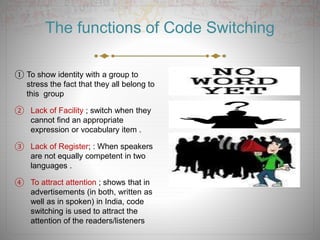
Code switching refers to alternating between two or more languages or language varieties in conversation. It occurs when speakers switch between languages to quote someone, give emphasis, or establish group membership. There are general rules that govern when and where code switching can occur within sentences based on matching grammar points between languages or determining the dominant language frame. While code switching demonstrates language proficiency, some communities view frequent code switching negatively.