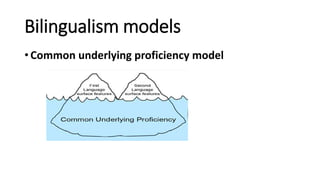
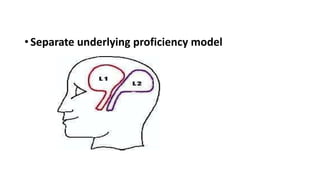
The document discusses language contact, a phenomenon where speakers of different languages communicate, leading to the transfer of linguistic features. It covers various concepts including diglossia, polyglossia, code-switching, bilingualism, and pidgin/creole languages, detailing definitions, types, and results of such contact. The document illustrates how these linguistic situations manifest in different contexts and communities.