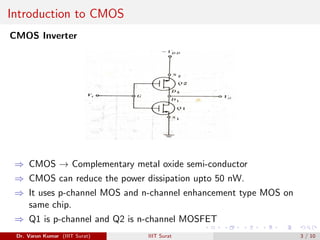
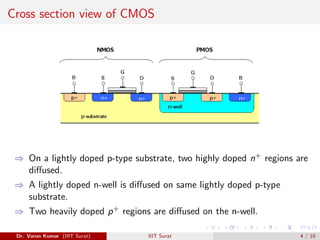
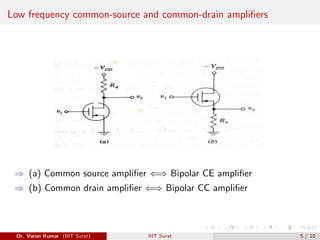
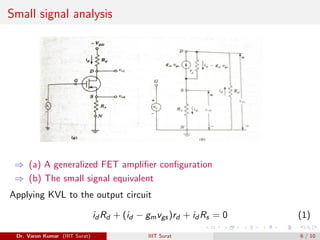
This document discusses FET amplifiers and biasing. It begins with an introduction to CMOS transistors and how they reduce power dissipation compared to other technologies. It then describes common source and common drain amplifier configurations, which are analogous to bipolar CE and CC amplifiers. The document provides equations for small signal analysis of these FET amplifiers. Finally, it briefly introduces FET biasing and factors that influence selection of an operating point such as output swing, distortion, power, gain, and current drift.


![CD Amplifier with a Drain Resistance
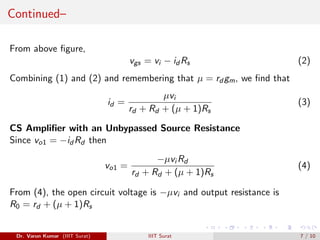
Since vo2 = id Rs, then from (3)
vo2 =
µvi Rs
rd + Rd + (µ + 1)Rs
=
[µvi /(µ + 1)]Rs
(rd + Rd )/(µ + 1) + Rs
(6)
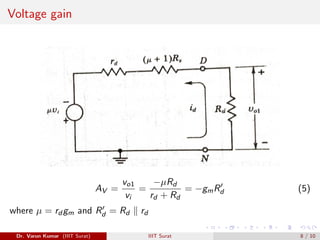
In CD amplifier, the open circuited voltage is µvi
(µ+1) and output resistance
is Ro = Rd +rd
(µ+1) and voltage gain AV = vo2
vi
Dr. Varun Kumar (IIIT Surat) IIIT Surat 9 / 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mosfetanditsbiasing-210626043925/85/CMOS-FET-Amplifier-9-320.jpg)
