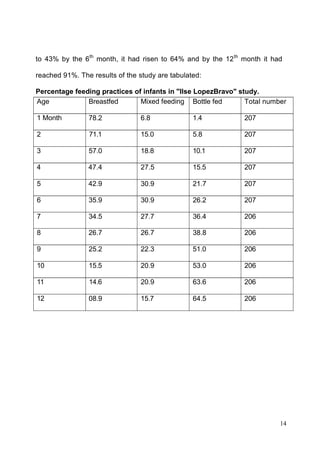
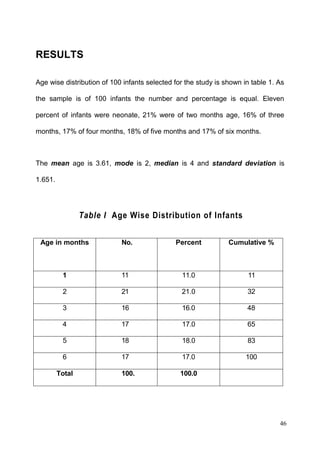
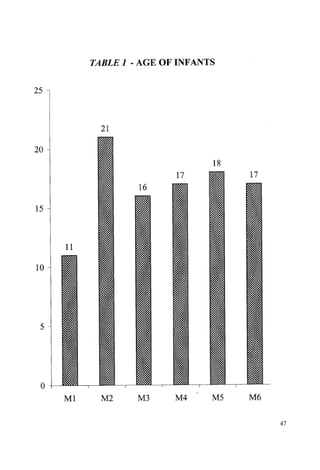
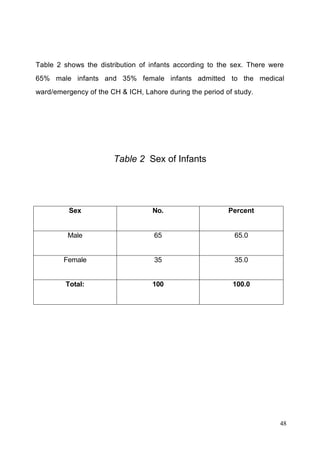
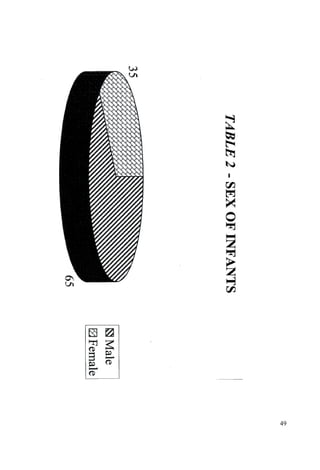
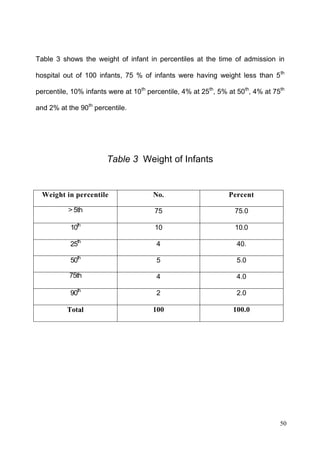
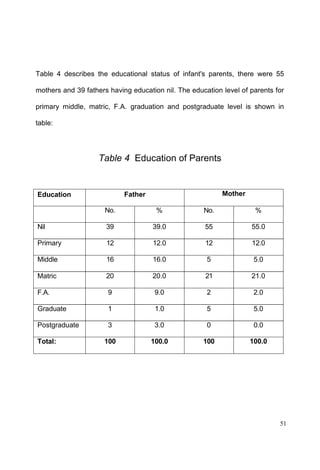
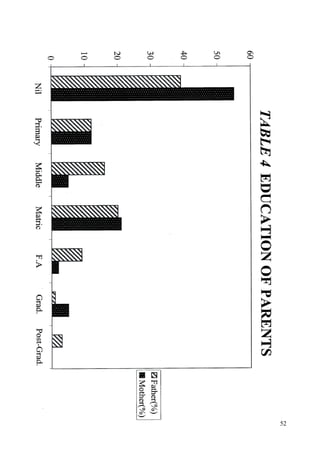
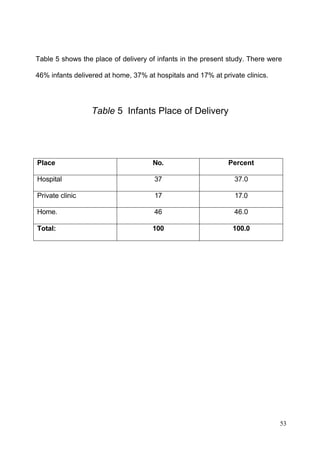
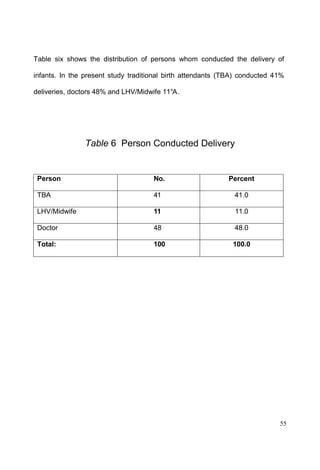
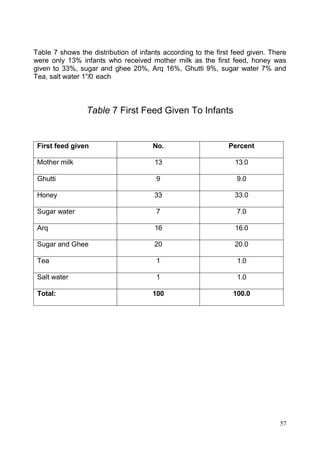
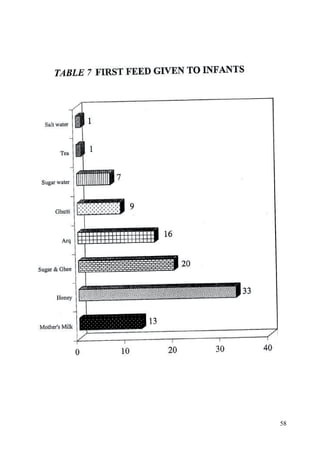
