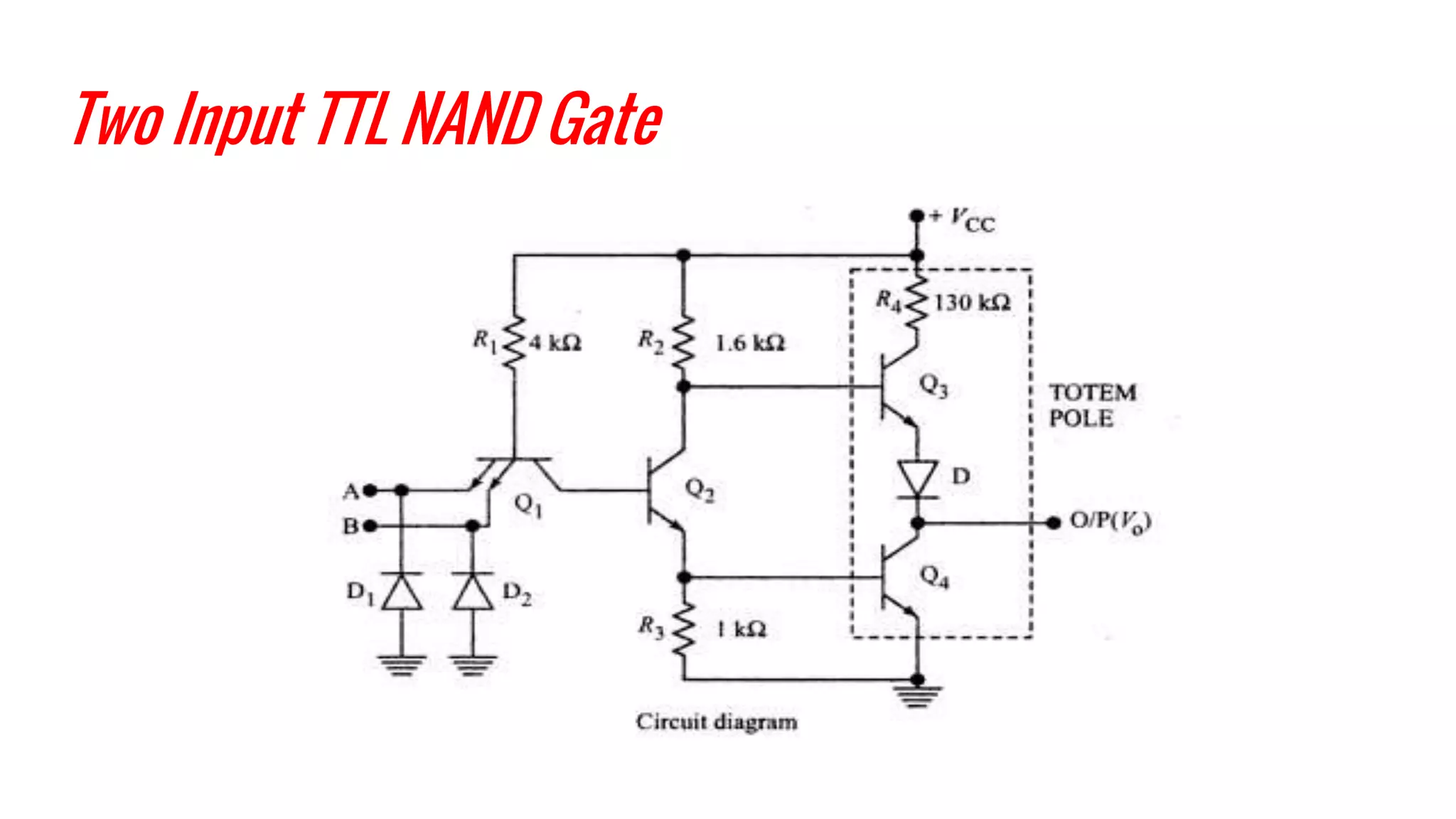
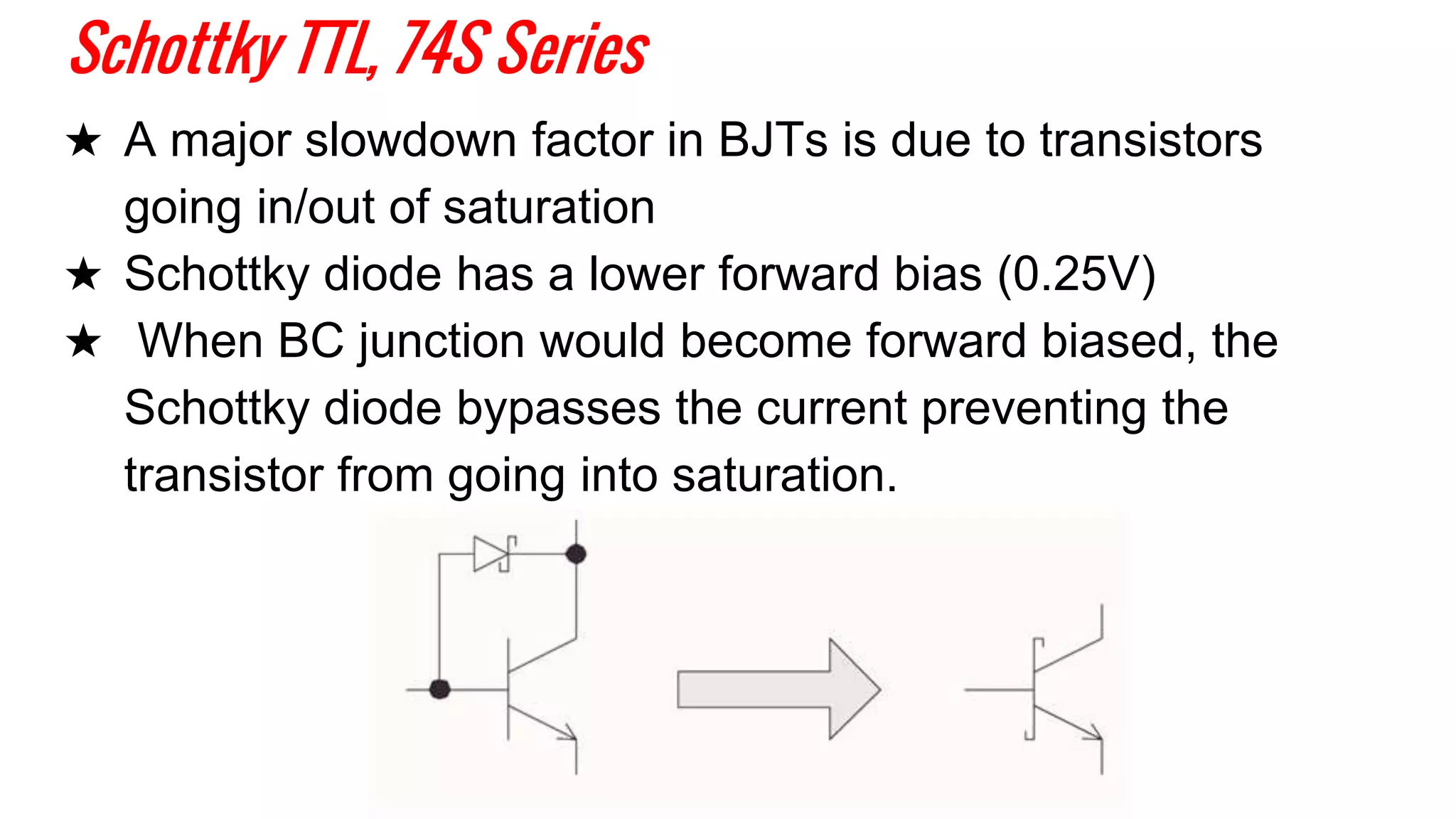
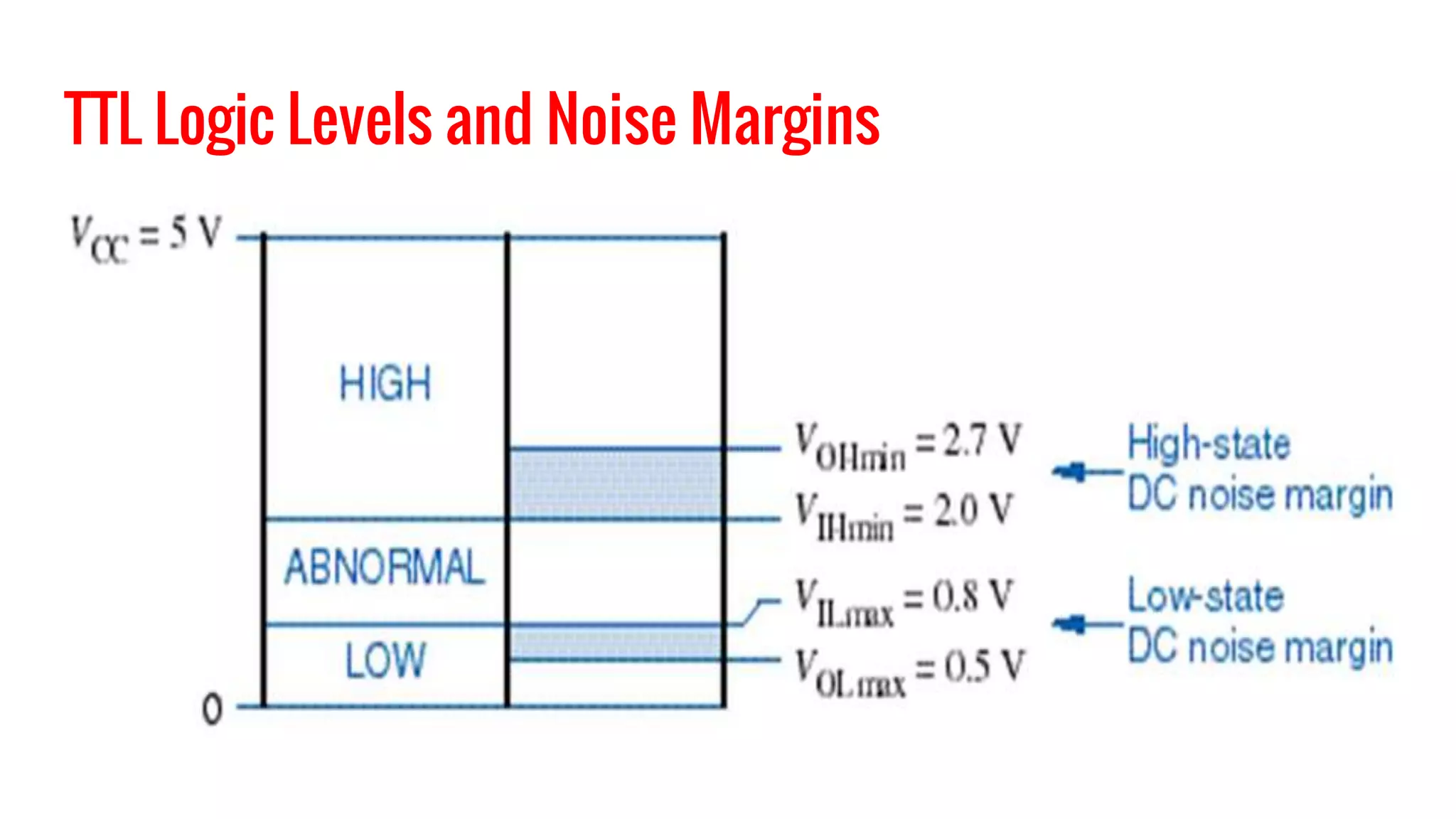
