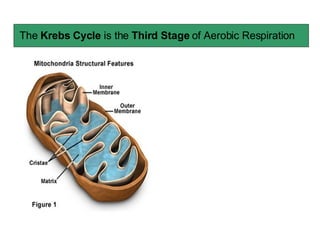
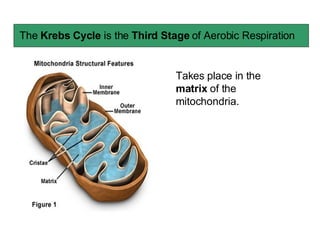
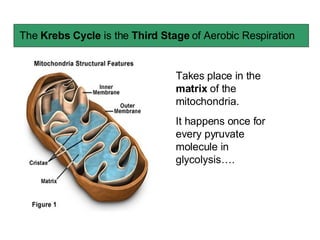
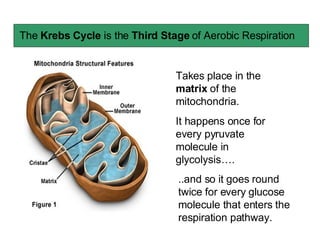
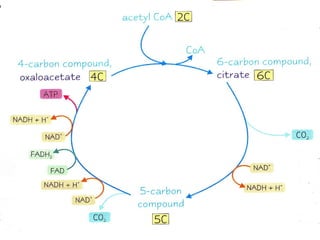
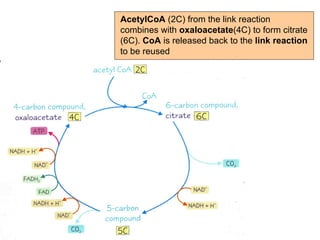
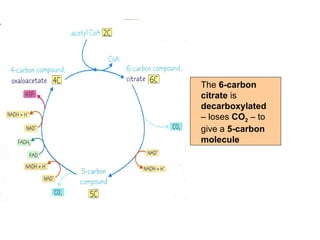
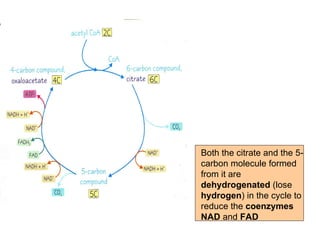
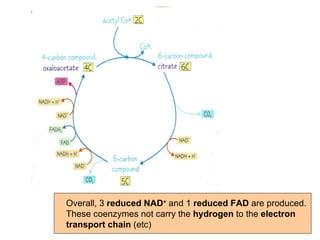
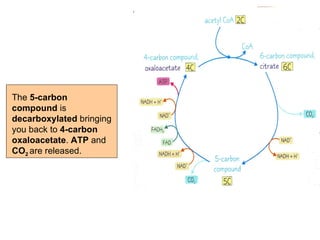
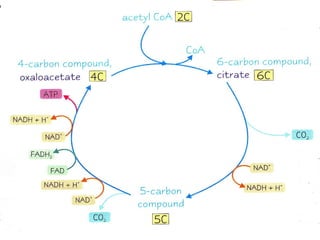
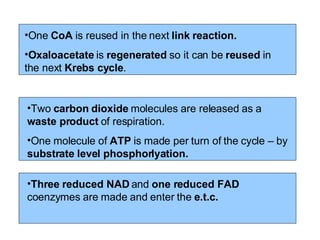
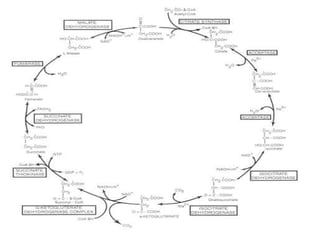
The document summarizes the Krebs cycle, which is the third stage of aerobic respiration. It occurs in the mitochondria and involves the breakdown of pyruvate from glycolysis to extract energy from food. Acetyl-CoA combines with oxaloacetate to form citrate and release CoA. Citrate and other molecules lose hydrogen to produce NADH and FADH2, which carry energy to the electron transport chain. The cycle regenerates oxaloacetate and produces ATP, carbon dioxide, and reduced coenzymes that enter the final stage of respiration.