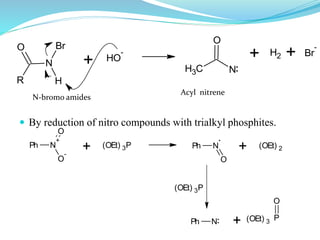
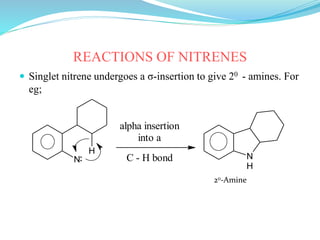
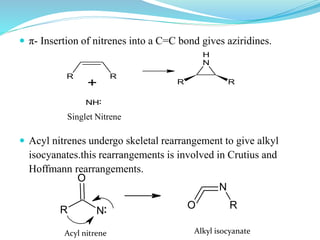
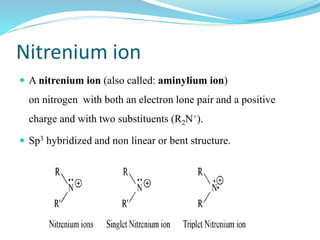
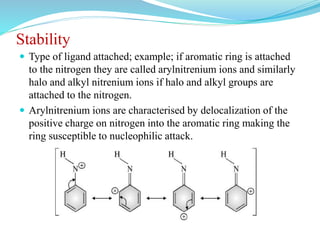
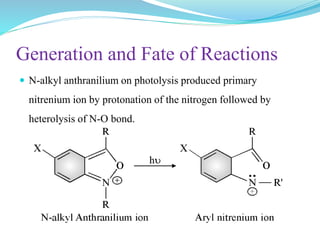
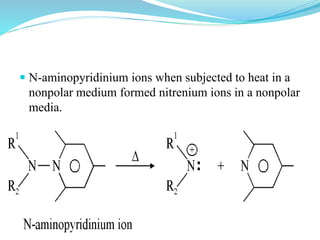
This document provides an overview of various carbon-based reaction intermediates including carbocations, carbanions, carbenes, free radicals, nitrenes, and nitrenium ions. It discusses their generation, structure, stability, reactions, and detection methods. Key points include that carbocations are positively charged carbon species that react as electrophiles, while carbanions are negatively charged carbon species that react as nucleophiles. Carbenes contain a carbon with six valence electrons in a triplet or singlet state. Free radicals contain one or more unpaired electrons. Nitrenes and nitrenium ions involve a reactive nitrogen species. Detection methods include NMR, EPR, UV-Vis spectroscopy, and trapping reactions.