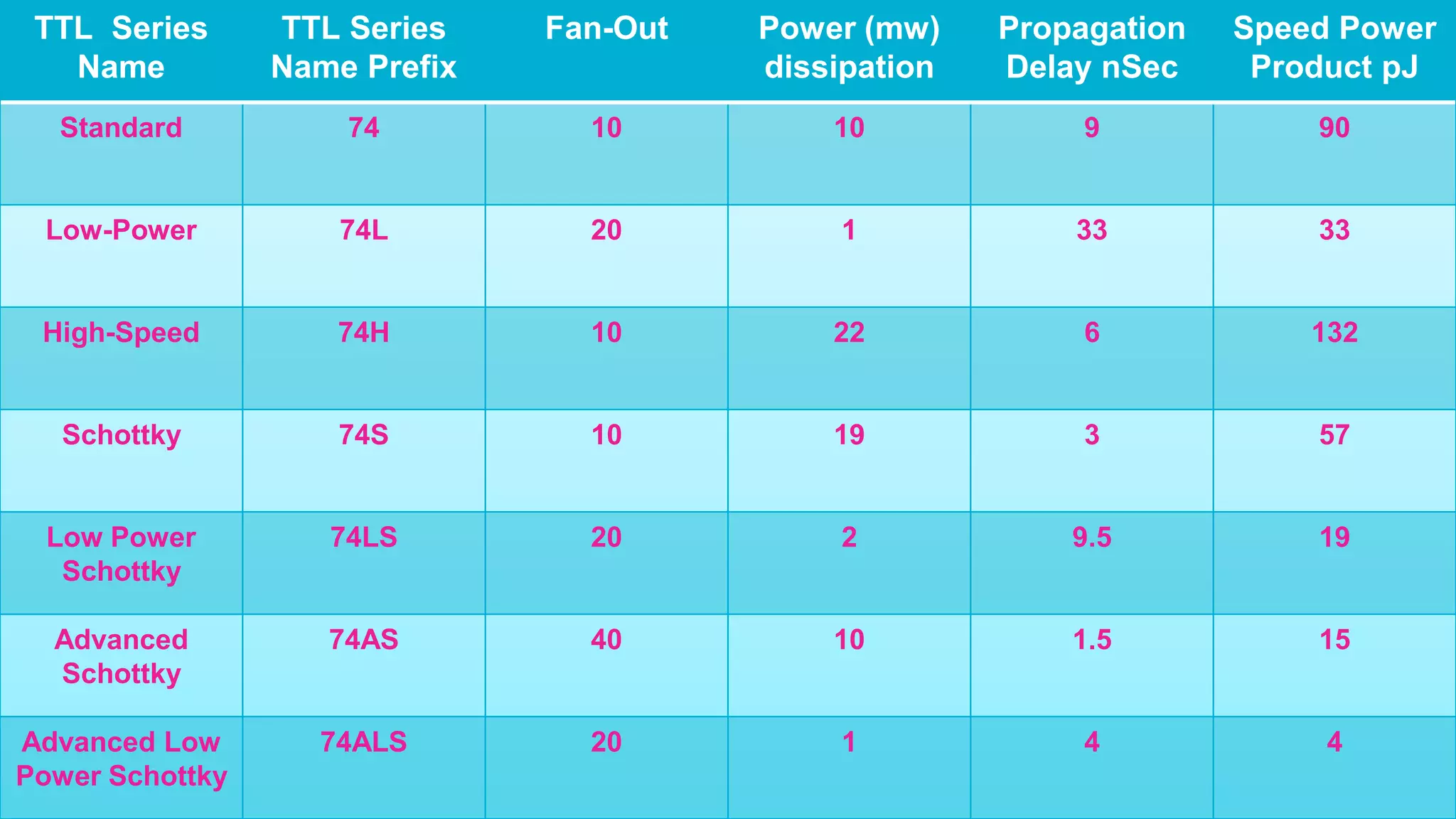
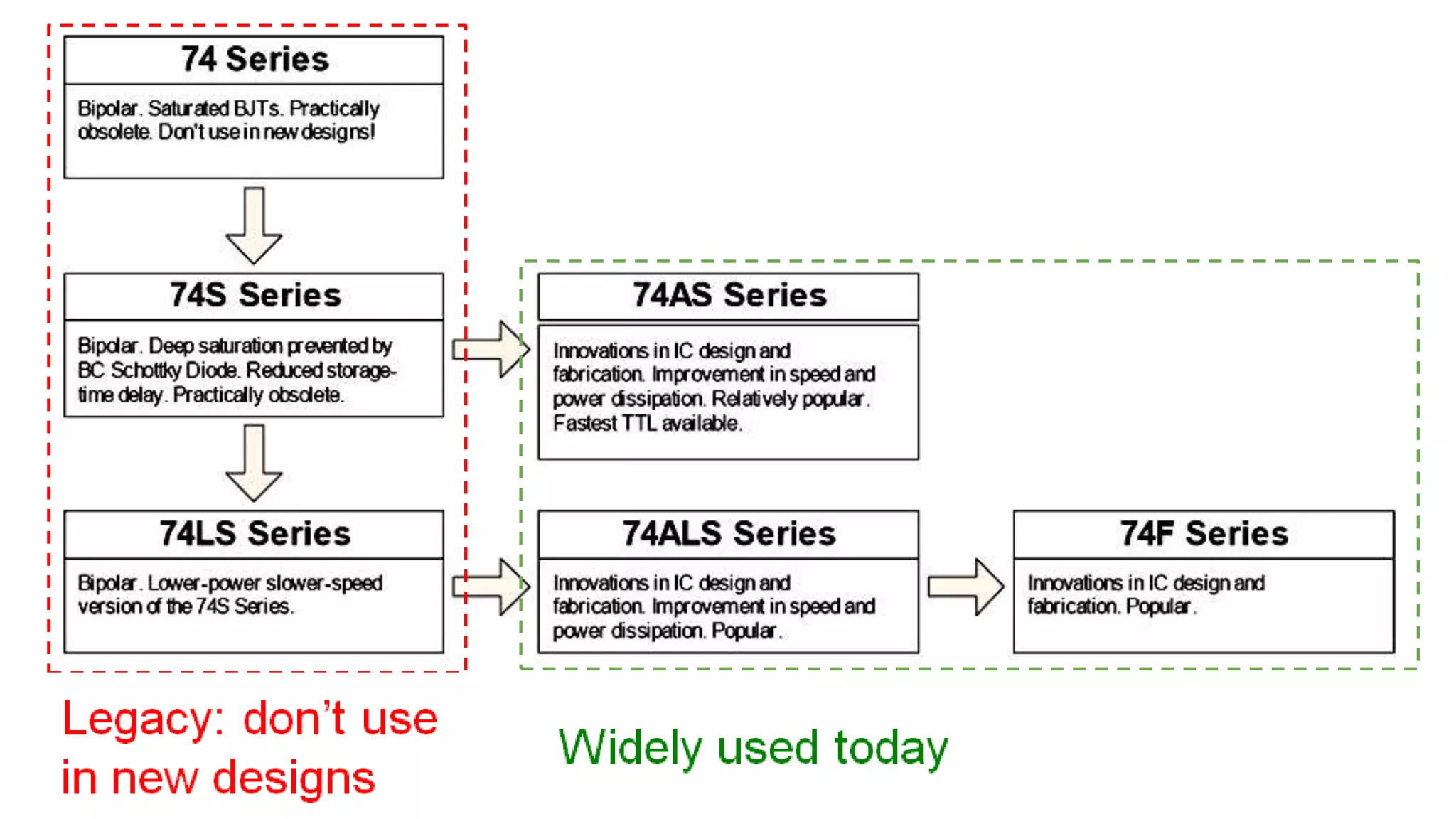
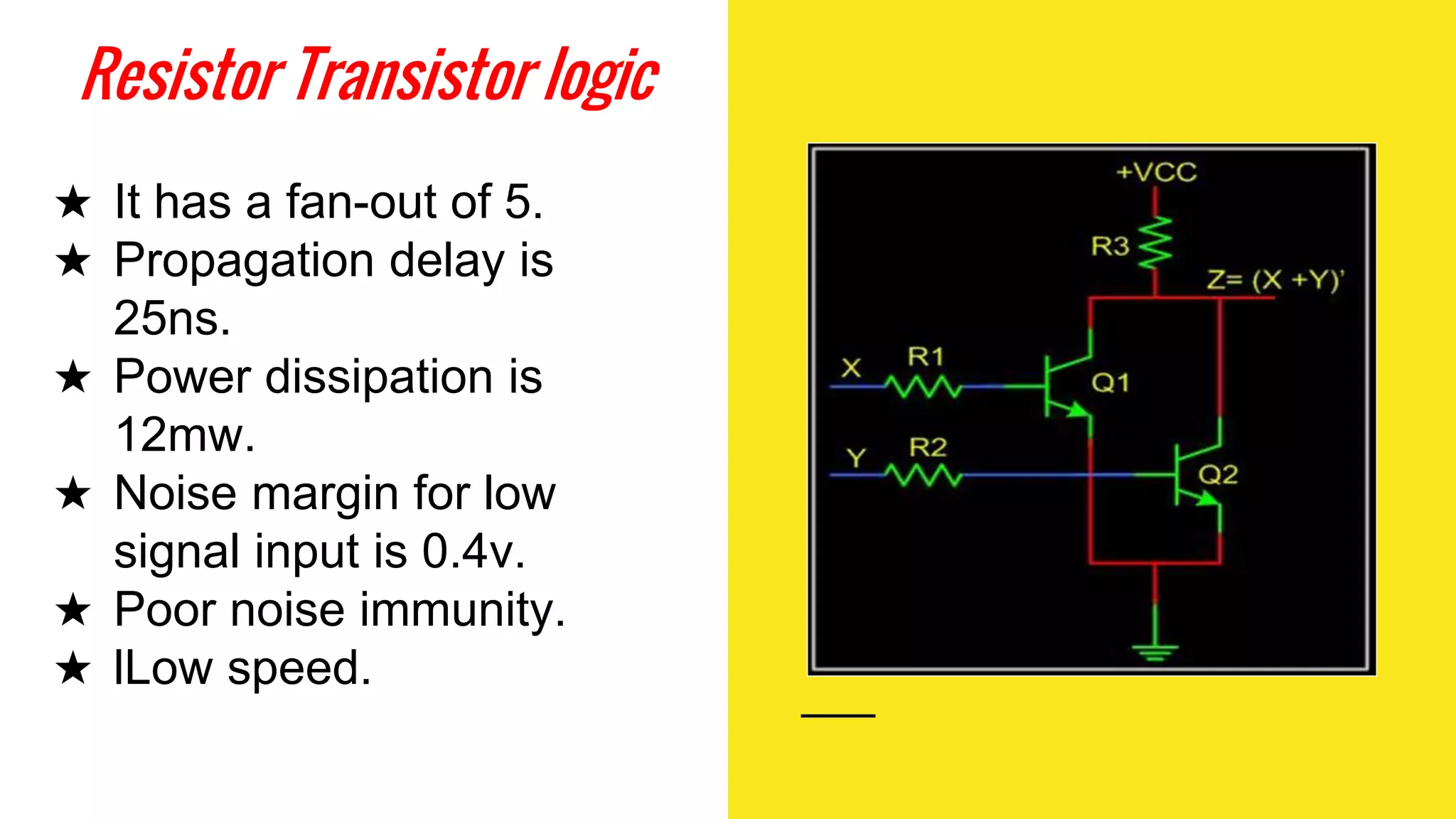