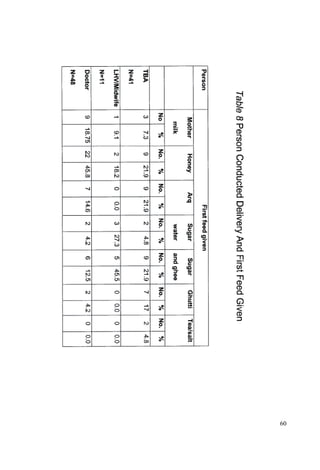
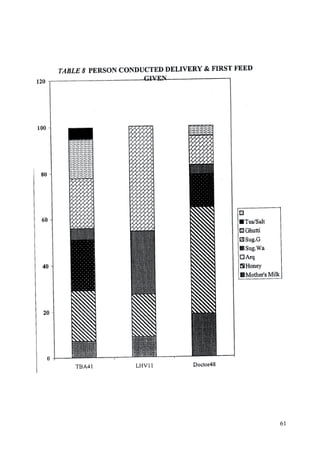
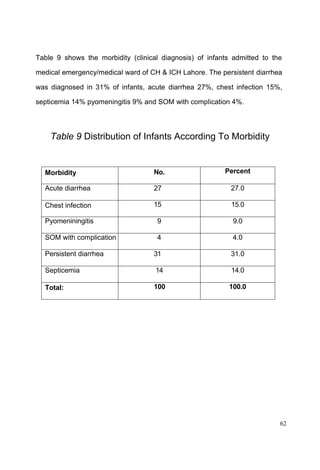
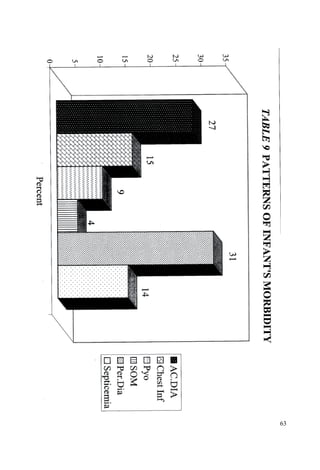
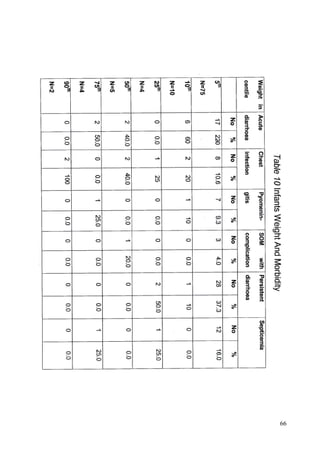
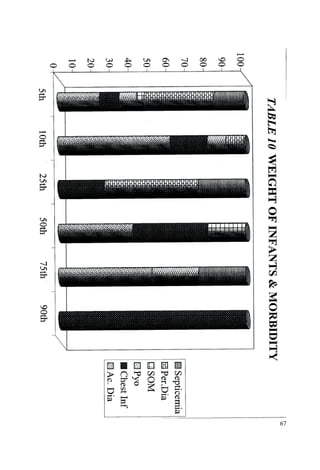
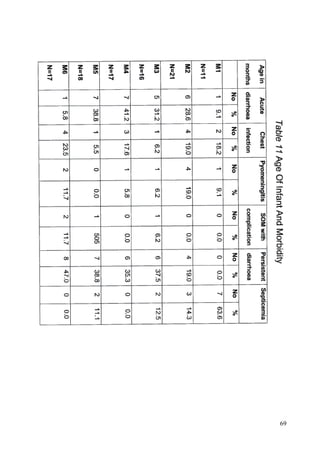
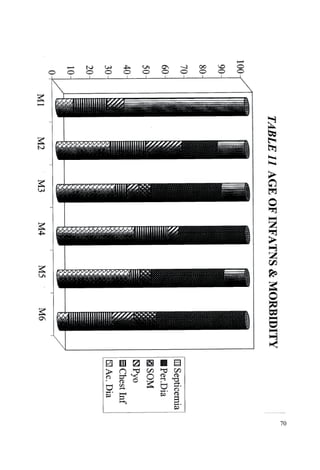
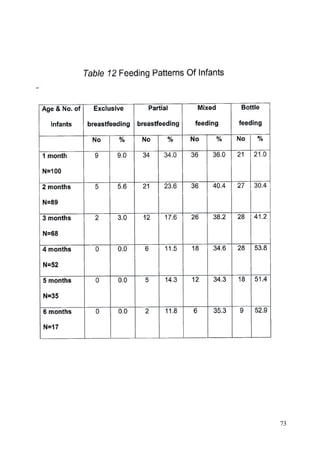
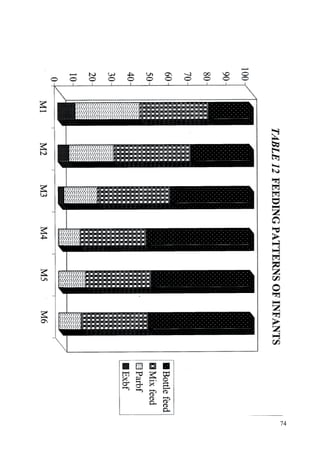
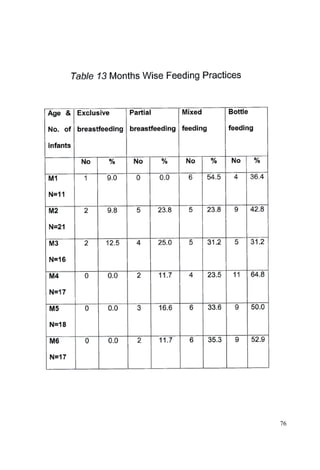
