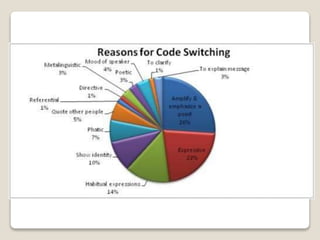
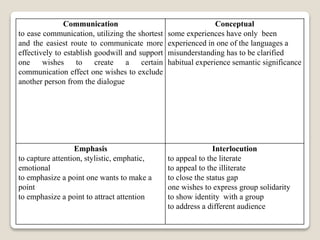
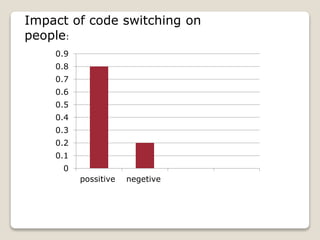
The document discusses the history and emergence of code-switching research, defining it as the alternation between two languages used by bilingual speakers. It examines reasons for and functions of code-switching, including to ease communication, convey social and linguistic meanings, emphasize points, and show group identity. Attitudes toward code-switching are also explored, having traditionally been viewed negatively but now seen as a natural part of bilingual communication.


![Code-switching in itself is perhaps not a
linguistic phenomenon, but rather a psychological one,
and its causes are obviously extra- linguistic. But
bilingualism is of great interest to the linguist
because it is the condition of what has been
called interference between languages. [Hans Vogt
1954:368]
Vogt ,assumes that code switching is not only natural,
but common. He suggests that all languages – if not all
language users – experience language contact, and that
contact phenomena, including language alternation, are
an important element of language change.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/code-switching-reason-141216125448-conversion-gate01/85/Code-switching-reason-3-320.jpg)