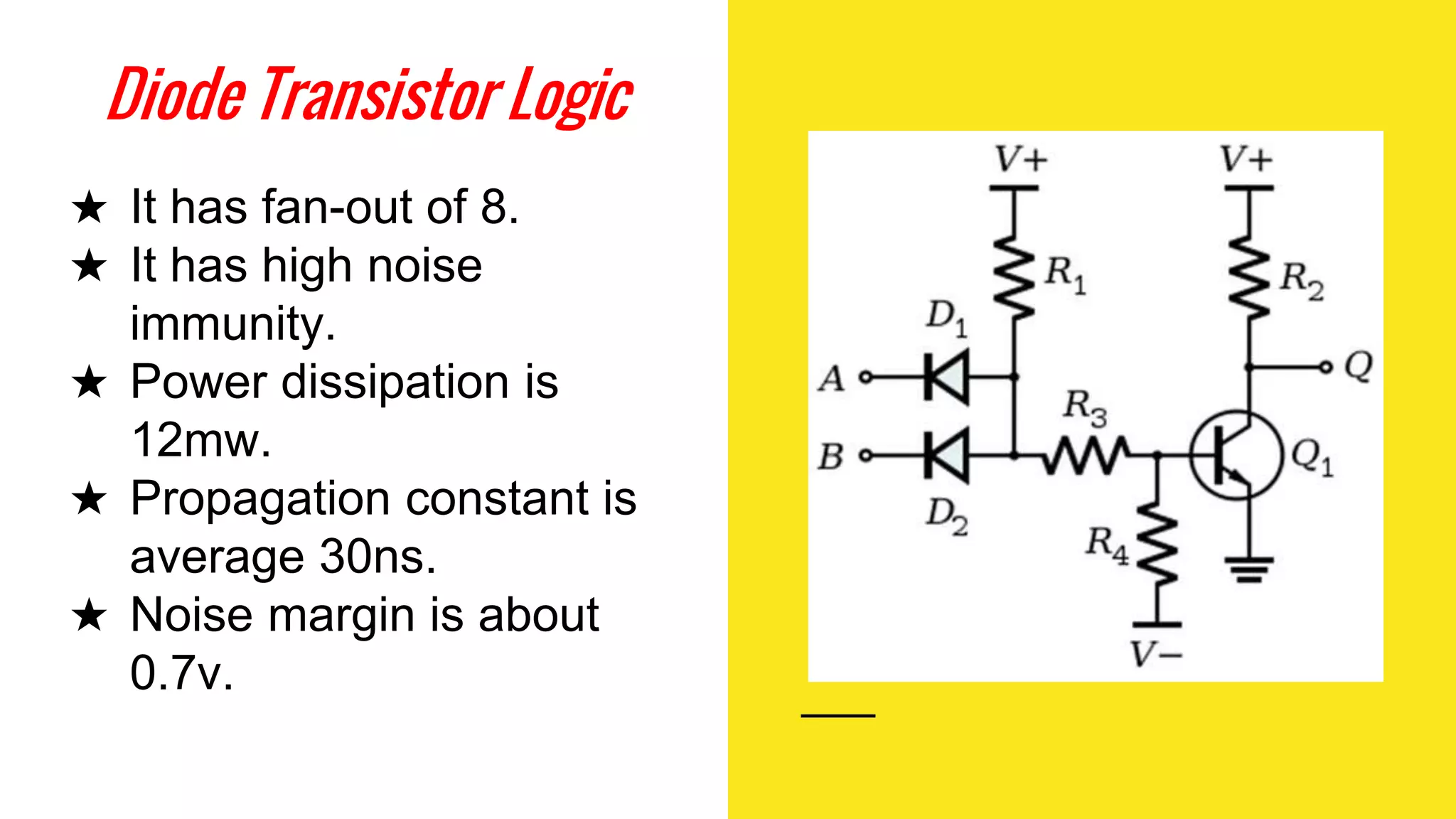
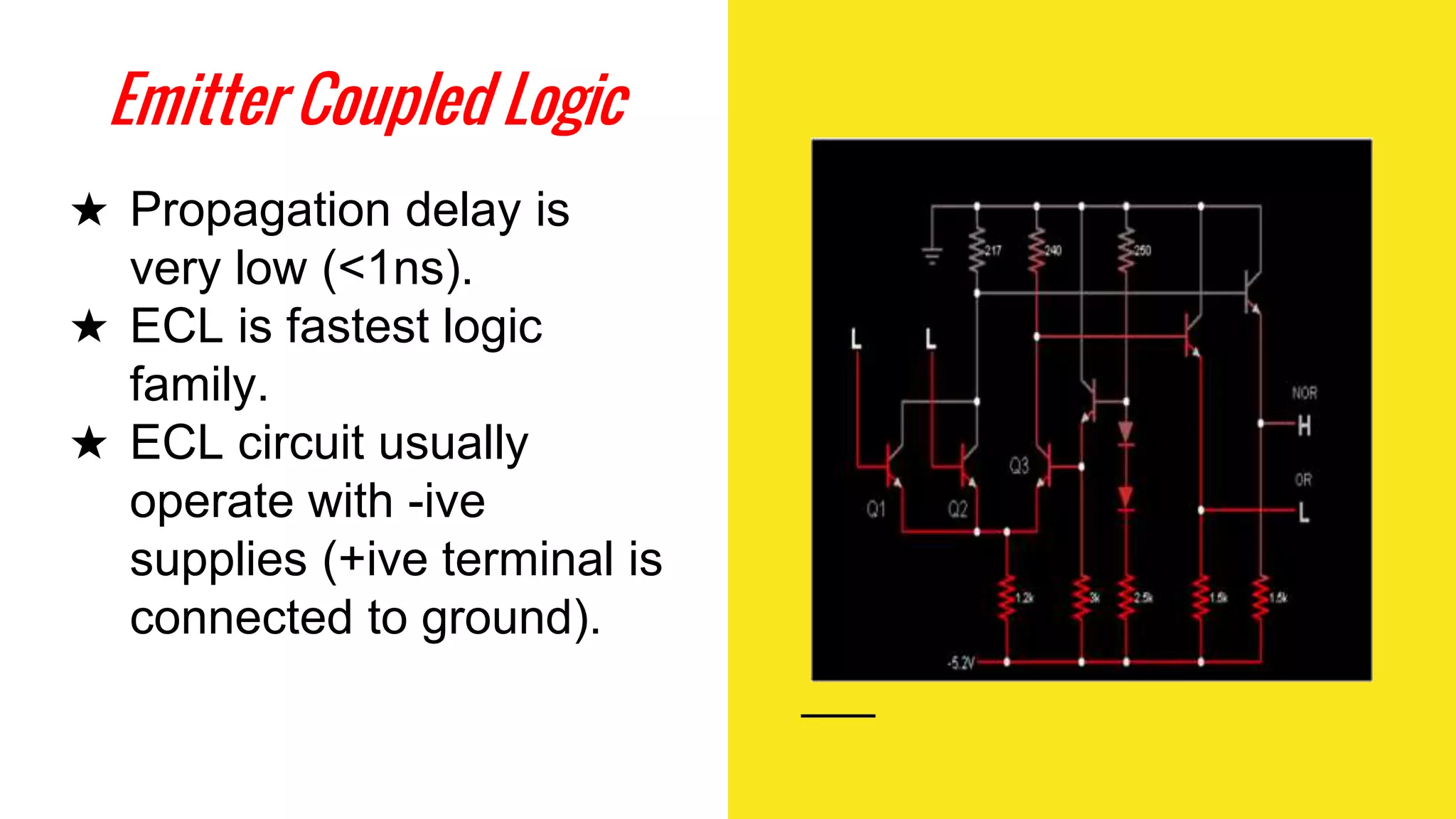
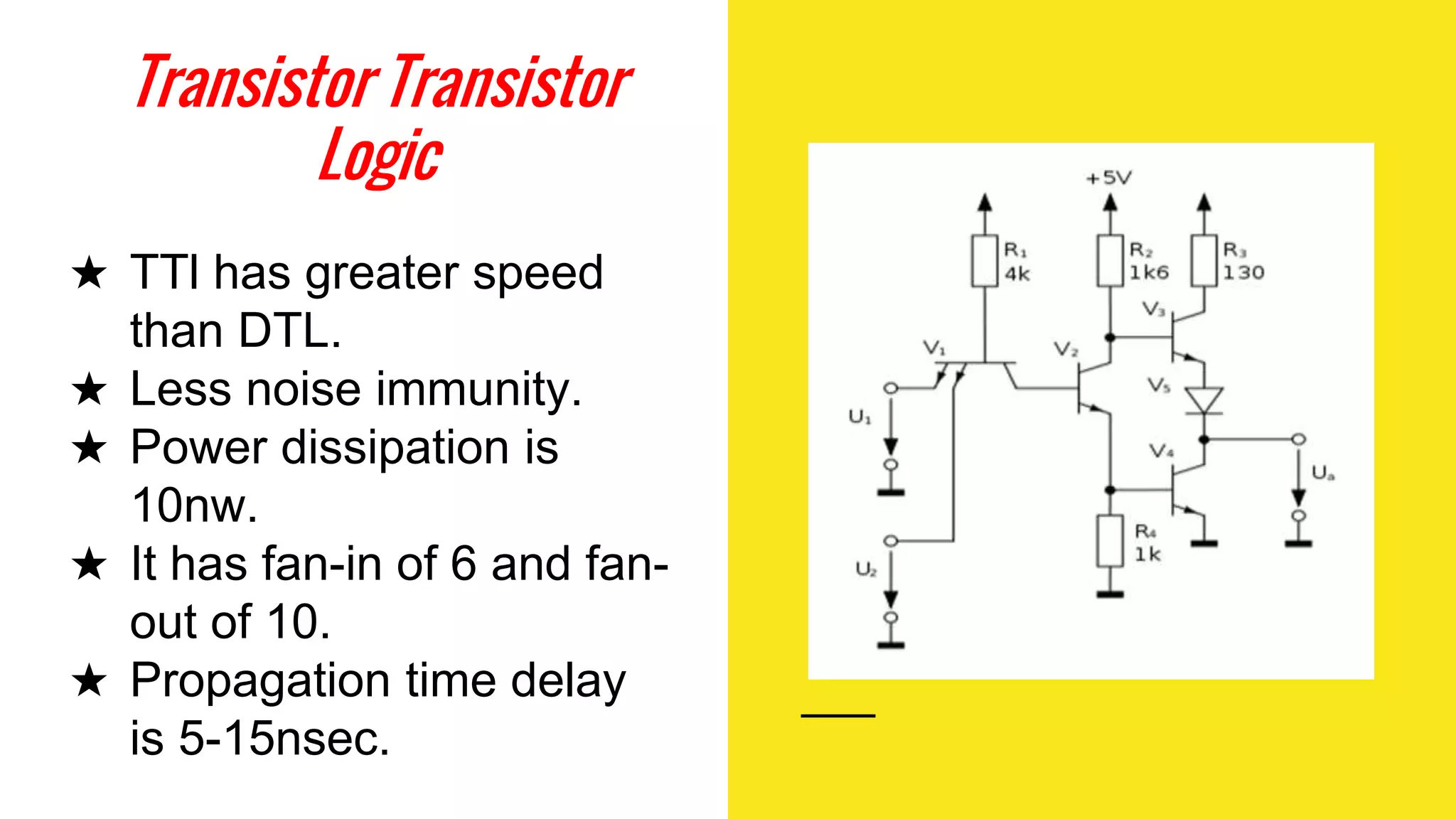