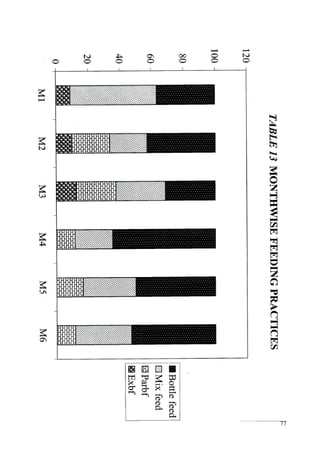
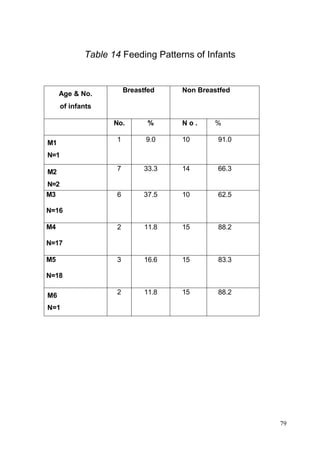
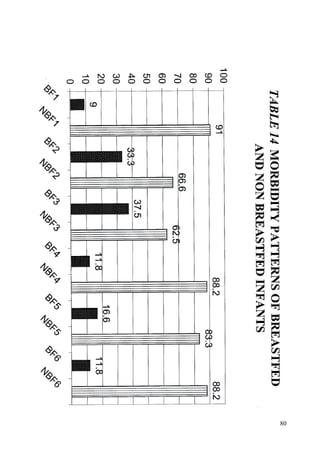
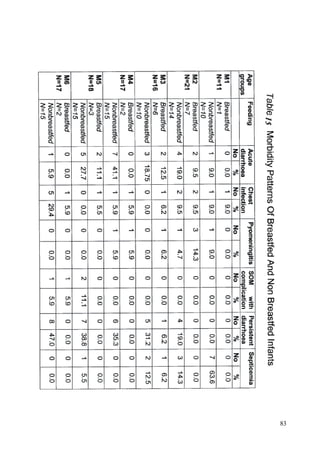
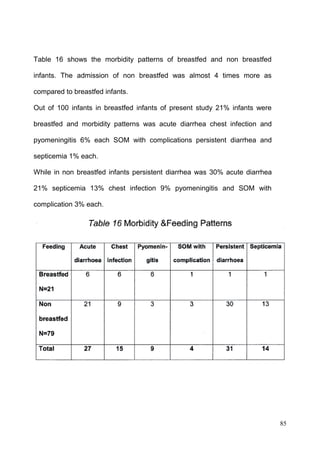
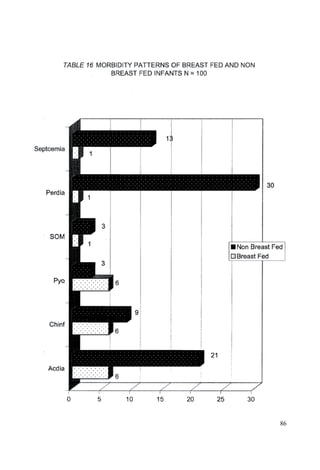
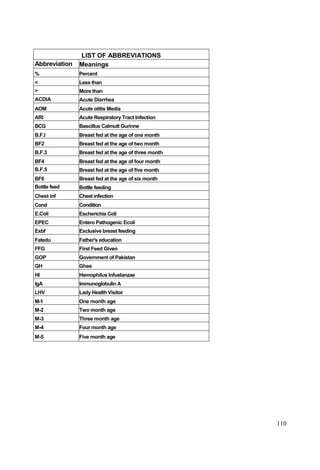
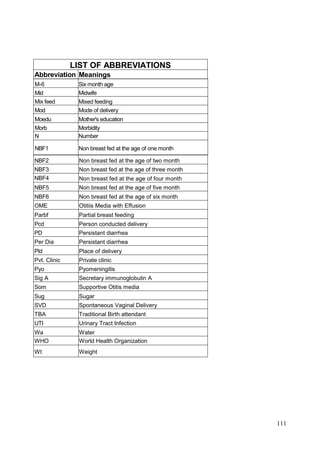
This document discusses the importance of breastfeeding for infant health and development. It reviews several studies that show breastfeeding reduces the risk of morbidity and mortality from various infectious diseases like diarrhea, otitis media, neonatal sepsis, and respiratory infections. However, in many societies false beliefs interfere with breastfeeding and infants are commonly given prelacteal feeds or mixed feeding instead of being exclusively breastfed. The purpose of the study described is to examine the patterns of infectious diseases in non-breastfed infants compared to breastfed infants admitted to the hospital.