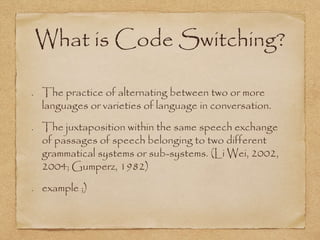
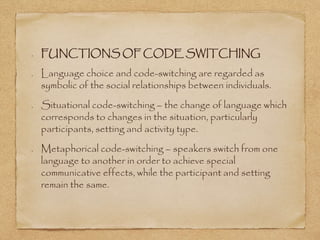
This document discusses code switching, which is the practice of alternating between two or more languages or varieties of language in a single conversation. It provides examples of code switching and explores reasons why bilinguals may code switch, such as situational or metaphorical reasons. The document also examines different types of code switching, such as intra-sentential, inter-sentential, and turn-taking code switching. It analyzes structural patterns and typology of code switching, as well as functions of code switching as relating to social relationships and language choice.









![“Code-switching is a verbal skill requiring a large
degree of linguistic competence in more than one
language, rather than a defect arising from insufficient
knowledge of one or the other ... [R]ather than
representing deviant behavior, [it] is actually a
suggestive indicator of degree of bilingual
competence.”
(cf. Grosjean, 2010, p57)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codeswitchingpresentation387-141011000718-conversion-gate02/85/Code-switching-presentation387-12-320.jpg)