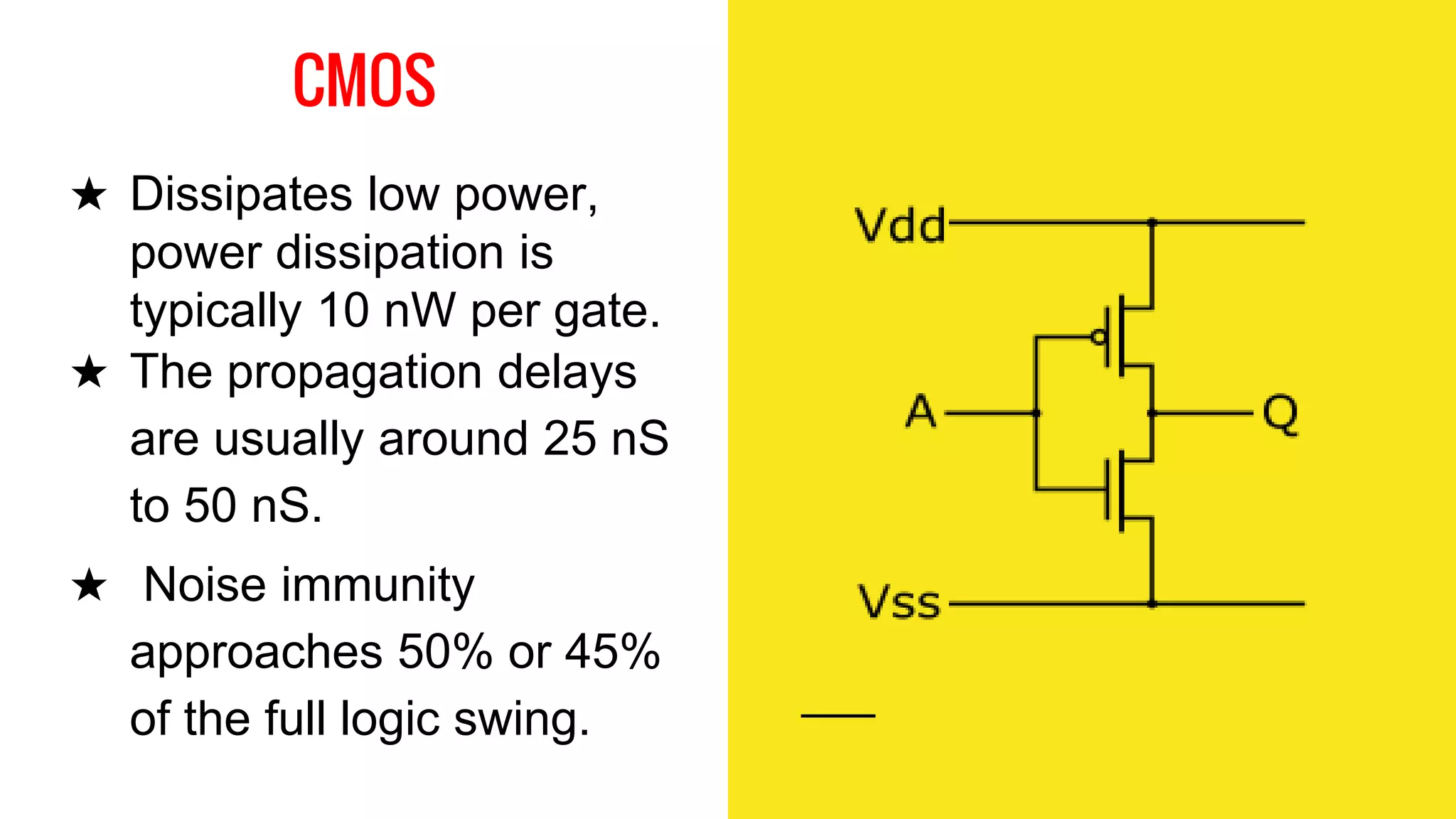
The document provides an overview of transistor-transistor logic (TTL) and its applications in digital circuits, detailing the evolution and variations of TTL technology since its introduction in 1963. It explains different TTL sub-families, their characteristics such as power dissipation and speed, and comparisons with other logic families like resistor-transistor logic and CMOS. Additionally, it outlines key parameters like propagation delay and speed-power product that are crucial for evaluating TTL performance.