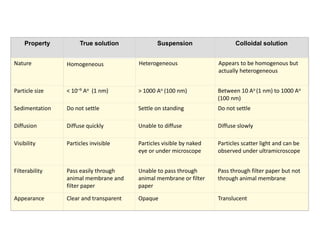
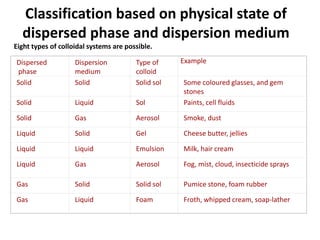
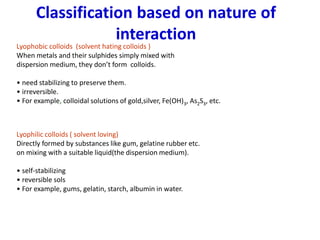
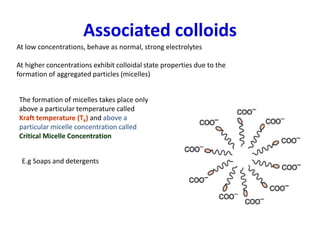
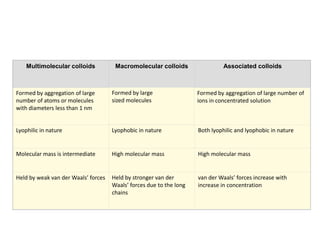
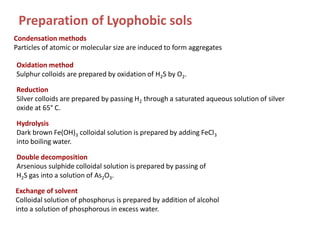
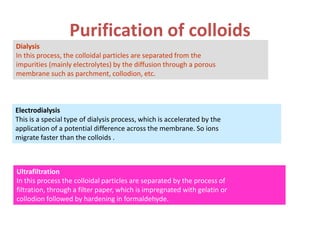
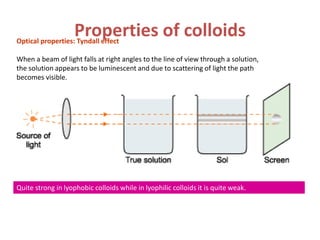
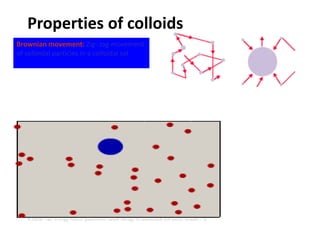
The document discusses colloids, which are heterogeneous mixtures with dispersed particles between 1-1000 nm. It classifies colloids based on the physical state of the dispersed and continuous phases, the nature of particle-solvent interactions, and the type of dispersed particles. Multimolecular, macromolecular, and associated colloids are described. Methods for preparing lyophobic and lyophilic colloids as well as purifying colloids are outlined. Key properties like Tyndall effect, Brownian motion, and coagulation are also summarized along with applications of colloids.