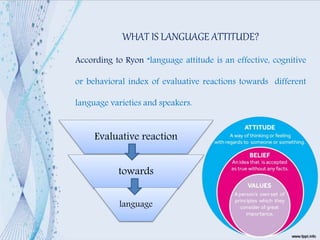
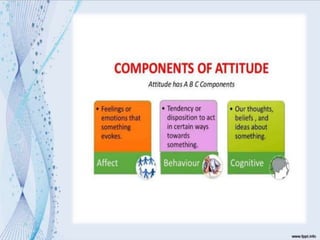
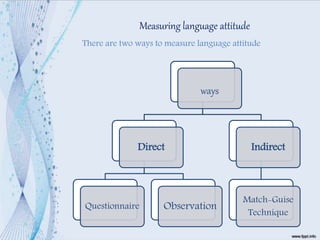
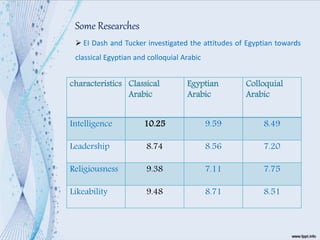
This document discusses language attitudes and methods for measuring them. It defines language attitude as an evaluation of a language variety or its speakers. Two main methods to measure attitudes are direct methods using questionnaires or observations, and indirect methods like the match-guise technique. The match-guise technique involves playing recordings of the same content in different languages without telling participants the purpose is to measure their language attitudes based on traits rated on a semantic differential scale. Some example studies applying this technique in Egypt and Mexico are summarized.